What Is A Wormhole?
What is a Wormhole?
Wormholes were first theorized in 1916, though that wasn’t what they were called at the time. While reviewing another physicist’s solution to the equations in Albert Einstein’s theory of general relativity, Austrian physicist Ludwig Flamm realized another solution was possible. He described a “white hole,” a theoretical time reversal of a black hole. Entrances to both black and white holes could be connected by a space-time conduit.

In 1935, Einstein and physicist Nathan Rosen used the theory of general relativity to elaborate on the idea, proposing the existence of “bridges” through space-time. These bridges connect two different points in space-time, theoretically creating a shortcut that could reduce travel time and distance. The shortcuts came to be called Einstein-Rosen bridges, or wormholes.

Certain solutions of general relativity allow for the existence of wormholes where the mouth of each is a black hole. However, a naturally occurring black hole, formed by the collapse of a dying star, does not by itself create a wormhole.
Wormholes are consistent with the general theory of relativity, but whether wormholes actually exist remains to be seen.

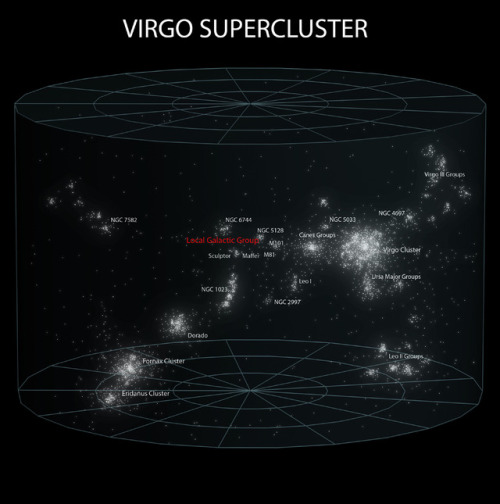
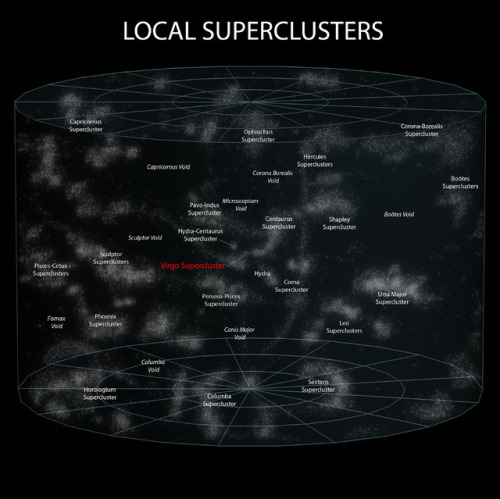
A wormhole could connect extremely long distances such as a billion light years or more, short distances such as a few meters, different universes, or different points in time
For a simplified notion of a wormhole, space can be visualized as a two-dimensional (2D) surface. In this case, a wormhole would appear as a hole in that surface, lead into a 3D tube (the inside surface of a cylinder), then re-emerge at another location on the 2D surface with a hole similar to the entrance. An actual wormhole would be analogous to this, but with the spatial dimensions raised by one. For example, instead of circular holes on a 2D plane, the entry and exit points could be visualized as spheres in 3D space.

Science fiction is filled with tales of traveling through wormholes. But the reality of such travel is more complicated, and not just because we’ve yet to spot one.

The first problem is size. Primordial wormholes are predicted to exist on microscopic levels, about 10–33 centimeters. However, as the universe expands, it is possible that some may have been stretched to larger sizes.
Another problem comes from stability. The predicted Einstein-Rosen wormholes would be useless for travel because they collapse quickly.

“You would need some very exotic type of matter in order to stabilize a wormhole,” said Hsu, “and it’s not clear whether such matter exists in the universe.”
But more recent research found that a wormhole containing “exotic” matter could stay open and unchanging for longer periods of time.

Exotic matter, which should not be confused with dark matter or antimatter, contains negative energy density and a large negative pressure. Such matter has only been seen in the behavior of certain vacuum states as part of quantum field theory.
If a wormhole contained sufficient exotic matter, whether naturally occurring or artificially added, it could theoretically be used as a method of sending information or travelers through space. Unfortunately, human journeys through the space tunnels may be challenging.

Wormholes may not only connect two separate regions within the universe, they could also connect two different universes. Similarly, some scientists have conjectured that if one mouth of a wormhole is moved in a specific manner, it could allow for time travel.

