185 posts
Latest Posts by ocrim1967 - Page 3









(Source)




















(Source)










(Source)










(Source)










(Source)










(Source)










(Source)










🐱:(source)

The year is 1965, and thanks to telecommunication engineers at our Jet Propulsions Laboratory, the first color version of one of our first Martian images had been created. Brought to life by hand coloring numbered strips, this image is a true blast to the past.
Fast forward to the 21st century and our Mars InSight mission now enables us to gawk at the Martian horizon as if we were there. InSight captured this panorama of its landing site on Dec. 9, 2018, the 14th Martian day, or sol, of its mission. The 290-degree perspective surveys the rim of the degraded crater InSight landed in and was made up of 30 photos stitched together.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Earth: Our Oasis in Space

Earth: It’s our oasis in space, the one place we know that harbors life. That makes it a weird place – so far, we haven’t found life anywhere else in the solar system…or beyond. We study our home planet and its delicate balance of water, atmosphere and comfortable temperatures from space, the air, the ocean and the ground.

To celebrate our home, we want to see what you love about our planet. Share a picture, or several, of Earth with #PictureEarth on social media. In return, we’ll share some of our best views of our home, like this one taken from a million miles away by the Earth Polychromatic Imaging Camera (yes, it’s EPIC).

From a DC-8 research plane flying just 1500 feet above Antarctic sea ice, we saw a massive iceberg newly calved off Pine Island Glacier. This is one in a series of large icebergs Pine Island has lost in the last few years – the glacier is one of the fastest melting in Antarctica.

It’s not just planes. We also saw the giant iceberg, known as B-46, from space. Landsat 8 tracked B-46’s progress after it broke off from Pine Island Glacier and began the journey northward, where it began to break apart and melt into the ocean.

Speaking of change, we’ve been launching Earth-observing satellites since 1958. In that time, we’ve seen some major changes. Cutting through soft, sandy soil on its journey to the Bay of Bengal, the Padma River in Bangladesh dances across the landscape in this time-lapse of 30 years’ worth of Landsat images.

Our space-based view of Earth helps us track other natural activities, too. With both a daytime and nighttime view, the Aqua satellite and the Suomi NPP satellite helped us see where wildfires were burning in California, while also tracking burn scars and smoke plumes..

Astronauts have an out-of-this-world view of Earth, literally. A camera mounted on the International Space Station captured this image of Hurricane Florence after it intensified to Category 4.

It’s not just missions studying Earth that capture views of our home planet. Parker Solar Probe turned back and looked at our home planet while en route to the Sun. Earth is the bright, round object.
Want to learn more about our home planet? Check out our third episode of NASA Science Live where we talked about Earth and what makes it so weird.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Far from Westeros, a Three-Eyed Raven Helps NASA Find Its Way
Perched on the outside of the International Space Station is Raven—a technology-filled module that helps NASA develop a relative navigation capability, which is essentially autopilot for spacecraft. Raven has been testing technologies to enable autonomous rendezvous in space, which means the ability to approach things in space without human involvement, even from the ground.

Developed by the Satellite Servicing Projects Division (SSPD), our three-eyed Raven has visible, infrared, and Lidar sensors and uses those “eyes” to image and track visiting spacecraft as they come and go from the space station. Although Raven is all-seeing, it only sees all in black and white. Color images do not offer an advantage in the case of Raven and Restore-L, which also utilize infrared and Lidar sensors.
The data from Raven’s sensors is sent to its processor, which autonomously sends commands that swivel Raven on its gimbal, or pointing system. When Raven turns using this system, it is able to track a vehicle. While these maneuvers take place, NASA operators evaluate the movements and make adjustments to perfect the relative navigation system technologies.

A few days ago, Raven completed its 21st observation of a spacecraft when it captured images of Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus vehicle delivering science investigations and supplies as part of its 11th commercial resupply services mission, including another SSPD payload called the Robotic External Leak Locator.

And just last month, Raven celebrated its two-year anniversary in space, marking the occasion with an observation of SpaceX’s Crew Dragon during the Demo-1 mission.

What is this—a spacecraft for ants??
While this shot of Dragon isn’t terribly impressive because of where the spacecraft docked on station, Raven has captured some truly great images when given the right viewing conditions.
From SpaceX Dragon resupply mission observations…

…to Cygnus supply vehicles.

Raven has observed six unique types of spacecraft.
It has also conducted a few observations not involving spacecraft, including the time it captured Hurricane Irma…

…or the time it captured station’s Dextre arm removing the Robotic Refueling Mission 3 payload, another mission developed by SSPD, from the Dragon spacecraft that delivered it to the orbiting laboratory.


Thus far, Raven has had a great, productive life aboard the station, but its work isn’t done yet! Whether it’s for Restore-L, which will robotically refuel a satellite, or getting humans to the Moon or Mars, the technologies Raven is demonstrating for a relative navigation system will support future NASA missions for decades to come.

