This Is What The Milky Way’s Magnetic Field Looks Like










This Is What The Milky Way’s Magnetic Field Looks Like
“The Milky Way’s gas, dust, stars and more create fascinating, measurable structures. Subtracting out all the foregrounds yields the cosmic background signal, which possesses tiny temperature imperfections. But the galactic foreground isn’t useless; it’s a map unto itself. All background light gets polarized by these foregrounds, enabling the reconstruction of our galaxy’s magnetic field.”
Have you ever wondered what our galaxy’s magnetic field looks like? As long as we restrict ourselves to looking in the type of light that human eyes can see, the optical portion of the spectrum, we’re extremely limited as far as what we can infer. However, if we move on to data from the microwave portion of the spectrum, and in particular we look at the data that comes from the polarization of background light (and the foreground light directly), we should be able to reconstruct our galaxy’s magnetic fields to the best precision ever. The Planck satellite, in addition to mapping the CMB to better precision than ever before, has enabled us to do exactly that.
Even though there are still some small questions and uncertainties, you won’t want to miss these incredible pictures that showcase just how far we’ve come!
More Posts from Ocrim1967 and Others
3 Ways To Eliminate eLearning Friction With Mobile Learning And Microlearning

“In a world that grows increasingly more mobile, it’s important to embrace mobile technology and microlearning to eliminate eLearning friction caused by distracted learners and a poor learning experience.”
Your Gut in Space
Finding the Right Balance for the Microbiota
Trillions of microorganisms live on and in the human body, many of them essential to its function and health. These organisms, collectively known as the microbiota, outnumber cells in the body by at least five times.

Microorganisms in the intestinal tract, the gut microbiota, play an especially important role in human health. An investigation on the International Space Station, Rodent Research-7 (RR-7), studies how the gut microbiota changes in response to spaceflight, and how that change in turn affects the immune system, metabolic system, and circadian or daily rhythms.

Research shows that the microbiota in the mammalian digestive tract has a major impact on an individual’s physiology and behavior. In humans, disruption of microbial communities has been linked to multiple health problems affecting intestinal, immune, mental and metabolic systems.

The investigation compares two different genetic strains of mice and two different durations of spaceflight. Twenty mice, ten of each strain, launch to the space station, and another 20 remain on the ground in identical conditions (except, of course, for the absence of gravity). Mice are a model organism that often serves as a scientific stand-in for other mammals and humans.

Fecal material collected from the mice every two weeks will be examined for changes in the gut microbiota. Researchers plan to analyze fecal and tissue samples after 30 and 90 days of flight to compare the effects of different durations of time in space.

With a better understanding of relationships between changes such as disruption in sleep and an imbalance of microbial populations, researchers can identify specific factors that contribute to changes in the microbiota. Further studies then can determine proactive measures and countermeasures to protect astronaut health during long-term missions.

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.










Not Only Didn’t We Find Water On An Earth-Like Exoplanet, But We Can’t With Current Technology
“Over the past few decades, astronomers have uncovered thousands of new exoplanets. Some of them are rocky; some are temperate; some have water. However, the idea that exoplanet K2-18b is rocky, Earth-like, and has liquid water is absurd, despite recent headlines. Light filters through K2-18b’s atmosphere when it passes in front of its star, enabling us to measure what’s absorbed. Based on those absorption lines, the presence of many chemicals can be inferred, including water. K2-18b is, truly, the first known habitable-zone exoplanet to contain water. However, it is not rocky; its mass and radius are too large, necessitating a large gas envelope around it.”
How incredible was that report that came out last week: the first Earth-like, rocky exoplanet with liquid water on its surface has been discovered! If it were true, it would be incredible. Well, what we did find is still pretty remarkable, but it’s very different from what you’ve likely heard.
We did find water on the exoplanet in question, K2-18b, but only in the vapor phase and only in the atmosphere.
The exoplanet is closer to Earth in terms of mass and radius than any other with water on it, but the planet is still too massive and large to be rocky. It must have an envelope of hydrogen and helium, and both have had their presence detected.
If we want to find atmospheric biosignatures around Earth-like worlds, we need better observatories. Let’s build them! Here’s the real story.



