Will We One Day Explore The Worlds Of Our Solar System? How Long Will This Take?









Will we one day explore the worlds of our solar system? How long will this take?
We have a diversity of worlds in our solar system. Majestic places…
Imagine being able to visit Mars and its hostile climate. Imagine being able to visit the moons of Jupiter, observe Io: the volcanic moon, Europa, the frozen moon and Ganymede a moon larger than Mercury itself and that has its own magnetic field. Imagine visiting the moons of Saturn and maybe passing close to your rings… Imagine orbiting or floating through Titan’s atmosphere and closely watching its lakes and seas of methane and liquid ethane. Imagine getting to know the geysers of Enceladus, the valleys of Tethys, and the craters of Mimas… Imagine being able to see the moons of Uranus and have a view of Verona Rupes, the largest cliff of the solar system, located in Miranda. Imagine being able to be in Triton and to be able to observe the cold and azualdo Neptune in the sky…
More Posts from Ocrim1967 and Others

10 Things: CubeSats — Going Farther
Now that the MarCOs — a pair of briefcase-sized interplanetary CubeSats — seem to have reached their limit far beyond Mars, we’re looking forward to an expanding era of small, versatile and powerful space-based science machines.
Here are ten ways we’re pushing the limits of miniaturized technology to see just how far it can take us.

1. MarCO: The Farthest (So Far)
MarCO, short for Mars Cube One, was the first interplanetary mission to use a class of mini-spacecraft called CubeSats.
The MarCOs — nicknamed EVE and WALL-E, after characters from a Pixar film — served as communications relays during InSight’s November 2018 Mars landing, beaming back data at each stage of its descent to the Martian surface in near-real time, along with InSight’s first image.
WALL-E sent back stunning images of Mars as well, while EVE performed some simple radio science.
All of this was achieved with experimental technology that cost a fraction of what most space missions do: $18.5 million provided by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, which built the CubeSats.
WALL-E was last heard from on Dec. 29; EVE, on Jan. 4. Based on trajectory calculations, WALL-E is currently more than 1 million miles (1.6 million kilometers) past Mars; EVE is farther, almost 2 million miles (3.2 million kilometers) past Mars.

MarCO-B took these images as it approached Mars in November 2018. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
2. What Are CubeSats?
CubeSats were pioneered by California Polytechnic State University in 1999 and quickly became popular tools for students seeking to learn all aspects of spacecraft design and development.
Today, they are opening up space research to public and private entities like never before. With off-the-shelf parts and a compact size that allows them to hitch a ride with other missions — they can, for example, be ejected from the International Space Station, up to six at a time — CubeSats have slashed the cost of satellite development, opening up doors to test new instruments as well as to create constellations of satellites working together.
CubeSats can be flown in swarms, capturing simultaneous, multipoint measurements with identical instruments across a large area. Sampling entire physical systems in this way would drive forward our ability to understand the space environment around us, in the same way multiple weather sensors help us understand global weather systems.
Ready to get started? Check out NASA’s CubeSats 101 Guide.

Engineer Joel Steinkraus uses sunlight to test the solar arrays on one of the Mars Cube One (MarCO) spacecraft at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
3. Measuring Up
The size and cost of spacecraft vary depending on the application; some are the size of a pint of ice cream while others, like the Hubble Space Telescope, are as big as a school bus.
Small spacecraft (SmallSats) generally have a mass less than 400 pounds (180 kilograms) and are about the size of a large kitchen fridge.
CubeSats are a class of nanosatellites that use a standard size and form factor. The standard CubeSat size uses a “one unit” or “1U” measuring 10x10x10 centimeters (or about 4x4x4 inches) and is extendable to larger sizes: 1.5, 2, 3, 6, and even 12U.

The Sojourner rover (seen here on Mars in 1997) is an example of small technology that pioneered bigger things. Generations of larger rovers are being built on its success.
4. A Legacy of Small Pathfinders
Not unlike a CubeSat, NASA’s first spacecraft — Explorer 1 — was a small, rudimentary machine. It launched in 1958 and made the first discovery in outer space, the Van Allen radiation belts that surround Earth. It was the birth of the U.S. space program.
In 1997, a mini-rover named Sojourner rolled onto Mars, a trial run for more advanced rovers such as NASA’s Spirit, Opportunity and Curiosity.
Innovation often begins with pathfinder technology, said Jakob Van Zyl, director of the Solar System Exploration Directorate at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Once engineers prove something can be done, science missions follow.