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com










At Last, Scientists Have Found The Galaxy’s Missing Exoplanets: Cold Gas Giants
“By using the same instrument and leaving virtually no long-term gaps in the data, long-term, precise Doppler measurements finally became possible. A total of five brand new planets, one confirmation of a suggested planet, and three updated planets were announced in this latest study, bringing the total number of Jupiter-or-larger planets beyond the Jupiter-Sun distance up to 26. It shows us what we’d always hoped for: that our Solar System isn’t so unusual in the Universe; it’s just difficult to observe and detect planets like the ones we have.”
We’ve long suspected that there was nothing special about our Solar System; that Sun-like stars should have a wide variety of planets around them, including many of the types of worlds found orbiting our Sun. However, owing to the difficulty in making the kinds of measurements that would reveal them to us, our work has revealed a sample of planets biased towards two types of planets: the short-period worlds and the well-separated, high-mass worlds. Planets like Jupiter or Saturn were elusive for so long. But now, owing to research programs dedicated to monitoring nearby stars on decadal timescales, we’ve revealed a remarkable number of these worlds, many of which are now candidates for future direct imaging surveys.
The missing gas giants of the Universe, including worlds like the ones actually found orbiting our Sun, are finally within reach. Here’s how we’ve revealed them at last!










This Is How To Bring Dark Skies Back In An Increasingly Developed World
“A dark night sky is something we not only all deserve, it’s something that we could very easily have for a relatively small investment. The benefits, in addition to long-term cost savings, education, and the environmental positives, can be taken in all at once by everyone who both lives in, or simply passes through, your town.
And for those of you still asking, “what benefit is that?” As soon as you encounter your first dark sky community, you’ll see for yourself that there’s no explanation required. To take it all in, just look up.”
When was the last time you saw the Milky Way? If you’re like 99% of the United States or Europe, it wasn’t from your own backyard. While you might assume that’s because we need to have well-lit areas where most of us live, that’s only partially correct. It’s because we choose to have brightly-lit areas to meet our safety and commercial nighttime needs, but there’s a fundamental difference between well-lit and brightly-lit. More than 20 independent communities have taken all the steps necessary to restore darkness to their areas, following the recommendations and getting certified by the IDA: the International Dark Sky Association.
Forget about asking, “why aren’t there more?” Instead, try being the change you want to see, and work to bring dark skies, as well as health and environmental benefits, back to your own community!

A Surprising Surge at Vavilov Ice Cap
After moving quite slowly for decades, the outlet glacier of Vavilov Ice Cap began sliding dozens of times faster than is typical. The ice moved fast enough for the fan-shaped edge of the glacier to protrude from an ice cap on October Revolution Island and spread widely across the Kara Sea. The Landsat images above were acquired on July 1, 2013, June 18, 2015, and June 24, 2018, respectively.
“The fact that an apparently stable, cold-based glacier suddenly went from moving 20 meters per year to 20 meters per day was extremely unusual, perhaps unprecedented,” said University of Colorado Boulder glaciologist Michael Willis. “The numbers here are simply nuts. Before this happened, as far as I knew, cold-based glaciers simply didn’t do that…couldn’t do that.”
Willis and his colleagues are still piecing together what triggered such a dramatic surge. They suspect that marine sediments immediately offshore are unusually slippery, perhaps containing clay. Also, water must have somehow found its way under the land-based part of the glacier, reducing friction and priming the ice to slide.
Full story here: go.nasa.gov/2Z931lc
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
How NASA Earth Data Aids America

Today we roll out a new communications project that highlights some of the many ways that NASA’s Earth observations help people strengthen communities across the United States.
Space for U.S. features stories on how Earth science data is used to make informed decisions about public health, disaster response and recovery and environmental protection. By highlighting advanced technology from a global perspective, our data helps provide people achieve groundbreaking insights.

For example, a family-owned coffee company in Maine used our sunlight, wind and temperature data to determine the placement of their power-generating solar wall.
Space for U.S. features 56 stories illustrating how our science has made an impact in every state in the nation as well as the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico and regions along the Atlantic, Pacific, Gulf of Mexico, and the Great Lakes.

For six decades, we’ve used the vantage point of space to better understand our home planet and improve lives. Using Space for U.S., you can browse through stories about how applied Earth science either by state or by topics such as animals, disasters, energy, health, land and water. Each click brings you a story about how people are putting NASA data to work.

Explore the true stories behind the innovative technology, groundbreaking insights, and extraordinary collaboration happening right here in the United States with Space for U.S.
Check out “Space for U.S.” today! www.nasa.gov/spaceforus

For more information on NASA Earth, head to www.nasa.gov/Earth or https://appliedsciences.nasa.gov.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
How Big is Our Galaxy, the Milky Way?
When we talk about the enormity of the cosmos, it’s easy to toss out big numbers – but far harder to wrap our minds around just how large, how far and how numerous celestial bodies like exoplanets – planets beyond our solar system – really are.
So. How big is our Milky Way Galaxy?
We use light-time to measure the vast distances of space.
It’s the distance that light travels in a specific period of time. Also: LIGHT IS FAST, nothing travels faster than light.

How far can light travel in one second? 186,000 miles. It might look even faster in metric: 300,000 kilometers in one second. See? FAST.