Animated Fine Art
Collection by E Lynx of famous artworks that have been animated and rendered in 3D which you can interact with their respective @sketchfab upload:
More Here
Black holes
A black hole is a region of spacetime exhibiting such strong gravitational effects that nothing—not even particles and electromagnetic radiation such as light—can escape from inside it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can deform spacetime to form a black hole. The boundary of the region from which no escape is possible is called the event horizon. Although the event horizon has an enormous effect on the fate and circumstances of an object crossing it, no locally detectable features appear to be observed. In many ways a black hole acts like an ideal black body, as it reflects no light.

The idea of a body so massive that even light could not escape was briefly proposed by astronomical pioneer and English clergyman John Michell in a letter published in November 1784. Michell’s simplistic calculations assumed that such a body might have the same density as the Sun, and concluded that such a body would form when a star’s diameter exceeds the Sun’s by a factor of 500, and the surface escape velocity exceeds the usual speed of light.

At the center of a black hole, as described by general relativity, lies a gravitational singularity, a region where the spacetime curvature becomes infinite. For a non-rotating black hole, this region takes the shape of a single point and for a rotating black hole, it is smeared out to form a ring singularity that lies in the plane of rotation. In both cases, the singular region has zero volume. It can also be shown that the singular region contains all the mass of the black hole solution. The singular region can thus be thought of as having infinite density.

How Do Black Holes Form?
Scientists think the smallest black holes formed when the universe began.
Stellar black holes are made when the center of a very big star falls in upon itself, or collapses. When this happens, it causes a supernova. A supernova is an exploding star that blasts part of the star into space.

Scientists think supermassive black holes were made at the same time as the galaxy they are in.
Supermassive black holes, which can have a mass equivalent to billions of suns, likely exist in the centers of most galaxies, including our own galaxy, the Milky Way. We don’t know exactly how supermassive black holes form, but it’s likely that they’re a byproduct of galaxy formation. Because of their location in the centers of galaxies, close to many tightly packed stars and gas clouds, supermassive black holes continue to grow on a steady diet of matter.

If Black Holes Are “Black,” How Do Scientists Know They Are There?
A black hole can not be seen because strong gravity pulls all of the light into the middle of the black hole. But scientists can see how the strong gravity affects the stars and gas around the black hole.
Scientists can study stars to find out if they are flying around, or orbiting, a black hole.

When a black hole and a star are close together, high-energy light is made. This kind of light can not be seen with human eyes. Scientists use satellites and telescopes in space to see the high-energy light.

On 11 February 2016, the LIGO collaboration announced the first observation of gravitational waves; because these waves were generated from a black hole merger it was the first ever direct detection of a binary black hole merger. On 15 June 2016, a second detection of a gravitational wave event from colliding black holes was announced.

Simulation of gravitational lensing by a black hole, which distorts the image of a galaxy in the background
Animated simulation of gravitational lensing caused by a black hole going past a background galaxy. A secondary image of the galaxy can be seen within the black hole Einstein ring on the opposite direction of that of the galaxy. The secondary image grows (remaining within the Einstein ring) as the primary image approaches the black hole. The surface brightness of the two images remains constant, but their angular size varies, hence producing an amplification of the galaxy luminosity as seen from a distant observer. The maximum amplification occurs when the background galaxy (or in the present case a bright part of it) is exactly behind the black hole.
Could a Black Hole Destroy Earth?
Black holes do not go around in space eating stars, moons and planets. Earth will not fall into a black hole because no black hole is close enough to the solar system for Earth to do that.