5. Testing in Space
NASA is continually developing new technologies — technologies that are smaller than ever before, components that could improve our measurements, on-board data processing systems that streamline data retrievals, or new methods for gathering observations. Each new technology is thoroughly tested in a lab, sometimes on aircraft, or even at remote sites across the world. But the space environment is different than Earth. To know how something is going to operate in space, testing in space is the best option.
Sending something unproven to orbit has traditionally been a risky endeavor, but CubeSats have helped to change that. The diminutive satellites typically take less than two years to build. CubeSats are often a secondary payload on many rocket launches, greatly reducing cost. These hitchhikers can be deployed from a rocket or sent to the International Space Station and deployed from orbit.
Because of their quick development time and easy access to space, CubeSats have become the perfect platform for demonstrating how a new technological advancement will perform in orbit.

RainCube is a mini weather satellite, no bigger than a shoebox, that will measure storms. It’s part of several new NASA experiments to track storms from space with many small satellites, instead of individual, large ones. Credit: UCAR
6. At Work in Earth Orbit
A few recent examples from our home world:
RainCube, a satellite no bigger than a suitcase, is a prototype for a possible fleet of similar CubeSats that could one day help monitor severe storms, lead to improving the accuracy of weather forecasts and track climate change over time.
IceCube tested instruments for their ability to make space-based measurements of the small, frozen crystals that make up ice clouds. Like other clouds, ice clouds affect Earth’s energy budget by either reflecting or absorbing the Sun’s energy and by affecting the emission of heat from Earth into space. Thus, ice clouds are key variables in weather and climate models.

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket lifts off from Launch Complex 1 for the NASA ELaNa19 mission. Credit: Trevor Mahlmann/Rocket Lab
7. First Dedicated CubeSat Launch
A series of new CubeSats is now in space, conducting a variety of scientific investigations and technology demonstrations following a Dec. 17, 2018 launch from New Zealand — the first time CubeSats have launched for NASA on a rocket designed specifically for small payloads.
This mission included 10 Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa)-19 payloads, selected by NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative:
CubeSat Compact Radiation Belt Explorer (CeREs) — High energy particle measurement in Earth’s radiation belt
Simulation-to-Flight 1 (STF-1) — Software condensing to support CubeSat implementations
Advanced Electrical Bus (ALBus) — Advances in solar arrays and high capacity batteries
CubeSat Handling Of Multisystem Precision Time Transfer (CHOMPTT) — Navigation plans for exo-planetary implementation
CubeSail — Deployment and control of a solar sail blade
NMTSat — Magnetic field, high altitude plasma density
Rsat — Manipulation of robotic arms
Ionospheric Scintillation Explorer (ISX) — Plasma fluctuations in the upper atmosphere
Shields-1 — Radiation shielding
DaVinci — High School to Grade School STEM education
8. The Little CubeSat That Could
CubeSat technology is still in its infancy, with mission success rates hovering near 50 percent. So, a team of scientists and engineers set out on a quest. Their goal? To build a more resilient CubeSat — one that could handle the inevitable mishaps that bedevil any spacecraft, without going kaput.
They wanted a little CubeSat that could.
They got to work in 2014 and, after three years of development, Dellingr was ready to take flight.
Read the Full Story: Dellingr: The Little CubeSat That Could

Artist’s concept of Lunar Flashlight. Credit: NASA
9. Going Farther
There are a handful of proposed NASA missions could take CubeSat technology farther:
CUVE would travel to Venus to investigate a longstanding mystery about the planet’s atmosphere using ultraviolet-sensitive instruments and a novel, carbon-nanotube light-gathering mirror.
Lunar Flashlight would use a laser to search for water ice in permanently shadowed craters on the south pole of Earth’s Moon.
Near-Earth Asteroid Scout, a SmallSat, would use a solar sail to propel it to do science on asteroids that pass close to Earth.
All three spacecraft would hitch rides to space with other missions, a key advantage of these compact science machines.

