What Is Gravitational Lensing?
What is Gravitational Lensing?
A gravitational lens is a distribution of matter (such as a cluster of galaxies) between a distant light source and an observer, that is capable of bending the light from the source as the light travels towards the observer. This effect is known as gravitational lensing, and the amount of bending is one of the predictions of Albert Einstein’s general theory of relativity.

This illustration shows how gravitational lensing works. The gravity of a large galaxy cluster is so strong, it bends, brightens and distorts the light of distant galaxies behind it. The scale has been greatly exaggerated; in reality, the distant galaxy is much further away and much smaller. Credit: NASA, ESA, L. Calcada
There are three classes of gravitational lensing:
1° Strong lensing: where there are easily visible distortions such as the formation of Einstein rings, arcs, and multiple images.

Einstein ring. credit: NASA/ESA&Hubble
2° Weak lensing: where the distortions of background sources are much smaller and can only be detected by analyzing large numbers of sources in a statistical way to find coherent distortions of only a few percent. The lensing shows up statistically as a preferred stretching of the background objects perpendicular to the direction to the centre of the lens. By measuring the shapes and orientations of large numbers of distant galaxies, their orientations can be averaged to measure the shear of the lensing field in any region. This, in turn, can be used to reconstruct the mass distribution in the area: in particular, the background distribution of dark matter can be reconstructed. Since galaxies are intrinsically elliptical and the weak gravitational lensing signal is small, a very large number of galaxies must be used in these surveys.

The effects of foreground galaxy cluster mass on background galaxy shapes. The upper left panel shows (projected onto the plane of the sky) the shapes of cluster members (in yellow) and background galaxies (in white), ignoring the effects of weak lensing. The lower right panel shows this same scenario, but includes the effects of lensing. The middle panel shows a 3-d representation of the positions of cluster and source galaxies, relative to the observer. Note that the background galaxies appear stretched tangentially around the cluster.
3° Microlensing: where no distortion in shape can be seen but the amount of light received from a background object changes in time. The lensing object may be stars in the Milky Way in one typical case, with the background source being stars in a remote galaxy, or, in another case, an even more distant quasar. The effect is small, such that (in the case of strong lensing) even a galaxy with a mass more than 100 billion times that of the Sun will produce multiple images separated by only a few arcseconds. Galaxy clusters can produce separations of several arcminutes. In both cases the galaxies and sources are quite distant, many hundreds of megaparsecs away from our Galaxy.
Gravitational lenses act equally on all kinds of electromagnetic radiation, not just visible light. Weak lensing effects are being studied for the cosmic microwave background as well as galaxy surveys. Strong lenses have been observed in radio and x-ray regimes as well. If a strong lens produces multiple images, there will be a relative time delay between two paths: that is, in one image the lensed object will be observed before the other image.

As an exoplanet passes in front of a more distant star, its gravity causes the trajectory of the starlight to bend, and in some cases results in a brief brightening of the background star as seen by a telescope. The artistic concept illustrates this effect. This phenomenon of gravitational microlensing enables scientists to search for exoplanets that are too distant and dark to detect any other way.Credits: NASA Ames/JPL-Caltech/T. Pyle
Explanation in terms of space–time curvature

Simulated gravitational lensing by black hole by: Earther
In general relativity, light follows the curvature of spacetime, hence when light passes around a massive object, it is bent. This means that the light from an object on the other side will be bent towards an observer’s eye, just like an ordinary lens. In General Relativity the speed of light depends on the gravitational potential (aka the metric) and this bending can be viewed as a consequence of the light traveling along a gradient in light speed. Light rays are the boundary between the future, the spacelike, and the past regions. The gravitational attraction can be viewed as the motion of undisturbed objects in a background curved geometry or alternatively as the response of objects to a force in a flat geometry.