Although adding exotic matter to a wormhole might stabilize it to the point that human passengers could travel safely through it, there is still the possibility that the addition of “regular” matter would be sufficient to destabilize the portal.
Today’s technology is insufficient to enlarge or stabilize wormholes, even if they could be found. However, scientists continue to explore the concept as a method of space travel with the hope that technology will eventually be able to utilize them.
source
source
images: x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x
More Posts from Ocrim1967 and Others
Your Gut in Space
Finding the Right Balance for the Microbiota
Trillions of microorganisms live on and in the human body, many of them essential to its function and health. These organisms, collectively known as the microbiota, outnumber cells in the body by at least five times.

Microorganisms in the intestinal tract, the gut microbiota, play an especially important role in human health. An investigation on the International Space Station, Rodent Research-7 (RR-7), studies how the gut microbiota changes in response to spaceflight, and how that change in turn affects the immune system, metabolic system, and circadian or daily rhythms.

Research shows that the microbiota in the mammalian digestive tract has a major impact on an individual’s physiology and behavior. In humans, disruption of microbial communities has been linked to multiple health problems affecting intestinal, immune, mental and metabolic systems.

The investigation compares two different genetic strains of mice and two different durations of spaceflight. Twenty mice, ten of each strain, launch to the space station, and another 20 remain on the ground in identical conditions (except, of course, for the absence of gravity). Mice are a model organism that often serves as a scientific stand-in for other mammals and humans.

Fecal material collected from the mice every two weeks will be examined for changes in the gut microbiota. Researchers plan to analyze fecal and tissue samples after 30 and 90 days of flight to compare the effects of different durations of time in space.

With a better understanding of relationships between changes such as disruption in sleep and an imbalance of microbial populations, researchers can identify specific factors that contribute to changes in the microbiota. Further studies then can determine proactive measures and countermeasures to protect astronaut health during long-term missions.

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.










At Last, Scientists Have Found The Galaxy’s Missing Exoplanets: Cold Gas Giants
“By using the same instrument and leaving virtually no long-term gaps in the data, long-term, precise Doppler measurements finally became possible. A total of five brand new planets, one confirmation of a suggested planet, and three updated planets were announced in this latest study, bringing the total number of Jupiter-or-larger planets beyond the Jupiter-Sun distance up to 26. It shows us what we’d always hoped for: that our Solar System isn’t so unusual in the Universe; it’s just difficult to observe and detect planets like the ones we have.”
We’ve long suspected that there was nothing special about our Solar System; that Sun-like stars should have a wide variety of planets around them, including many of the types of worlds found orbiting our Sun. However, owing to the difficulty in making the kinds of measurements that would reveal them to us, our work has revealed a sample of planets biased towards two types of planets: the short-period worlds and the well-separated, high-mass worlds. Planets like Jupiter or Saturn were elusive for so long. But now, owing to research programs dedicated to monitoring nearby stars on decadal timescales, we’ve revealed a remarkable number of these worlds, many of which are now candidates for future direct imaging surveys.
The missing gas giants of the Universe, including worlds like the ones actually found orbiting our Sun, are finally within reach. Here’s how we’ve revealed them at last!










Why 2020 Might Be The Best Geminid Meteor Shower Of All-Time
“As the large parent body of the Geminids, asteroid 3200 Phaethon, continues on its tight orbit around the Sun, it will continue to expel matter and be torn apart, bit by tiny bit. The asteroid is about the size of the one that struck Earth 65 million years ago, causing our last great mass extinction. But instead of colliding with us all at once, this ~6 km wide asteroid is slowly dissipating in the presence of the Sun, creating tails of matter and ions but also an ever-thickening debris stream.
With each mid-December that rolls past, Earth slams through that debris stream, creating a show that gets progressively more spectacular with each set of orbits that regularly tick by. Over the past 15 years, the Geminids have regularly been one of the two best displays of meteor showers on Earth, and it’s eminently possible that 2020 will set a new record. The Moon, the Earth, and all of the other predictable conditions are just right for a spectacular show. If the clouds cooperate on December 13 and 14, treat yourself to the greatest natural show of the year. With all that 2020 has brought us, we can all use a cosmic treat like this one.”
Can everyone just have a good thing to enjoy? Can we all just have something nice that we don’t have to fight over? Well, nature might deliver what humanity has been unable to bring us for 2020: a natural show that can’t be stopped by anything, except for clouds.
Get your Geminid fix today, and then look up on December 13/14 to fully enjoy the show!
Sixty Years of Exploration, Innovation, and Discovery!