Expedition 56 Flight Engineer Serena Auñón-Chancellor installs the NanoRacks Cubesat Deployer-14 (NRCSD-14) on the Multipurpose Experiment Platform inside the Japanese Kibo laboratory module. The NRCSD-14 was then placed in the Kibo airlock and moved outside of the space station to deploy a variety of CubeSats into Earth orbit. Credit: NASA
10. And We’re Just Getting Started
Even if they’re never revived, the team considers MarCO a spectacular success.
A number of the critical spare parts for each MarCO will be used in other CubeSat missions. That includes their experimental radios, antennas and propulsion systems. Several of these systems were provided by commercial vendors, making it easier for other CubeSats to use them as well.
More small spacecraft are on the way. NASA is set to launch a variety of new CubeSats in coming years.
“There’s big potential in these small packages,” said John Baker, the MarCO program manager at JPL. “CubeSats — part of a larger group of spacecraft called SmallSats — are a new platform for space exploration affordable to more than just government agencies.”
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

5 New Competitions for the Artemis Generation!
A common question we get is, “How can I work with NASA?”
The good news is—just in time for the back-to-school season—we have a slew of newly announced opportunities for citizen scientists and researchers in the academic community to take a shot at winning our prize competitions.
As we plan to land humans on the Moon by 2024 with our upcoming Artemis missions, we are urging students and universities to get involved and offer solutions to the challenges facing our path to the Moon and Mars. Here are five NASA competitions and contests waiting for your ideas on everything from innovative ways to drill for water on other planets to naming our next rover:
1. The BIG Idea Challenge: Studying Dark Regions on the Moon
Before astronauts step on the Moon again, we will study its surface to prepare for landing, living and exploring there. Although it is Earth’s closest neighbor, there is still much to learn about the Moon, particularly in the permanently shadowed regions in and near the polar regions.

Through the annual Breakthrough, Innovative and Game-changing (BIG) Idea Challenge, we’re asking undergraduate and graduate student teams to submit proposals for sample lunar payloads that can demonstrate technology systems needed to explore areas of the Moon that never see the light of day. Teams of up to 20 students and their faculty advisors are invited to propose unique solutions in response to one of the following areas:
• Exploration of permanently shadowed regions in lunar polar regions • Technologies to support in-situ resource utilization in these regions • Capabilities to explore and operate in permanently shadowed regions
Interested teams are encouraged to submit a Notice of Intent by September 27 in order to ensure an adequate number of reviewers and to be invited to participate in a Q&A session with the judges prior to the proposal deadline. Proposal and video submission are due by January 16, 2020.
2. RASC-AL 2020: New Concepts for the Moon and Mars
Although boots on the lunar surface by 2024 is step one in expanding our presence beyond low-Earth orbit, we’re also readying our science, technology and human exploration missions for a future on Mars.
The 2020 Revolutionary Aerospace Systems Concepts – Academic Linkage (RASC-AL) Competition is calling on undergraduate and graduate teams to develop new concepts that leverage innovations for both our Artemis program and future human missions to the Red Planet. This year’s competition branches beyond science and engineering with a theme dedicated to economic analysis of commercial opportunities in deep space.

Competition themes range from expanding on how we use current and future assets in cislunar space to designing systems and architectures for exploring the Moon and Mars. We’re seeking proposals that demonstrate originality and creativity in the areas of engineering and analysis and must address one of the five following themes: a south pole multi-purpose rover, the International Space Station as a Mars mission analog, short surface stay Mars mission, commercial cislunar space development and autonomous utilization and maintenance on the Gateway or Mars-class transportation.
The RASC-AL challenge is open to undergraduate and graduate students majoring in science, technology, engineering, or mathematics at an accredited U.S.-based university. Submissions are due by March 5, 2020 and must include a two-minute video and a detailed seven to nine-page proposal that presents novel and robust applications that address one of the themes and support expanding humanity’s ability to thrive beyond Earth.
3. The Space Robotics Challenge for Autonomous Rovers
Autonomous robots will help future astronauts during long-duration missions to other worlds by performing tedious, repetitive and even strenuous tasks. These robotic helpers will let crews focus on the more meticulous areas of exploring. To help achieve this, our Centennial Challenges initiative, along with Space Center Houston of Texas, opened the second phase of the Space Robotics Challenge. This virtual challenge aims to advance autonomous robotic operations for missions on the surface of distant planets or moons.