A galaxy perfectly aligned with a supernova (supernova PS1-10afx) acts as a cosmic magnifying glass, making it appear 100 billion times more dazzling than our Sun. Image credit: Anupreeta More/Kavli IPMU.
To learn more, click here.
More Posts from Ocrim1967 and Others

Shredded Star Leads to Important Black Hole Discovery
This artist’s illustration shows the region around a supermassive black hole after a star wandered too close and was ripped apart by extreme gravitational forces. Some of the remains of the star are pulled into an X-ray-bright disk where they circle the black hole before passing over the “event horizon,” the boundary beyond which nothing, including light, can escape. The elongated spot depicts a bright region in the disk, which causes a regular variation in the X-ray brightness of the source, allowing the spin rate of the black hole to be estimated. The curved region in the upper left shows where light from the other side of the disk has been curved over the top of the black hole.

This event was first detected by a network of optical telescopes called the All-Sky Automated Survey for Supernovae (ASASSN) in November 2014. Astronomers dubbed the new source ASASSN14-li and traced the bright flash of light to a galaxy about 290 million light years from Earth. They also identified it as a “tidal disruption” event, where one cosmic object is shredded by another through gravity.
Astronomers then used other telescopes including a flotilla of high-energy telescopes in space — NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory, ESA’s XMM-Newton and NASA’s Neil Gehrels Swift observatory — to study the X-rays emitted as the remains of a star swirled toward the black hole at the center of the galaxy.

The tidal disruption in ASASSN-14li is intriguing because it allowed astronomers to measure the spin rate of the black hole. A black hole has two fundamental properties: mass and spin. While it has been relatively easy for astronomers to determine the mass of black holes, it has been much more difficult to get accurate measurements of their spins.
This debris from the shredded star gave astronomers an avenue to get a direct measure of the black hole’s spin in ASASSN-14li. They found that the event horizon around this black hole is about 300 times the diameter of the Earth, yet rotates once every two minutes (compared to the 24 hours it takes to complete one rotation). This means that the black hole is spinning at least half as fast as the speed of light.

Scientists have determined spin rates for some stellar-mass black holes (those that typically weigh between 5 and 30 solar masses) in our Milky Way galaxy by observing rapid and regular variations in their X-ray brightness. A few supermassive black holes have shown similar variations, but they were only observed to repeat over a few cycles, rather than the 300,000 cycles seen for ASASSN-14li. With only a few cycles, the association of the variations with the spin of the black hole is not secure.
These results will likely encourage astronomers to observe future tidal disruption events for long durations to look for similar, regular variations in their X-ray brightness. source
Cosmic rays
Cosmic rays provide one of our few direct samples of matter from outside the solar system. They are high energy particles that move through space at nearly the speed of light. Most cosmic rays are atomic nuclei stripped of their atoms with protons (hydrogen nuclei) being the most abundant type but nuclei of elements as heavy as lead have been measured. Within cosmic-rays however we also find other sub-atomic particles like neutrons electrons and neutrinos.

Since cosmic rays are charged – positively charged protons or nuclei, or negatively charged electrons – their paths through space can be deflected by magnetic fields (except for the highest energy cosmic rays). On their journey to Earth, the magnetic fields of the galaxy, the solar system, and the Earth scramble their flight paths so much that we can no longer know exactly where they came from. That means we have to determine where cosmic rays come from by indirect means.

Because cosmic rays carry electric charge, their direction changes as they travel through magnetic fields. By the time the particles reach us, their paths are completely scrambled, as shown by the blue path. We can’t trace them back to their sources. Light travels to us straight from their sources, as shown by the purple path.

One way we learn about cosmic rays is by studying their composition. What are they made of? What fraction are electrons? protons (often referred to as hydrogen nuclei)? helium nuclei? other nuclei from elements on the periodic table? Measuring the quantity of each different element is relatively easy, since the different charges of each nucleus give very different signatures. Harder to measure, but a better fingerprint, is the isotopic composition (nuclei of the same element but with different numbers of neutrons). To tell the isotopes apart involves, in effect, weighing each atomic nucleus that enters the cosmic ray detector.

All of the natural elements in the periodic table are present in cosmic rays. This includes elements lighter than iron, which are produced in stars, and heavier elements that are produced in violent conditions, such as a supernova at the end of a massive star’s life.