How far can light travel in one minute? 11,160,000 miles. We’re moving now! Light could go around the Earth a bit more than 448 times in one minute.

Speaking of Earth, how long does it take light from the Sun to reach our planet? 8.3 minutes. (It takes 43.2 minutes for sunlight to reach Jupiter, about 484 million miles away.) Light is fast, but the distances are VAST.

In an hour, light can travel 671 million miles. We’re still light-years from the nearest exoplanet, by the way. Proxima Centauri b is 4.2 light-years away. So… how far is a light-year? 5.8 TRILLION MILES.

A trip at light speed to the very edge of our solar system – the farthest reaches of the Oort Cloud, a collection of dormant comets way, WAY out there – would take about 1.87 years.
Our galaxy contains 100 to 400 billion stars and is about 100,000 light-years across!
One of the most distant exoplanets known to us in the Milky Way is Kepler-443b. Traveling at light speed, it would take 3,000 years to get there. Or 28 billion years, going 60 mph. So, you know, far.
SPACE IS BIG.

Read more here: go.nasa.gov/2FTyhgH
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.










This Is What We Know About Black Holes In Advance Of The Event Horizon Telescope’s First Image
“For hundreds of years, humanity has expected black holes to exist. Over the course of all of our lifetimes, we’ve collected an entire suite of evidence that points not only to their existence, but to a fantastic agreement between their expected theoretical properties and what we’ve observed. But perhaps the most important prediction of all — that of the event horizon’s existence and properties — has never been directly tested before.
With simultaneous observations in hand from hundreds of telescopes across the globe, scientists have finished reconstructing an image, based on real data, of the largest black hole as seen from Earth: the 4 million solar mass monster at the center of the Milky Way. What we’ll see on April 10 will either further confirm General Relativity or cause us to rethink all that we believe about gravity. Eager with anticipation, the world now awaits.”
The Event Horizon Telescope will, on April 10 (tomorrow, at the time of this writing), release an image two years in the making: of the event horizon of the black hole at the Milky Way’s center. Many will look at this as the first definitive proof that black holes truly exist, but we mustn’t forget all the (overwhelming!) evidence we already have in hand. There is a ton that we already know about black holes that has been demonstrated observationally, and all of it is in spectacular agreement with what we theoretically expect.
On the eve of the Event Horizon Telescope’s big announcement, take some time to get a little perspective, and learn what we already know about black holes!
6 Ways NASA Technology Makes You Healthier
An important part of our mission is keeping astronauts strong and healthy during stays in space, but did you know that our technology also helps keep you healthy? And the origins of these space innovations aren’t always what you’d expect.
As we release the latest edition of NASA Spinoff, our yearly publication that celebrates all the ways NASA technology benefits us here on Earth, let’s look at some ways NASA is improving wellness for astronauts—and everyone else.
1. Weightless weight-lifting

Without gravity to work against, astronauts lose bone and muscle mass in space. To fight it, they work out regularly. But to get them a good burn, we had to get creative. After all, pumping iron doesn’t do much good when the weights float.
The solution? Elastic resistance. Inventor Paul Francis was already working on a portable home gym that relied on spiral-shaped springs made of an elastic material. He thought the same idea would work on the space station and after additional development and extensive testing, we agreed.
Our Interim Resistive Exercise Device launched in 2000 to help keep astronauts fit. And Francis’ original plan took off too. The technology perfected for NASA is at the heart of the Bowflex Revolution as well as a new line of handheld devices called OYO DoubleFlex, both of which enable an intensive—and extensive—workout, right at home.
2. Polymer coating keeps hearts beating

A key ingredient in a lifesaving treatment for many patients with congestive heart failure is made from a material a NASA researcher stumbled upon while working on a supersonic jet in the 1990s.
Today, a special kind of pacemaker that helps synchronize the left and right sides of the heart utilizes the unique substance known as LaRC-SI. The strong material can be cast extremely thin, which makes it easier to insert in the tightly twisted veins of the heart, and because it insulates so well, the pacemaker’s electric pulses go exactly where they should.
Since it was approved by the FDA in 2009, the device has been implanted hundreds of thousands of times.
3. Sutures strong enough for interplanetary transport

Many people mistakenly think we created Teflon. Not true: DuPont invented the unique polymer in 1938. But an innovative new way to use the material was developed to help us transport samples back from Mars and now aids in stitching up surgery patients.
Our scientists would love to get pristine Martian samples into our labs for more advanced testing. One complicating factor? The red dust makes it hard to get a clean seal on the sample container. That means the sample could get contaminated on its way back to Earth.
The team building the cannister had an idea, but they needed a material with very specific properties to make it work. They decided to use Polytetrafluoroethylene (that’s the scientific name for Teflon), which works really well in space.
The material we commonly recognize as Teflon starts as a powder, and to transform it into a nonstick coating, the powder gets processed a certain way. But process it differently, and you can get all kinds of different results.
For our Mars sample return cannister prototype, the powder was compressed at high pressures into a block, which was then forced through an extruder. (Imagine pressing playdough through a mold). It had never been done before, but the end result was durable, flexible and extremely thin: exactly what we needed.
And since the material can be implanted safely in the human body—it was also perfect as super strong sutures for after surgery.
4. Plant pots that clean the air