Exactly sixty years ago today, we opened our doors for the first time. And since then, we have opened up a universe of discovery and innovation.
There are so many achievements to celebrate from the past six decades, there’s no way we can go through all of them. If you want to dive deeper into our history of exploration, check out NASA: 60 Years and Counting.
In the meantime, take a moonwalk down memory lane with us while we remember a few of our most important accomplishments from the past sixty years!

In 1958, President Eisenhower signed the National Aeronautics and Space Act, which effectively created our agency. We officially opened for business on October 1.
To learn more about the start of our space program, watch our video: How It All Began.

Alongside the U.S. Air Force, we implemented the X-15 hypersonic aircraft during the 1950s and 1960s to improve aircraft and spacecraft.
The X-15 is capable of speeds exceeding Mach 6 (4,500 mph) at altitudes of 67 miles, reaching the very edge of space.
Dubbed the “finest and most productive research aircraft ever seen,” the X-15 was officially retired on October 24, 1968. The information collected by the X-15 contributed to the development of the Mercury, Gemini, Apollo, and Space Shuttle programs.
To learn more about how we have revolutionized aeronautics, watch our Leading Edge of Flight video.

On July 20, 1969, Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin became the first humans to walk on the moon. The crew of Apollo 11 had the distinction of completing the first return of soil and rock samples from beyond Earth.
Astronaut Gene Cernan, during Apollo 17, was the last person to have walked on the surface of the moon. (For now!)
The Lunar Roving Vehicle was a battery-powered rover that the astronauts used during the last three Apollo missions.
To learn more about other types of technology that we have either invented or improved, watch our video: Trailblazing Technology.

Our long-term Earth-observing satellite program began on July 23, 1972 with the launch of Landsat 1, the first in a long series (Landsat 9 is expected to launch in 2020!) We work directly with the U.S. Geological Survey to use Landsat to monitor and manage resources such as food, water, and forests.
Landsat data is one of many tools that help us observe in immense detail how our planet is changing. From algae blooms to melting glaciers to hurricane flooding, Landsat is there to help us understand our own planet better.
Off the Earth, for the Earth.
To learn more about how we contribute to the Earth sciences, watch our video: Home, Sweet Home.

Space Transportation System-1, or STS-1, was the first orbital spaceflight of our Space Shuttle program.
The first orbiter, Columbia, launched on April 12, 1981. Over the next thirty years, Challenger, Discovery, Atlantis, and Endeavour would be added to the space shuttle fleet.
Together, they flew 135 missions and carried 355 people into space using the first reusable spacecraft.

On January 16, 1978, we selected a class of 35 new astronauts–including the first women and African-American astronauts.
And on June 18, 1983, Sally Ride became the first American woman to enter space on board Challenger for STS-7.
To learn more about our astronauts, then and now, watch our Humans in Space video.

Everybody loves Hubble! The Hubble Space Telescope was launched into orbit on April 24, 1990, and has been blowing our minds ever since.
Hubble has not only captured stunning views of our distant stars and galaxies, but has also been there for once-in-a-lifetime cosmic events. For example, on January 6, 2010, Hubble captured what appeared to be a head-on collision between two asteroids–something no one has ever seen before.
In this image, Hubble captures the Carina Nebula illuminating a three-light-year tall pillar of gas and dust.
To learn more about how we have contributed to our understanding of the solar system and beyond, watch our video: What’s Out There?

Cooperation to build the International Space Station began in 1993 between the United States, Russia, Japan, and Canada.
The dream was fully realized on November 2, 2000, when Expedition 1 crew members boarded the station, signifying humanity’s permanent presence in space!
Although the orbiting lab was only a couple of modules then, it has grown tremendously since then!
To learn more about what’s happening on the orbiting outpost today, visit the Space Station page.

We have satellites in the sky, humans in orbit, and rovers on Mars. Very soon, we will be returning humankind to the Moon, and using it as a platform to travel to Mars and beyond.
And most importantly, we bring the universe to you.
What are your favorite NASA moments? We were only able to share a few of ours here, but if you want to learn about more important NASA milestones, check out 60 Moments in NASA History or our video, 60 Years in 60 Seconds.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.