Detailed differences in their abundances can tell us about cosmic ray sources and their trip through the galaxy. About 90% of the cosmic ray nuclei are hydrogen (protons), about 9% are helium (alpha particles), and all of the rest of the elements make up only 1%. Even in this one percent there are very rare elements and isotopes. Elements heavier than iron are significantly more rare in the cosmic-ray flux but measuring them yields critical information to understand the source material and acceleration of cosmic rays.

Even if we can’t trace cosmic rays directly to a source, they can still tell us about cosmic objects. Most galactic cosmic rays are probably accelerated in the blast waves of supernova remnants. The remnants of the explosions – expanding clouds of gas and magnetic field – can last for thousands of years, and this is where cosmic rays are accelerated. Bouncing back and forth in the magnetic field of the remnant randomly lets some of the particles gain energy, and become cosmic rays. Eventually they build up enough speed that the remnant can no longer contain them, and they escape into the galaxy.

Cosmic rays accelerated in supernova remnants can only reach a certain maximum energy, which depends on the size of the acceleration region and the magnetic field strength. However, cosmic rays have been observed at much higher energies than supernova remnants can generate, and where these ultra-high-energies come from is an open big question in astronomy. Perhaps they come from outside the galaxy, from active galactic nuclei, quasars or gamma ray bursts.

Or perhaps they’re the signature of some exotic new physics: superstrings, exotic dark matter, strongly-interacting neutrinos, or topological defects in the very structure of the universe. Questions like these tie cosmic-ray astrophysics to basic particle physics and the fundamental nature of the universe. (source)











Ask Ethan: Is Spacetime Really A Fabric?
“I’d like somebody to finally acknowledge and admit that showing balls on a bed sheet doesn’t cut it as a picture of reality.”
Okay, I admit it: visualizing General Relativity as balls on a bedsheet doesn’t make a whole lot of sense. For one, if this is what gravity is supposed to be, what pulls the balls “down” onto the bedsheet? For another, if space is three dimensional, why are we talking about a 2D “fabric” of space? And for another, why do these lines curve away from the mass, rather than towards it?
It’s true: this visualization of General Relativity is highly flawed. But, believe it or not, all visualizations of General Relativity inherently have similar flaws. The reason is that space itself is not an observable thing! In Einstein’s theory, General Relativity provides the link between the matter and energy in the Universe, which determines the geometric curvature of spacetime, and how the rest of the matter and energy in the Universe moves in response to that. In this Universe, we can only measure matter and energy, not space itself. We can visualize it how we like, but all visualizations are inherently flawed.
Come get the story of how to make as much sense as possible out of the Universe we actually have.