It may surprise you, but the most polluted air you breathe is likely the air inside your home and office. That’s especially true these days with energy-efficient insulation: the hot air gets sealed in, but so do any toxins coming off the paint, furniture, cooking gas, etc.
This was a problem NASA began worrying about decades ago, when we started planning for long duration space missions. After all, there’s no environment more insulated than a spaceship flying through the vacuum of space.
On Earth, plants are a big part of the “life support” system cleaning our air, so we wondered if they could do the same indoors or in space.
The results from extensive research surprised us: we learned the most important air scrubbing happens not through a plant’s leaves, but around its roots. And now you can get the cleanest air out of your houseplants by using a special plant pot, available online, developed with that finding in mind: it maximizes air flow through the soil, multiplying the plant’s ability to clean your air.
5. Gas sensor detects pollution from overhead

Although this next innovation wasn’t created with pollution in mind, it’s now helping keep an eye on one of the biggest greenhouse gasses: methane.
We created this tiny methane “sniffer” to help us look for signs of life on Mars. On Earth, the biggest source of methane is actually bacteria, so when one of our telescopes on the ground caught a glimpse of the gas on Mars, we knew we needed to take a closer look.
We sent this new, extremely sensitive sensor on the Curiosity Rover, but we knew it could also be put to good use here on our home planet. We adapted it, and today it gets mounted on drones and cars to quickly and accurately detect gas leaks and methane emissions from pipelines, oil wells and more.
The sensor can also be used to better study emissions from swamps and other natural sources, to better understand and perhaps mitigate their effects on climate change.
6. DNA “paint” highlights cellular damage

There’s been a lot of news lately about DNA editing: can genes be changed safely to make people healthier? Should they be?
As scientists and ethicists tackle these big questions, they need to be sure they know exactly what’s changing in the genome when they use the editing tools that already exist.
Well, thanks to a tool NASA helped create, we can actually highlight any abnormalities in the genetic code with special fluorescent “paint.”
But that’s not all the “paint” can do. We actually created it to better understand any genetic damage our astronauts incurred during their time in space, where radiation levels are far higher than on Earth. Down here, it could help do the same. For example, it can help doctors select the right cancer treatment by identifying the exact mutation in cancer cells.
You can learn more about all these innovations, and dozens more, in the 2019 edition of NASA Spinoff. Read it online or request a limited quantity print copy and we’ll mail it to you!










(Source)
Our Favorite Valentines Throughout the Universe
Today is Valentine’s Day. What better way to express that you love someone than with an intergalactic love gram? Check out some of our favorites and send them to all of your cosmic companions:
Your love is galactic

The Hubble Space Telescope revolutionized nearly all areas of astronomical research — and captured some truly lovely images. Here, a pair of intersecting galaxies swirl into the shape of a rose as a result of gravitational tidal pull. What type of roses are you getting for your love — red or galactic?
I think you’re n{ice}

IceBridge is the largest airborne survey of Earth’s polar ice ever flown. It captures 3-D views of Arctic and Antarctic ice sheets, ice shelves and sea ice. This lovely heart-shaped glacier feature was discovered in northwest Greenland during an IceBridge flight in 2017. Which of your lover’s features would you say are the coolest?
You’re absolutely magnetic

Even though we can’t see them, magnetic fields are all around us. One of the solar system’s largest magnetospheres belongs to Jupiter. Right now, our Juno spacecraft is providing scientists with their first glimpses of this unseen force. Is your attraction to your loved one magnetic?
You’re MARS-velous

This heart-shaped feature on the Martian landscape was captured by our Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. It was created by a small impact crater that blew darker material on the surface away. What impact has your loved one had on you?
I <3 you

From three billion miles away, Pluto sent a “love note” back to Earth, via our New Horizons spacecraft. This stunning image of Pluto’s “heart” shows one of the world’s most dominant features, estimated to be 1,000 miles (1,600 km) across at its widest point. Will you pass this love note on to someone special in your life?
Light of my life

Our Solar Dynamics Observatory keeps an eye on our closest star that brings energy to you and your love. The observatory helps us understand where the Sun’s energy comes from, how the inside of the Sun works, how energy is stored and released in the Sun’s atmosphere and much more. Who would you say is your ray of sunshine?
Do any of these cosmic phenomena remind you of someone in your universe? Download these cards here to send to all the stars in your sky.
Want something from the Red Planet to match your bouquet of red roses? Here is our collection of Martian Valentines.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

A high-definition video camera outside the space station captured stark and sobering views of Hurricane Florence, a Category 4 storm. Image Credit: ESA/NASA–A. Gerst

The scene is a late-spring afternoon in the Amazonis Planitia region of northern Mars. The view covers an area about four-tenths of a mile (644 meters) across. North is toward the top. The length of the dusty whirlwind’s shadow indicates that the dust plume reaches more than half a mile (800 meters) in height. The plume is about 30 yards or meters in diameter. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona

A false-color image of the Great Red Spot of Jupiterfrom Voyager 1. The white oval storm directly below the Great Red Spot has the approximate diameter of Earth. NASA, Caltech/JPL

The huge storm (great white spot) churning through the atmosphere in Saturn’s northern hemisphere overtakes itself as it encircles the planet in this true-color view from NASA’s Cassini spacecraft. Credit: Cassini Imaging Team, SSI, JPL, ESA, NASA; Color Composite: Jean-Luc Dauvergne

The spinning vortex of Saturn’s north polar storm resembles a deep red rose of giant proportions surrounded by green foliage in this false-color image from NASA’s Cassini spacecraft. Measurements have sized the eye at 1,250 miles (2,000 kilometers) across with cloud speeds as fast as 330 miles per hour (150 meters per second). This image is among the first sunlit views of Saturn’s north pole captured by Cassini’s imaging cameras. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SSI

Colorized infrared image of Uranus obtained on August 6, 2014, with adaptive optics on the 10-meter Keck telescope; white spots are large storms. Image credit: Imke de Pater, University of California, Berkeley / Keck Observatory images.

Neptune’s Great Dark Spot, a large anticyclonic storm similar to Jupiter’s Great Red Spot, observed by NASA’s Voyager 2 spacecraft in 1989. Credit: NASA / Jet Propulsion Lab

This true color image captured by NASA’S Cassini spacecraft before a distant flyby of Saturn’s moon Titan on June 27, 2012, shows a south polar vortex, or a swirling mass of gas around the pole in the atmosphere. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Space Science Institute

This artist’s concept shows what the weather might look like on cool star-like bodies known as brown dwarfs. These giant balls of gas start out life like stars, but lack the mass to sustain nuclear fusion at their cores, and instead, fade and cool with time.
New research from NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope suggests that most brown dwarfs are racked with colossal storms akin to Jupiter’s famous “Great Red Spot.” These storms may be marked by fierce winds, and possibly lightning. The turbulent clouds might also rain down molten iron, hot sand or salts – materials thought to make up the cloud layers of brown dwarfs.
Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Western Ontario/Stony Brook University

In this image, the nightmare world of HD 189733 b is the killer you never see coming. To the human eye, this far-off planet looks bright blue. But any space traveler confusing it with the friendly skies of Earth would be badly mistaken. The weather on this world is deadly. Its winds blow up to 5,400 mph (2 km/s) at seven times the speed of sound, whipping all would-be travelers in a sickening spiral around the planet. And getting caught in the rain on this planet is more than an inconvenience; it’s death by a thousand cuts. This scorching alien world possibly rains glass—sideways—in its howling winds. The cobalt blue color comes not from the reflection of a tropical ocean, as on Earth, but rather a hazy, blow-torched atmosphere containing high clouds laced with silicate particles. Image Credit: ESO/M. Kornmesser
Stellar Winds
Stellar winds are fast moving flows of material (protons, electrons and atoms of heavier metals) that are ejected from stars. These winds are characterised by a continuous outflow of material moving at speeds anywhere between 20 and 2,000 km/s.
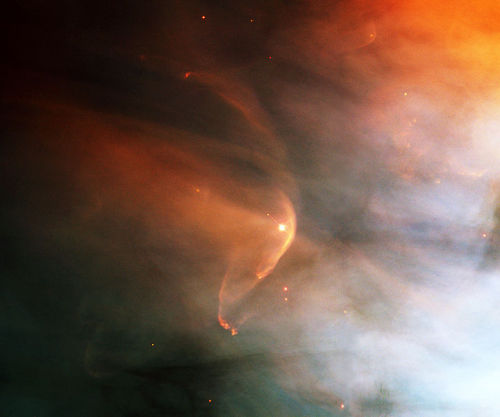

In the case of the Sun, the wind ‘blows’ at a speed of 200 to 300 km/s from quiet regions, and 700 km/s from coronal holes and active regions.
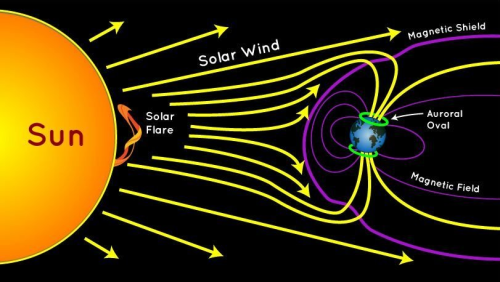
The causes, ejection rates and speeds of stellar winds vary with the mass of the star. In relatively cool, low-mass stars such as the Sun, the wind is caused by the extremely high temperature (millions of degrees Kelvin) of the corona.

his high temperature is thought to be the result of interactions between magnetic fields at the star’s surface, and gives the coronal gas sufficient energy to escape the gravitational attraction of the star as a wind. Stars of this type eject only a tiny fraction of their mass per year as a stellar wind (for example, only 1 part in 1014 of the Sun’s mass is ejected in this way each year), but this still represents losses of millions of tonnes of material each second. Even over their entire lifetime, stars like our Sun lose only a tiny fraction of 1% of their mass through stellar winds.
In contrast, hot, massive stars can produce stellar winds a billion times stronger than those of low-mass stars. Over their short lifetimes, they can eject many solar masses (perhaps up to 50% of their initial mass) of material in the form of 2,000 km/sec winds.