Lunar eclipse 2019
Image credit: Dan Wery



Created using still images taken by the Cassini spacecraft during it’s flyby of Jupiter and while at Saturn. Shown is Io and Europa over Jupiter’s Great Red Spot.
NASA/JPL-Caltech/SSI/CICLOPS/Kevin M. Gill








(Source)










Here’s Why Black Holes Are Crullers, Not Donuts
“Just a few years ago, we didn’t even know whether it was a certainty that black holes had an event horizon, as we’d never observed one directly. In 2017, a series of observations were finally taken that could settle the issue. After a wait of two years, the first direct image of a black hole was released, and it showed us that the event horizon was, in fact, real as predicted, and that its properties agreed with Einstein’s predictions.
Now, another two years later, the polarization data has been added into the fold, and we can now reconstruct the magnetic properties of the plasma surrounding the black hole, along with how those features are imprinted onto the emitted photons. We still only have the one black hole that’s been directly imaged, but we can see how the light, the polarization, and the magnetic properties of the plasma surrounding the event horizon all change over time.”
You’ve seen the photo, but have you learned the science? Black holes are crullers, not donuts, and magnetized plasma is the reason why.

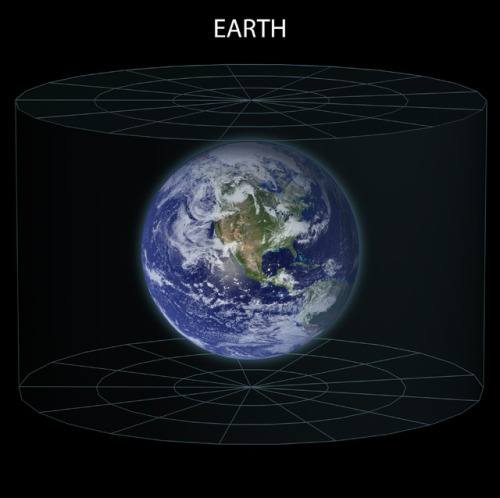
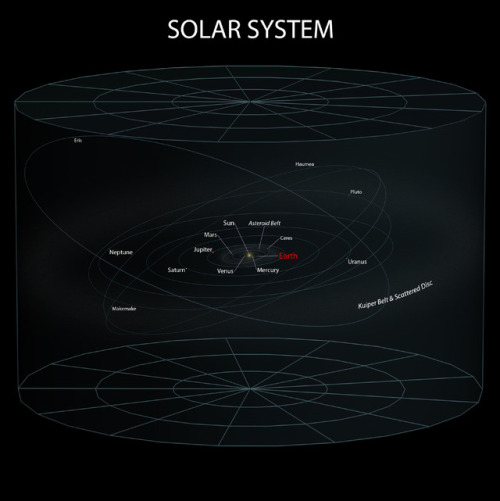
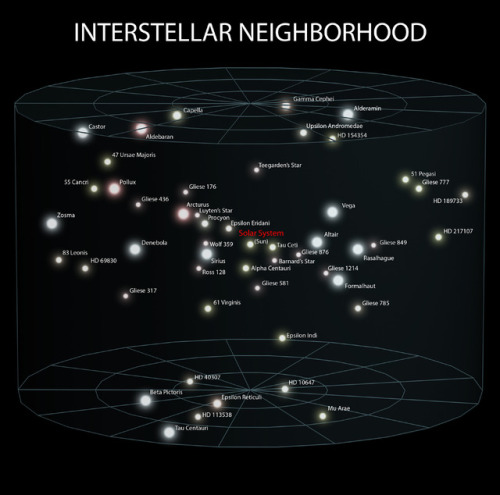