Observations of Earth, Soyuz, moon and Space Shuttle Endeavor made from the International Space Station.
source: images.nasa.gov
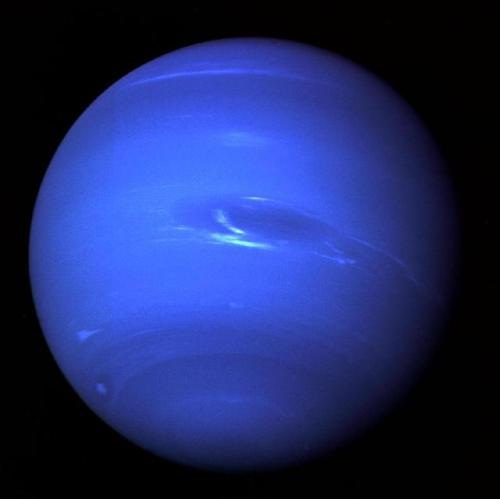
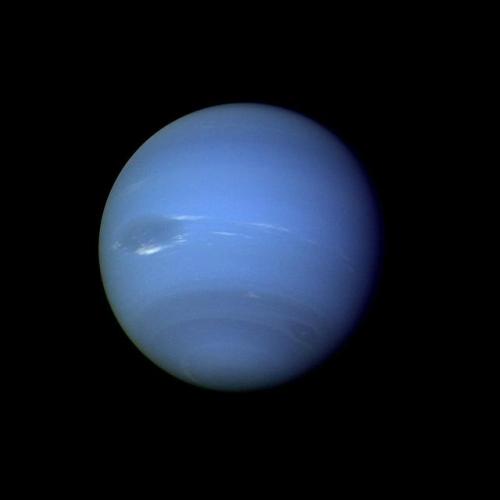
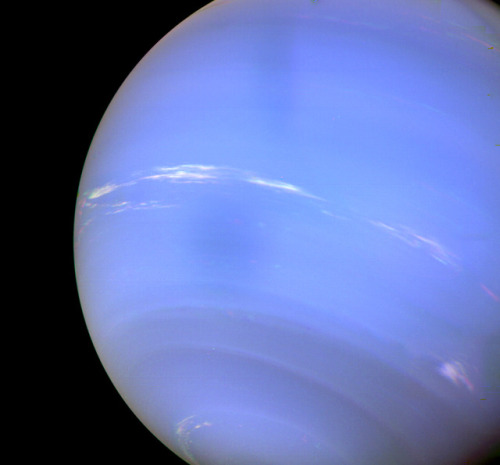
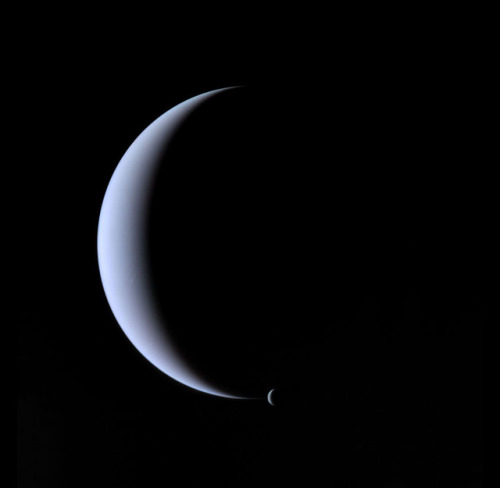




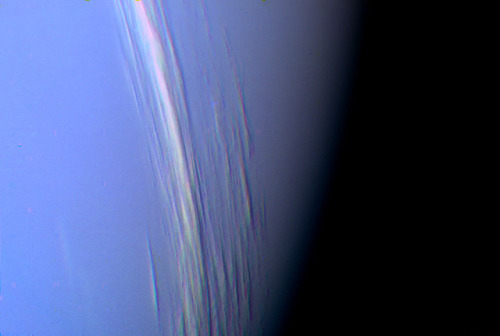





Neptune ♆
On this day in 1846 was discovered the planet Neptune.
The ice giant Neptune was the first planet located through mathematical predictions rather than through regular observations of the sky. (Galileo had recorded it as a fixed star during observations with his small telescope in 1612 and 1613.) When Uranus didn’t travel exactly as astronomers expected it to, a French mathematician, Urbain Joseph Le Verrier, proposed the position and mass of another as yet unknown planet that could cause the observed changes to Uranus’ orbit. After being ignored by French astronomers, Le Verrier sent his predictions to Johann Gottfried Galle at the Berlin Observatory, who found Neptune on his first night of searching in 1846. Seventeen days later, its largest moon, Triton, was also discovered.
Neptune is invisible to the naked eye because of its extreme distance from Earth. Interestingly, the highly eccentric orbit of the dwarf planet Pluto brings Pluto inside Neptune’s orbit for a 20-year period out of every 248 Earth years. Pluto can never crash into Neptune, though, because for every three laps Neptune takes around the Sun, Pluto makes two. This repeating pattern prevents close approaches of the two bodies.
Nearly 4.5 billion kilometers (2.8 billion miles) from the Sun, Neptune orbits the Sun once every 165 years.
Uranus’ blue-green color is also the result of atmospheric methane, but Neptune is a more vivid, brighter blue, so there must be an unknown component that causes the more intense color.
Despite its great distance and low energy input from the Sun, Neptune’s winds can be three times stronger than Jupiter’s and nine times stronger than Earth’s.
Winds on Neptune travel faster than the speed of sound.
In 1989, Voyager 2 tracked a large, oval-shaped, dark storm in Neptune’s southern hemisphere. This “Great Dark Spot” was large enough to contain the entire Earth.
Neptune has five known rings. Voyager 2’s observations confirmed that these unusual rings are not uniform but have four thick regions (clumps of dust) called arcs. The rings are thought to be relatively young and short-lived.
Neptune has 14 known moons, six of which were discovered by Voyager 2.
Triton, Neptune’s largest moon, orbits the planet in the opposite direction compared with the rest of the moons, suggesting that it may have been captured by Neptune in the distant past.
To know more about the planet Neptune click here and here.
Images credit: NASA/JPL- Caltech (some images processed by Kevin M. Gill)