Even if a black hole the same mass as the sun were to take the place of the sun, Earth still would not fall in. The black hole would have the same gravity as the sun. Earth and the other planets would orbit the black hole as they orbit the sun now.
The sun will never turn into a black hole. The sun is not a big enough star to make a black hole.
More posts about black holes
Source 1, 2 & 3





Loving Vincent (2017) dir. Dorota Kobiela, Hugh Welchman

cosmic microwave background
The cosmic microwave background (CMB) is electromagnetic radiation as a remnant from an early stage of the universe in Big Bang cosmology. In older literature, the CMB is also variously known as cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBR) or “relic radiation”. The CMB is a faint cosmic background radiation filling all space that is an important source of data on the early universe because it is the oldest electromagnetic radiation in the universe, dating to the epoch of recombination.
With a traditional optical telescope, the space between stars and galaxies (the background) is completely dark. However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope shows a faint background noise, or glow, almost isotropic, that is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the radio spectrum. The accidental discovery of the CMB in 1964 by American radio astronomers Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s, and earned the discoverers the 1978 Nobel Prize in Physics.

The discovery of CMB is landmark evidence of the Big Bang origin of the universe. When the universe was young, before the formation of stars and planets, it was denser, much hotter, and filled with a uniform glow from a white-hot fog of hydrogen plasma. As the universe expanded, both the plasma and the radiation filling it grew cooler. When the universe cooled enough, protons and electrons combined to form neutral hydrogen atoms. Unlike the uncombined protons and electrons, these newly conceived atoms could not absorb the thermal radiation, and so the universe became transparent instead of being an opaque fog. Cosmologists refer to the time period when neutral atoms first formed as the recombination epoch, and the event shortly afterwards when photons started to travel freely through space rather than constantly being scattered by electrons and protons in plasma is referred to as photon decoupling.

Basically, cosmic microwave background radiation is the fossil of light, resulting from a time when the Universe was hot and dense, only 380,000 years after the Big Bang.
Cosmic microwave background radiation is an electromagnetic radiation that fills the entire universe, whose spectrum is that of a blackbody at a temperature of 2.725 kelvin.

Cosmic microwave background radiation, along with the spacing from galaxies and the abundance of light elements, is one of the strongest observational evidences of the Big Bang model, which describes the evolution of the universe. Penzias and Wilson received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1978 for this discovery
source, source in portuguese
images credit: Image credit: Institute of Astronomy / National Tsing Hua University/ NASA/ESA Hubble, wikipedia










Ask Ethan: Why Are There Only Three Generations Of Particles?
“It is eminently possible that there are more particles out there than the Standard Model, as we know it, presently predicts. In fact, given all the components of the Universe that aren’t accounted for in the Standard Model, from dark matter to dark energy to inflation to the origin of the matter-antimatter asymmetry, it’s practically unreasonable to conclude that there aren’t additional particles.
But if the additional particles fit into the structure of the Standard Model as an additional generation, there are tremendous constraints. They could not have been created in great abundance during the early Universe. None of them can be less massive than 45.6 GeV/c^2. And they could not imprint an observable signature on the cosmic microwave background or in the abundance of the light elements.
Experimental results are the way we learn about the Universe, but the way those results fit into our most successful theoretical frameworks is how we conclude what else does and doesn’t exist in our Universe. Unless a future accelerator result surprises us tremendously, three generations is all we get: no more, no less, and nobody knows why.”
There are three generations of (fermionic) particles in the Universe. In addition to the lightest quarks (up and down), the electron and positron, and the electron neutrino and anti-neutrino, there are two extra, heavy “copies” of this structure. The charm-and-strange quarks plus the top-and-bottom quarks fill the remaining generations of quarks, while the muon and muon neutrino and anti-neutrino plus the tau and tau neutrino and anti-neutrino comprise the next generation of leptons.
Theoretically, there’s nothing demanding three and only three generations, but experiments have shown that there are no more to within absurd constraints. Here’s the full story of how we know there are only three generations.
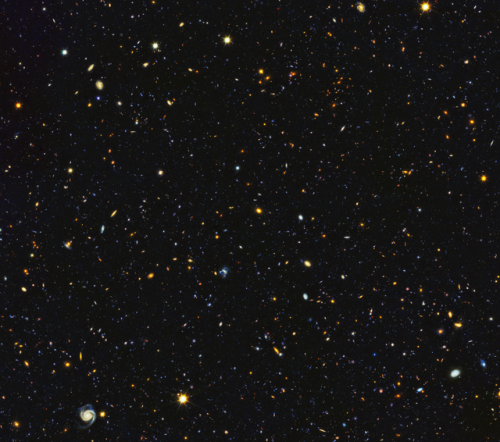