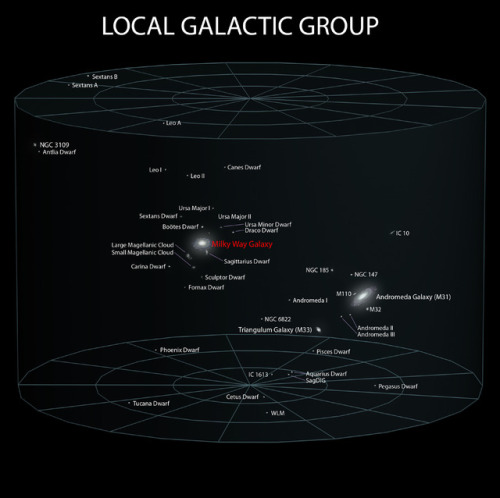

~ wikimedia commons
5 Ways the Moon Landing Changed Life on Earth
When Neil Armstrong took his first steps on the Moon 50 years ago, he famously said “that’s one small step for a man, one giant leap for mankind.” He was referring to the historic milestone of exploring beyond our own planet — but there’s also another way to think about that giant leap: the massive effort to develop technologies to safely reach, walk on the Moon and return home led to countless innovations that have improved life on Earth.
Armstrong took one small step on the lunar surface, but the Moon landing led to a giant leap forward in innovations for humanity.
Here are five examples of technology developed for the Apollo program that we’re still using today:
1. Food Safety Standards
As soon as we started planning to send astronauts into space, we faced the problem of what to feed them — and how to ensure the food was safe to eat. Can you imagine getting food poisoning on a spacecraft, hundreds of thousands of miles from home?
We teamed up with a familiar name in food production: the Pillsbury Company. The company soon realized that existing quality control methods were lacking. There was no way to be certain, without extensive testing that destroyed the sample, that the food was free of bacteria and toxins.
Pillsbury revamped its entire food-safety process, creating what became the Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point system. Its aim was to prevent food safety problems from occurring, rather than catch them after the fact. They managed this by analyzing and controlling every link in the chain, from the raw materials to the processing equipment to the people handling the food.
Today, this is one of the space program’s most far-reaching spinoffs. Beyond keeping the astronaut food supply safe, the Hazard Analysis and Critical Point system has also been adopted around the world — and likely reduced the risk of bacteria and toxins in your local grocery store.

2. Digital Controls for Air and Spacecraft
The Apollo spacecraft was revolutionary for many reasons. Did you know it was the first vehicle to be controlled by a digital computer? Instead of pushrods and cables that pilots manually adjusted to manipulate the spacecraft, Apollo’s computer sent signals to actuators at the flick of a switch.
Besides being physically lighter and less cumbersome, the switch to a digital control system enabled storing large quantities of data and programming maneuvers with complex software.
Before Apollo, there were no digital computers to control airplanes either. Working together with the Navy and Draper Laboratory, we adapted the Apollo digital flight computer to work on airplanes. Today, whatever airline you might be flying, the pilot is controlling it digitally, based on the technology first developed for the flight to the Moon.

3. Earthquake-ready Shock Absorbers
A shock absorber descended from Apollo-era dampers and computers saves lives by stabilizing buildings during earthquakes.
Apollo’s Saturn V rockets had to stay connected to the fueling tubes on the launchpad up to the very last second. That presented a challenge: how to safely move those tubes out of the way once liftoff began. Given how fast they were moving, how could we ensure they wouldn’t bounce back and smash into the vehicle?
We contracted with Taylor Devices, Inc. to develop dampers to cushion the shock, forcing the company to push conventional shock isolation technology to the limit.
Shortly after, we went back to the company for a hydraulics-based high-speed computer. For that challenge, the company came up with fluidic dampers—filled with compressible fluid—that worked even better. We later applied the same technology on the Space Shuttle’s launchpad.
The company has since adapted these fluidic dampers for buildings and bridges to help them survive earthquakes. Today, they are successfully protecting structures in some of the most quake-prone areas of the world, including Tokyo, San Francisco and Taiwan.

4. Insulation for Space
We’ve all seen runners draped in silvery “space blankets” at the end of marathons, but did you know the material, called radiant barrier insulation, was actually created for space?
Temperatures outside of Earth’s atmosphere can fluctuate widely, from hundreds of degrees below to hundreds above zero. To better protect our astronauts, during the Apollo program we invented a new kind of effective, lightweight insulation.
We developed a method of coating mylar with a thin layer of vaporized metal particles. The resulting material had the look and weight of thin cellophane packaging, but was extremely reflective—and pound-for-pound, better than anything else available.
Today the material is still used to protect astronauts, as well as sensitive electronics, in nearly all of our missions. But it has also found countless uses on the ground, from space blankets for athletes to energy-saving insulation for buildings. It also protects essential components of MRI machines used in medicine and much, much more.