These stellar winds are driven directly by the radiation pressure from photons escaping the star. In some cases, high-mass stars can eject virtually all of their outer envelopes in winds. The result is a Wolf-Rayet star.
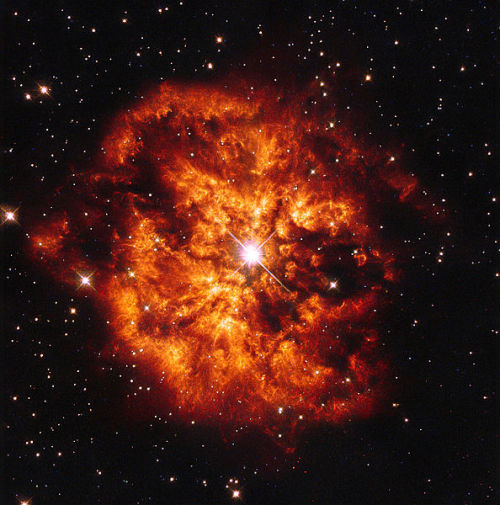

Stellar winds play an important part in the chemical evolution of the Universe, as they carry dust and metals back into the interstellar medium where they will be incorporated into the next generation of stars.
source (read more) + Wolf–Rayet star
Greatest Hits — Craters We Love
Our solar system was built on impacts — some big, some small — some fast, some slow. This week, in honor of a possible newly-discovered large crater here on Earth, here’s a quick run through of some of the more intriguing impacts across our solar system.
1. Mercury: A Basin Bigger Than Texas

Mercury does not have a thick atmosphere to protect it from space debris. The small planet is riddled with craters, but none as spectacular as the Caloris Basin. “Basin” is what geologists call craters larger than about 186 miles (300 kilometers) in diameter. Caloris is about 950 miles (1,525 kilometers) across and is ringed by mile-high mountains.
For scale, the state of Texas is 773 miles (1,244 kilometers) wide from east to west.
2. Venus: Tough on Space Rocks

Venus’ ultra-thick atmosphere finishes off most meteors before they reach the surface. The planet’s volcanic history has erased many of its craters, but like almost any place with solid ground in our solar system, there are still impact scars to be found. Most of what we know of Venus’ craters comes from radar images provided by orbiting spacecraft, such as NASA’s Magellan.
Mead Crater is the largest known impact site on Venus. It is about 170 miles (275 kilometers) in diameter. The relatively-flat, brighter inner floor of the crater indicates it was filled with impact melt and/or lava.
3. Earth: Still Craters After All These Years

Evidence of really big impacts — such as Arizona’s Meteor Crater — are harder to find on Earth. The impact history of our home world has largely been erased by weather and water or buried under lava, rock or ice. Nonetheless, we still find new giant craters occasionally.
A NASA glaciologist has discovered a possible impact crater buried under more than a mile of ice in northwest Greenland.
This follows the finding, announced in November 2018, of a 19-mile (31-kilometer) wide crater beneath Hiawatha Glacier – the first meteorite impact crater ever discovered under Earth’s ice sheets.
If the second crater, which has a width of over 22 miles (35 kilometers), is ultimately confirmed as the result of a meteorite impact, it will be the 22nd largest impact crater found on Earth.
4. Moon: Our Cratered Companion

Want to imagine what Earth might look like without its protective atmosphere, weather, water and other crater-erasing features? Look up at the Moon. The Moon’s pockmarked face offers what may be humanity’s most familiar view of impact craters.
One of the easiest to spot is Tycho, the tight circle and bright, radiating splat are easy slightly off center on the lower-left side of the full moon. Closer views of the 53-mile (85 kilometer)-wide crater from orbiting spacecraft reveal a beautiful central peak, topped with an intriguing boulder that would fill about half of a typical city block.
5. Mars: Still Taking Hits

Mars has just enough atmosphere to ensure nail-biting spacecraft landings, but not enough to prevent regular hits from falling space rocks. This dark splat on the Martian south pole is less than a year old, having formed between July and September 2018. The two-toned blast pattern tells a geologic story. The larger, lighter-colored blast pattern could be the result of scouring by winds from the impact shockwave on ice. The darker-colored inner blast pattern is because the impactor penetrated the thin ice layer, blasting the dark sand underneath in all directions.
6. Ceres: What Lies Beneath

The bright spots in Ceres’ Occator crater intrigued the world from the moment the approaching Dawn spacecraft first photographed it in 2015. Closer inspection from orbit revealed the spots to be the most visible example of hundreds of bright, salty deposits that decorate the dwarf planet like a smattering of diamonds. The science behind these bright spots is even more compelling: they are mainly sodium carbonate and ammonium chloride that somehow made their way to the surface in a slushy brine from within or below the crust. Thanks to Dawn, scientists have a better sense of how these reflective areas formed and changed over time — processes indicative of an active, evolving world.
7. Comet Tempel 1: We Did It!