Astronomers have just assembled one of the most comprehensive portraits yet of the universe’s evolutionary history, based on a broad spectrum of observations by the Hubble Space Telescope and other space and ground-based telescopes. In particular, Hubble’s ultraviolet vision opens a new window on the evolving universe, tracking the birth of stars over the last 11 billion years back to the cosmos’ busiest star-forming period, about 3 billion years after the big bang. This photo encompasses a sea of approximately 15,000 galaxies — 12,000 of which are star-forming — widely distributed in time and space. This mosaic is 14 times the area of the Hubble Ultra Violet Ultra Deep Field released in 2014.
Credits: NASA, ESA, P. Oesch (University of Geneva), and M. Montes (University of New South Wales)
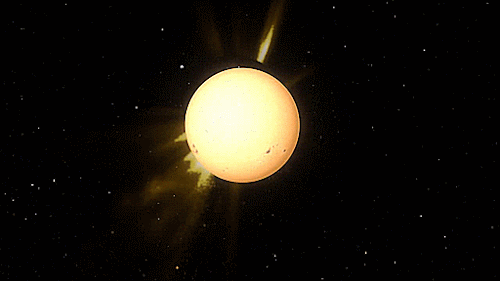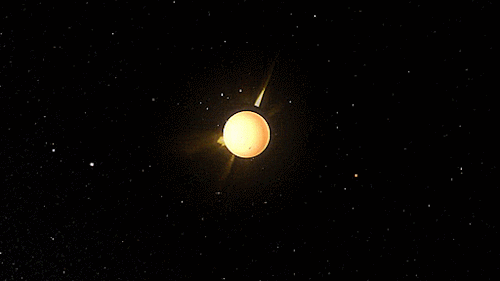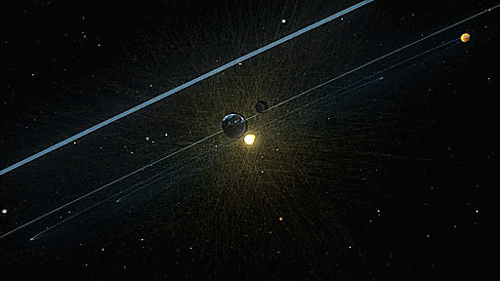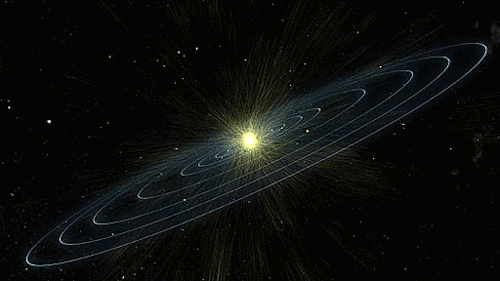