(Source)







Psalm 19-1-4
Black holes
A black hole is a region of spacetime exhibiting such strong gravitational effects that nothing—not even particles and electromagnetic radiation such as light—can escape from inside it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can deform spacetime to form a black hole. The boundary of the region from which no escape is possible is called the event horizon. Although the event horizon has an enormous effect on the fate and circumstances of an object crossing it, no locally detectable features appear to be observed. In many ways a black hole acts like an ideal black body, as it reflects no light.

The idea of a body so massive that even light could not escape was briefly proposed by astronomical pioneer and English clergyman John Michell in a letter published in November 1784. Michell’s simplistic calculations assumed that such a body might have the same density as the Sun, and concluded that such a body would form when a star’s diameter exceeds the Sun’s by a factor of 500, and the surface escape velocity exceeds the usual speed of light.

At the center of a black hole, as described by general relativity, lies a gravitational singularity, a region where the spacetime curvature becomes infinite. For a non-rotating black hole, this region takes the shape of a single point and for a rotating black hole, it is smeared out to form a ring singularity that lies in the plane of rotation. In both cases, the singular region has zero volume. It can also be shown that the singular region contains all the mass of the black hole solution. The singular region can thus be thought of as having infinite density.

How Do Black Holes Form?
Scientists think the smallest black holes formed when the universe began.
Stellar black holes are made when the center of a very big star falls in upon itself, or collapses. When this happens, it causes a supernova. A supernova is an exploding star that blasts part of the star into space.

Scientists think supermassive black holes were made at the same time as the galaxy they are in.
Supermassive black holes, which can have a mass equivalent to billions of suns, likely exist in the centers of most galaxies, including our own galaxy, the Milky Way. We don’t know exactly how supermassive black holes form, but it’s likely that they’re a byproduct of galaxy formation. Because of their location in the centers of galaxies, close to many tightly packed stars and gas clouds, supermassive black holes continue to grow on a steady diet of matter.

If Black Holes Are “Black,” How Do Scientists Know They Are There?
A black hole can not be seen because strong gravity pulls all of the light into the middle of the black hole. But scientists can see how the strong gravity affects the stars and gas around the black hole.
Scientists can study stars to find out if they are flying around, or orbiting, a black hole.

When a black hole and a star are close together, high-energy light is made. This kind of light can not be seen with human eyes. Scientists use satellites and telescopes in space to see the high-energy light.

On 11 February 2016, the LIGO collaboration announced the first observation of gravitational waves; because these waves were generated from a black hole merger it was the first ever direct detection of a binary black hole merger. On 15 June 2016, a second detection of a gravitational wave event from colliding black holes was announced.

Simulation of gravitational lensing by a black hole, which distorts the image of a galaxy in the background
Animated simulation of gravitational lensing caused by a black hole going past a background galaxy. A secondary image of the galaxy can be seen within the black hole Einstein ring on the opposite direction of that of the galaxy. The secondary image grows (remaining within the Einstein ring) as the primary image approaches the black hole. The surface brightness of the two images remains constant, but their angular size varies, hence producing an amplification of the galaxy luminosity as seen from a distant observer. The maximum amplification occurs when the background galaxy (or in the present case a bright part of it) is exactly behind the black hole.
Could a Black Hole Destroy Earth?
Black holes do not go around in space eating stars, moons and planets. Earth will not fall into a black hole because no black hole is close enough to the solar system for Earth to do that.