Scientists have long known we can learn a lot from impact craters — so, in 2005, they made one themselves and watched it happen.
On July 4, 2005, NASA’s Deep Impact spacecraft trained its instruments on an 816-pound (370-kilogram) copper impactor as it smashed into comet Tempel 1.
One of the more surprising findings: The comet has a loose, “fluffy” structure, held together by gravity and contains a surprising amount of organic compounds that are part of the basic building blocks of life.
8. Mimas: May the 4th Be With You

Few Star Wars fans — us included — can resist Obi Wan Kenobi’s memorable line “That’s no moon…” when images of Saturn’s moon Mimas pop up on a screen. Despite its Death Star-like appearance, Mimas is most definitely a moon. Our Cassini spacecraft checked, a lot — and the superlaser-looking depression is simply an 81-mile (130-kilometer) wide crater named for the moon’s discoverer, William Herschel.
9. Europa: Say What?

The Welsh name of this crater on Jupiter’s ocean moon Europa looks like a tongue-twister, but it is easiest pronounced as “pool.” Pwyll is thought to be one of the youngest features we know of on Europa. The bright splat from the impact extends more than 600 miles (about 1,000 kilometers) around the crater, a fresh blanket over rugged, older terrain. “Fresh,” or young, is a relative term in geology; the crater and its rays are likely millions of years old.
10. Show Us Your Greatest Hits

Got a passion for Stickney, the dominant bowl-shaped crater on one end of Mars’ moon Phobos? Or a fondness for the sponge-like abundance of impacts on Saturn’s battered moon Hyperion (pictured)? There are countless craters to choose from. Share your favorites with us on Twitter, Instagram and Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com










(Source)
10 Things: CubeSats — Going Farther
Now that the MarCOs — a pair of briefcase-sized interplanetary CubeSats — seem to have reached their limit far beyond Mars, we’re looking forward to an expanding era of small, versatile and powerful space-based science machines.
Here are ten ways we’re pushing the limits of miniaturized technology to see just how far it can take us.

1. MarCO: The Farthest (So Far)
MarCO, short for Mars Cube One, was the first interplanetary mission to use a class of mini-spacecraft called CubeSats.
The MarCOs — nicknamed EVE and WALL-E, after characters from a Pixar film — served as communications relays during InSight’s November 2018 Mars landing, beaming back data at each stage of its descent to the Martian surface in near-real time, along with InSight’s first image.
WALL-E sent back stunning images of Mars as well, while EVE performed some simple radio science.
All of this was achieved with experimental technology that cost a fraction of what most space missions do: $18.5 million provided by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, which built the CubeSats.
WALL-E was last heard from on Dec. 29; EVE, on Jan. 4. Based on trajectory calculations, WALL-E is currently more than 1 million miles (1.6 million kilometers) past Mars; EVE is farther, almost 2 million miles (3.2 million kilometers) past Mars.

MarCO-B took these images as it approached Mars in November 2018. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
2. What Are CubeSats?
CubeSats were pioneered by California Polytechnic State University in 1999 and quickly became popular tools for students seeking to learn all aspects of spacecraft design and development.
Today, they are opening up space research to public and private entities like never before. With off-the-shelf parts and a compact size that allows them to hitch a ride with other missions — they can, for example, be ejected from the International Space Station, up to six at a time — CubeSats have slashed the cost of satellite development, opening up doors to test new instruments as well as to create constellations of satellites working together.
CubeSats can be flown in swarms, capturing simultaneous, multipoint measurements with identical instruments across a large area. Sampling entire physical systems in this way would drive forward our ability to understand the space environment around us, in the same way multiple weather sensors help us understand global weather systems.
Ready to get started? Check out NASA’s CubeSats 101 Guide.

Engineer Joel Steinkraus uses sunlight to test the solar arrays on one of the Mars Cube One (MarCO) spacecraft at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
3. Measuring Up
The size and cost of spacecraft vary depending on the application; some are the size of a pint of ice cream while others, like the Hubble Space Telescope, are as big as a school bus.
Small spacecraft (SmallSats) generally have a mass less than 400 pounds (180 kilograms) and are about the size of a large kitchen fridge.
CubeSats are a class of nanosatellites that use a standard size and form factor. The standard CubeSat size uses a “one unit” or “1U” measuring 10x10x10 centimeters (or about 4x4x4 inches) and is extendable to larger sizes: 1.5, 2, 3, 6, and even 12U.

The Sojourner rover (seen here on Mars in 1997) is an example of small technology that pioneered bigger things. Generations of larger rovers are being built on its success.
4. A Legacy of Small Pathfinders
Not unlike a CubeSat, NASA’s first spacecraft — Explorer 1 — was a small, rudimentary machine. It launched in 1958 and made the first discovery in outer space, the Van Allen radiation belts that surround Earth. It was the birth of the U.S. space program.
In 1997, a mini-rover named Sojourner rolled onto Mars, a trial run for more advanced rovers such as NASA’s Spirit, Opportunity and Curiosity.
Innovation often begins with pathfinder technology, said Jakob Van Zyl, director of the Solar System Exploration Directorate at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Once engineers prove something can be done, science missions follow.