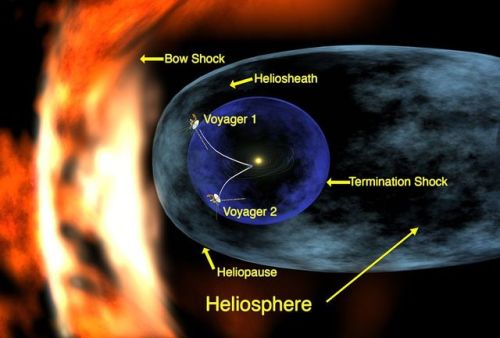
The heliosphere is the bubble-like region of space dominated by the Sun, which extends far beyond the orbit of Pluto. Plasma “blown” out from the Sun, known as the solar wind, creates and maintains this bubble against the outside pressure of the interstellar medium, the hydrogen and helium gas that permeates the Milky Way Galaxy. The solar wind flows outward from the Sun until encountering the termination shock, where motion slows abruptly. The Voyager spacecraft have explored the outer reaches of the heliosphere, passing through the shock and entering the heliosheath, a transitional region which is in turn bounded by the outermost edge of the heliosphere, called the heliopause. The shape of the heliosphere is controlled by the interstellar medium through which it is traveling, as well as the Sun and is not perfectly spherical. The limited data available and unexplored nature of these structures have resulted in many theories. The word “heliosphere” is said to have been coined by Alexander J. Dessler, who is credited with first use of the word in the scientific literature.
On September 12, 2013, NASA announced that Voyager 1 left the heliopause on August 25, 2012, when it measured a sudden increase in plasma density of about forty times. Because the heliopause marks one boundary between the Sun’s solar wind and the rest of the galaxy, a spacecraft such as Voyager 1 which has departed the heliosphere, can be said to have reached interstellar space. source
-
 808beat liked this · 3 years ago
808beat liked this · 3 years ago -
 mineralcontent liked this · 3 years ago
mineralcontent liked this · 3 years ago -
 evidenceofabsence reblogged this · 3 years ago
evidenceofabsence reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 evidenceofabsence liked this · 3 years ago
evidenceofabsence liked this · 3 years ago -
 0612zzz0309 liked this · 3 years ago
0612zzz0309 liked this · 3 years ago -
 redriskel reblogged this · 5 years ago
redriskel reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 solpq liked this · 5 years ago
solpq liked this · 5 years ago -
 haruryuu reblogged this · 5 years ago
haruryuu reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 ergoproxy-yep-blog liked this · 5 years ago
ergoproxy-yep-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 dirty90ninety liked this · 5 years ago
dirty90ninety liked this · 5 years ago -
 mybedofdreams reblogged this · 5 years ago
mybedofdreams reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 iamthesquarerootof-1 liked this · 5 years ago
iamthesquarerootof-1 liked this · 5 years ago -
 mohammedelias-blog liked this · 5 years ago
mohammedelias-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 dubstepfromsaturn liked this · 5 years ago
dubstepfromsaturn liked this · 5 years ago -
 mathquant-blog liked this · 5 years ago
mathquant-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 supportingfandoms liked this · 5 years ago
supportingfandoms liked this · 5 years ago -
 javsworld liked this · 5 years ago
javsworld liked this · 5 years ago -
 madmacboy liked this · 5 years ago
madmacboy liked this · 5 years ago -
 seerandscientist liked this · 5 years ago
seerandscientist liked this · 5 years ago -
 normalvillain reblogged this · 5 years ago
normalvillain reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 ocrim1967 reblogged this · 5 years ago
ocrim1967 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 ocrim1967 liked this · 5 years ago
ocrim1967 liked this · 5 years ago -
 sciencestories-blog liked this · 5 years ago
sciencestories-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 ninergirl1d reblogged this · 5 years ago
ninergirl1d reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 ninergirl1d liked this · 5 years ago
ninergirl1d liked this · 5 years ago -
 tclhb liked this · 5 years ago
tclhb liked this · 5 years ago -
 mipsygal-blog liked this · 5 years ago
mipsygal-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 tenigam reblogged this · 5 years ago
tenigam reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 tenigam liked this · 5 years ago
tenigam liked this · 5 years ago -
 cauadiandradi-blog reblogged this · 5 years ago
cauadiandradi-blog reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 rrrbbbrrr reblogged this · 5 years ago
rrrbbbrrr reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 thatasshole2118 liked this · 5 years ago
thatasshole2118 liked this · 5 years ago -
 cr--ed liked this · 5 years ago
cr--ed liked this · 5 years ago -
 jackary-t liked this · 5 years ago
jackary-t liked this · 5 years ago -
 lazybagofbones reblogged this · 5 years ago
lazybagofbones reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 bellchimeblr reblogged this · 5 years ago
bellchimeblr reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 birdflu2k11 liked this · 5 years ago
birdflu2k11 liked this · 5 years ago -
 classysludgespyland liked this · 5 years ago
classysludgespyland liked this · 5 years ago -
 universejelly reblogged this · 5 years ago
universejelly reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 universejelly liked this · 5 years ago
universejelly liked this · 5 years ago