Even if a black hole the same mass as the sun were to take the place of the sun, Earth still would not fall in. The black hole would have the same gravity as the sun. Earth and the other planets would orbit the black hole as they orbit the sun now.
The sun will never turn into a black hole. The sun is not a big enough star to make a black hole.
More posts about black holes
Source 1, 2 & 3
Sixty Years of Exploration, Innovation, and Discovery!

Exactly sixty years ago today, we opened our doors for the first time. And since then, we have opened up a universe of discovery and innovation.
There are so many achievements to celebrate from the past six decades, there’s no way we can go through all of them. If you want to dive deeper into our history of exploration, check out NASA: 60 Years and Counting.
In the meantime, take a moonwalk down memory lane with us while we remember a few of our most important accomplishments from the past sixty years!

In 1958, President Eisenhower signed the National Aeronautics and Space Act, which effectively created our agency. We officially opened for business on October 1.
To learn more about the start of our space program, watch our video: How It All Began.

Alongside the U.S. Air Force, we implemented the X-15 hypersonic aircraft during the 1950s and 1960s to improve aircraft and spacecraft.
The X-15 is capable of speeds exceeding Mach 6 (4,500 mph) at altitudes of 67 miles, reaching the very edge of space.
Dubbed the “finest and most productive research aircraft ever seen,” the X-15 was officially retired on October 24, 1968. The information collected by the X-15 contributed to the development of the Mercury, Gemini, Apollo, and Space Shuttle programs.
To learn more about how we have revolutionized aeronautics, watch our Leading Edge of Flight video.

On July 20, 1969, Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin became the first humans to walk on the moon. The crew of Apollo 11 had the distinction of completing the first return of soil and rock samples from beyond Earth.
Astronaut Gene Cernan, during Apollo 17, was the last person to have walked on the surface of the moon. (For now!)
The Lunar Roving Vehicle was a battery-powered rover that the astronauts used during the last three Apollo missions.
To learn more about other types of technology that we have either invented or improved, watch our video: Trailblazing Technology.

Our long-term Earth-observing satellite program began on July 23, 1972 with the launch of Landsat 1, the first in a long series (Landsat 9 is expected to launch in 2020!) We work directly with the U.S. Geological Survey to use Landsat to monitor and manage resources such as food, water, and forests.
Landsat data is one of many tools that help us observe in immense detail how our planet is changing. From algae blooms to melting glaciers to hurricane flooding, Landsat is there to help us understand our own planet better.
Off the Earth, for the Earth.
To learn more about how we contribute to the Earth sciences, watch our video: Home, Sweet Home.

Space Transportation System-1, or STS-1, was the first orbital spaceflight of our Space Shuttle program.
The first orbiter, Columbia, launched on April 12, 1981. Over the next thirty years, Challenger, Discovery, Atlantis, and Endeavour would be added to the space shuttle fleet.
Together, they flew 135 missions and carried 355 people into space using the first reusable spacecraft.

On January 16, 1978, we selected a class of 35 new astronauts–including the first women and African-American astronauts.
And on June 18, 1983, Sally Ride became the first American woman to enter space on board Challenger for STS-7.
To learn more about our astronauts, then and now, watch our Humans in Space video.

Everybody loves Hubble! The Hubble Space Telescope was launched into orbit on April 24, 1990, and has been blowing our minds ever since.
Hubble has not only captured stunning views of our distant stars and galaxies, but has also been there for once-in-a-lifetime cosmic events. For example, on January 6, 2010, Hubble captured what appeared to be a head-on collision between two asteroids–something no one has ever seen before.
In this image, Hubble captures the Carina Nebula illuminating a three-light-year tall pillar of gas and dust.
To learn more about how we have contributed to our understanding of the solar system and beyond, watch our video: What’s Out There?