5. Testing in Space
NASA is continually developing new technologies — technologies that are smaller than ever before, components that could improve our measurements, on-board data processing systems that streamline data retrievals, or new methods for gathering observations. Each new technology is thoroughly tested in a lab, sometimes on aircraft, or even at remote sites across the world. But the space environment is different than Earth. To know how something is going to operate in space, testing in space is the best option.
Sending something unproven to orbit has traditionally been a risky endeavor, but CubeSats have helped to change that. The diminutive satellites typically take less than two years to build. CubeSats are often a secondary payload on many rocket launches, greatly reducing cost. These hitchhikers can be deployed from a rocket or sent to the International Space Station and deployed from orbit.
Because of their quick development time and easy access to space, CubeSats have become the perfect platform for demonstrating how a new technological advancement will perform in orbit.

RainCube is a mini weather satellite, no bigger than a shoebox, that will measure storms. It’s part of several new NASA experiments to track storms from space with many small satellites, instead of individual, large ones. Credit: UCAR
6. At Work in Earth Orbit
A few recent examples from our home world:
RainCube, a satellite no bigger than a suitcase, is a prototype for a possible fleet of similar CubeSats that could one day help monitor severe storms, lead to improving the accuracy of weather forecasts and track climate change over time.
IceCube tested instruments for their ability to make space-based measurements of the small, frozen crystals that make up ice clouds. Like other clouds, ice clouds affect Earth’s energy budget by either reflecting or absorbing the Sun’s energy and by affecting the emission of heat from Earth into space. Thus, ice clouds are key variables in weather and climate models.

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket lifts off from Launch Complex 1 for the NASA ELaNa19 mission. Credit: Trevor Mahlmann/Rocket Lab
7. First Dedicated CubeSat Launch
A series of new CubeSats is now in space, conducting a variety of scientific investigations and technology demonstrations following a Dec. 17, 2018 launch from New Zealand — the first time CubeSats have launched for NASA on a rocket designed specifically for small payloads.
This mission included 10 Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa)-19 payloads, selected by NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative:
CubeSat Compact Radiation Belt Explorer (CeREs) — High energy particle measurement in Earth’s radiation belt
Simulation-to-Flight 1 (STF-1) — Software condensing to support CubeSat implementations
Advanced Electrical Bus (ALBus) — Advances in solar arrays and high capacity batteries
CubeSat Handling Of Multisystem Precision Time Transfer (CHOMPTT) — Navigation plans for exo-planetary implementation
CubeSail — Deployment and control of a solar sail blade
NMTSat — Magnetic field, high altitude plasma density
Rsat — Manipulation of robotic arms
Ionospheric Scintillation Explorer (ISX) — Plasma fluctuations in the upper atmosphere
Shields-1 — Radiation shielding
DaVinci — High School to Grade School STEM education
8. The Little CubeSat That Could
CubeSat technology is still in its infancy, with mission success rates hovering near 50 percent. So, a team of scientists and engineers set out on a quest. Their goal? To build a more resilient CubeSat — one that could handle the inevitable mishaps that bedevil any spacecraft, without going kaput.
They wanted a little CubeSat that could.
They got to work in 2014 and, after three years of development, Dellingr was ready to take flight.
Read the Full Story: Dellingr: The Little CubeSat That Could

Artist’s concept of Lunar Flashlight. Credit: NASA
9. Going Farther
There are a handful of proposed NASA missions could take CubeSat technology farther:
CUVE would travel to Venus to investigate a longstanding mystery about the planet’s atmosphere using ultraviolet-sensitive instruments and a novel, carbon-nanotube light-gathering mirror.
Lunar Flashlight would use a laser to search for water ice in permanently shadowed craters on the south pole of Earth’s Moon.
Near-Earth Asteroid Scout, a SmallSat, would use a solar sail to propel it to do science on asteroids that pass close to Earth.
All three spacecraft would hitch rides to space with other missions, a key advantage of these compact science machines.

Expedition 56 Flight Engineer Serena Auñón-Chancellor installs the NanoRacks Cubesat Deployer-14 (NRCSD-14) on the Multipurpose Experiment Platform inside the Japanese Kibo laboratory module. The NRCSD-14 was then placed in the Kibo airlock and moved outside of the space station to deploy a variety of CubeSats into Earth orbit. Credit: NASA
10. And We’re Just Getting Started
Even if they’re never revived, the team considers MarCO a spectacular success.
A number of the critical spare parts for each MarCO will be used in other CubeSat missions. That includes their experimental radios, antennas and propulsion systems. Several of these systems were provided by commercial vendors, making it easier for other CubeSats to use them as well.
More small spacecraft are on the way. NASA is set to launch a variety of new CubeSats in coming years.
“There’s big potential in these small packages,” said John Baker, the MarCO program manager at JPL. “CubeSats — part of a larger group of spacecraft called SmallSats — are a new platform for space exploration affordable to more than just government agencies.”
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com















Lunar eclipse 2019
Image credit: Dan Wery