Image courtesy of the U.S. Marines
5. Healthcare Monitors
Patients in hospitals are hooked up to sensors that send important health data to the nurse’s station and beyond — which means when an alarm goes off, the right people come running to help.
This technology saves lives every day. But before it reached the ICU, it was invented for something even more extraordinary: sending health data from space down to Earth.
When the Apollo astronauts flew to the Moon, they were hooked up to a system of sensors that sent real-time information on their blood pressure, body temperature, heart rate and more to a team on the ground.
The system was developed for us by Spacelabs Healthcare, which quickly adapted it for hospital monitoring. The company now has telemetric monitoring equipment in nearly every hospital around the world, and it is expanding further, so at-risk patients and their doctors can keep track of their health even outside the hospital.

Only a few people have ever walked on the Moon, but the benefits of the Apollo program for the rest of us continue to ripple widely.
In the years since, we have continued to create innovations that have saved lives, helped the environment, and advanced all kinds of technology.
Now we’re going forward to the Moon with the Artemis program and on to Mars — and building ever more cutting-edge technologies to get us there. As with the many spinoffs from the Apollo era, these innovations will transform our lives for generations to come.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
-
 gregorlenko liked this · 1 year ago
gregorlenko liked this · 1 year ago -
 rank-sentimentalist reblogged this · 1 year ago
rank-sentimentalist reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 rank-sentimentalist liked this · 1 year ago
rank-sentimentalist liked this · 1 year ago -
 quinlovelia liked this · 1 year ago
quinlovelia liked this · 1 year ago -
 viladis1971 liked this · 1 year ago
viladis1971 liked this · 1 year ago -
 magickalchaos reblogged this · 1 year ago
magickalchaos reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 stuffandparables reblogged this · 1 year ago
stuffandparables reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 vocatuselixir liked this · 1 year ago
vocatuselixir liked this · 1 year ago -
 maroonpurpleprince liked this · 1 year ago
maroonpurpleprince liked this · 1 year ago -
 saturniinne liked this · 1 year ago
saturniinne liked this · 1 year ago -
 bastardsaint reblogged this · 1 year ago
bastardsaint reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 eyomarax reblogged this · 1 year ago
eyomarax reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 1-universe-1-spirit-1 reblogged this · 2 years ago
1-universe-1-spirit-1 reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 septimaseverina reblogged this · 2 years ago
septimaseverina reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 beefyfurrystuff liked this · 2 years ago
beefyfurrystuff liked this · 2 years ago -
 carefreemelon liked this · 2 years ago
carefreemelon liked this · 2 years ago -
 xploseof reblogged this · 2 years ago
xploseof reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 legally-a-bastard reblogged this · 2 years ago
legally-a-bastard reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 josephaudreleroix liked this · 2 years ago
josephaudreleroix liked this · 2 years ago -
 draemun reblogged this · 2 years ago
draemun reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 draemun liked this · 2 years ago
draemun liked this · 2 years ago -
 jazzietu reblogged this · 2 years ago
jazzietu reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 misantropagentile liked this · 2 years ago
misantropagentile liked this · 2 years ago -
 clown-alley-dot-com liked this · 2 years ago
clown-alley-dot-com liked this · 2 years ago -
 willbdeactivatingsoon liked this · 2 years ago
willbdeactivatingsoon liked this · 2 years ago -
 yourtoradorasextendedwarranty liked this · 2 years ago
yourtoradorasextendedwarranty liked this · 2 years ago -
 elpis-muse liked this · 2 years ago
elpis-muse liked this · 2 years ago -
 goethefaustworld liked this · 2 years ago
goethefaustworld liked this · 2 years ago -
 snickerslizard liked this · 2 years ago
snickerslizard liked this · 2 years ago -
 kaseycryptid-reactivated39253199 liked this · 2 years ago
kaseycryptid-reactivated39253199 liked this · 2 years ago -
 socoperspective liked this · 2 years ago
socoperspective liked this · 2 years ago -
 wanderer001 reblogged this · 2 years ago
wanderer001 reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 wanderer001 liked this · 2 years ago
wanderer001 liked this · 2 years ago -
 labseraph liked this · 2 years ago
labseraph liked this · 2 years ago -
 toastedphantom liked this · 2 years ago
toastedphantom liked this · 2 years ago -
 askmarietheapprentice reblogged this · 2 years ago
askmarietheapprentice reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 beardedmrbean reblogged this · 2 years ago
beardedmrbean reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 cyberpunkessence2 liked this · 2 years ago
cyberpunkessence2 liked this · 2 years ago -
 andthenthereweren0n3 liked this · 2 years ago
andthenthereweren0n3 liked this · 2 years ago -
 macafeenix liked this · 2 years ago
macafeenix liked this · 2 years ago