Cooperation to build the International Space Station began in 1993 between the United States, Russia, Japan, and Canada.
The dream was fully realized on November 2, 2000, when Expedition 1 crew members boarded the station, signifying humanity’s permanent presence in space!
Although the orbiting lab was only a couple of modules then, it has grown tremendously since then!
To learn more about what’s happening on the orbiting outpost today, visit the Space Station page.

We have satellites in the sky, humans in orbit, and rovers on Mars. Very soon, we will be returning humankind to the Moon, and using it as a platform to travel to Mars and beyond.
And most importantly, we bring the universe to you.
What are your favorite NASA moments? We were only able to share a few of ours here, but if you want to learn about more important NASA milestones, check out 60 Moments in NASA History or our video, 60 Years in 60 Seconds.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
-
 thisworldisntrealhoney liked this · 1 year ago
thisworldisntrealhoney liked this · 1 year ago -
 lovepalecollectorpeachme liked this · 1 year ago
lovepalecollectorpeachme liked this · 1 year ago -
 sleepy-soft-boi reblogged this · 2 years ago
sleepy-soft-boi reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 happilykrispygalaxypensieri liked this · 2 years ago
happilykrispygalaxypensieri liked this · 2 years ago -
 starfaringships reblogged this · 2 years ago
starfaringships reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 spockvarietyhour liked this · 2 years ago
spockvarietyhour liked this · 2 years ago -
 darkcomicsbookslibrariesthing liked this · 2 years ago
darkcomicsbookslibrariesthing liked this · 2 years ago -
 polenasty liked this · 2 years ago
polenasty liked this · 2 years ago -
 alxsparks liked this · 2 years ago
alxsparks liked this · 2 years ago -
 werewolfin liked this · 2 years ago
werewolfin liked this · 2 years ago -
 utsuro-bune-0 reblogged this · 2 years ago
utsuro-bune-0 reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 utsuro-bune-0 liked this · 2 years ago
utsuro-bune-0 liked this · 2 years ago -
 playwith reblogged this · 2 years ago
playwith reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 nosemeocurreunnombrexd2570534vc liked this · 2 years ago
nosemeocurreunnombrexd2570534vc liked this · 2 years ago -
 colordesigns reblogged this · 2 years ago
colordesigns reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 stretch-en-wallz liked this · 2 years ago
stretch-en-wallz liked this · 2 years ago -
 stefanopreto reblogged this · 2 years ago
stefanopreto reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 stefanopreto liked this · 2 years ago
stefanopreto liked this · 2 years ago -
 cronostitan liked this · 2 years ago
cronostitan liked this · 2 years ago -
 chiprupt liked this · 2 years ago
chiprupt liked this · 2 years ago -
 flowersandspacestuff liked this · 2 years ago
flowersandspacestuff liked this · 2 years ago -
 ilokilok liked this · 2 years ago
ilokilok liked this · 2 years ago -
 stevenmiami liked this · 2 years ago
stevenmiami liked this · 2 years ago -
 stoicdaddypants reblogged this · 2 years ago
stoicdaddypants reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 autumnemrys reblogged this · 2 years ago
autumnemrys reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 autumnemrys liked this · 2 years ago
autumnemrys liked this · 2 years ago -
 kaze-no-tsubasa reblogged this · 2 years ago
kaze-no-tsubasa reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 lenbryant reblogged this · 2 years ago
lenbryant reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 thisperspective reblogged this · 2 years ago
thisperspective reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 lenbryant liked this · 2 years ago
lenbryant liked this · 2 years ago -
 readwing liked this · 2 years ago
readwing liked this · 2 years ago -
 silentexplorer liked this · 2 years ago
silentexplorer liked this · 2 years ago -
 tachvintlogic reblogged this · 2 years ago
tachvintlogic reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 kaiannanthi reblogged this · 2 years ago
kaiannanthi reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 kaiannanthi liked this · 2 years ago
kaiannanthi liked this · 2 years ago -
 carloshgc-char reblogged this · 2 years ago
carloshgc-char reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 sixtydaychips liked this · 2 years ago
sixtydaychips liked this · 2 years ago