This new phase invites competitors 18 and older from the public, industry and academia to develop code for a team of virtual robots that will support a simulated in-situ resource utilization mission—meaning gathering and using materials found locally—on the Moon.
The deadline to submit registration forms is December 20.
4. Moon to Mars Ice & Prospecting Challenge to Design Hardware, Practice Drilling for Water on the Moon and Mars
A key ingredient for our human explorers staying anywhere other than Earth is water. One of the most crucial near-term plans for deep space exploration includes finding and using water to support a sustained presence on our nearest neighbor and on Mars.
To access and extract that water, NASA needs new technologies to mine through various layers of lunar and Martian dirt and into ice deposits we believe are buried beneath the surface. A special edition of the RASC-AL competition, the Moon to Mars Ice and Prospecting Challenge, seeks to advance critical capabilities needed on the surface of the Moon and Mars. The competition, now in its fourth iteration, asks eligible undergraduate and graduate student teams to design and build hardware that can identify, map and drill through a variety of subsurface layers, then extract water from an ice block in a simulated off-world test bed.
Interested teams are asked to submit a project plan detailing their proposed concept’s design and operations by November 14. Up to 10 teams will be selected and receive a development stipend. Over the course of six months teams will build and test their systems in preparation for a head-to-head competition at our Langley Research Center in June 2020.
5. Name the Mars 2020 Rover!
Red rover, red rover, send a name for Mars 2020 right over! We’re recruiting help from K-12 students nationwide to find a name for our next Mars rover mission.
The Mars 2020 rover is a 2,300-pound robotic scientist that will search for signs of past microbial life, characterize the planet’s climate and geology, collect samples for future return to Earth, and pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet.
K-12 students in U.S. public, private and home schools can enter the Mars 2020 Name the Rover essay contest. One grand prize winner will name the rover and be invited to see the spacecraft launch in July 2020 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. To enter the contest, students must submit by November 1 their proposed rover name and a short essay, no more than 150 words, explaining why their proposed name should be chosen.
Just as the Apollo program inspired innovation in the 1960s and ‘70s, our push to the Moon and Mars is inspiring students—the Artemis generation—to solve the challenges for the next era of space exploration.
For more information on all of our open prizes and challenges, visit: https://www.nasa.gov/solve/explore_opportunities
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
WHO IS HE?
In Genesis, He is the seed of the woman. In Exodus, He is the Passover Lamb. In Leviticus, He is our High Priest. In Numbers, He is pillar of cloud by day and a pillar of fire by night. In Deuteronomy, He is the prophet like unto Moses. In Joshua, He is the captain of our salvation. In Judges, He is our judge and lawgiver. In Ruth, He is our kinsman redeemer. In I and II Samuel, He is our trusted prophet. In Kings and Chronicles, He is our reigning king. In Erza, He is our faithful scribe. In Nehemiah, He is the rebuilder of the broken down walls of human life. In Ester, He is our Mordecai. In Job, He is our ever-living redeemer: “For I know my redeemer lives.” In Psalms, He is our shepherd. In Proverbs and Ecclesiastes, He is our wisdom. In Song of Solomon, He is the lover and the bridegroom. In Isaiah, He is the prince of peace. In Jeremiah, He is the righteous branch. In Lamentations, He is the weeping prophet. In Ezekiel, He is the wonderful four-faced man. In Daniel, He is the fourth man walking in the midst of the burning fiery furnaces of life. In Hosea, He is the husband forever married to the backslider. In Joel, He is the mighty baptizer in the Holy Ghost. In Amos, He is my burden bearer. In Obadiah, He is mighty to save. In Jonah, He is God’s great foreign missionary. In Micah, He is the messenger of beautiful feet. In Nahum, He is the avenger of God’s elect. In Habakkuk, He is God’s evangelist, crying, “Revive thy work in the midst of the years.” In Zephaniah, He is our Savior. In Haggai, He is the restorer of the lost heritage of Israel. In Zechariah, He is fountain opened up on the house of David for sin and uncleanness. In Malachi, He is the Son of Righteousness arisen with healing in His wings. In Matthew, He is the Messiah. In Mark, He is the wonder worker. In Luke, He is the Son of Man. In John, He is the Son of God. In Acts, He is the mighty baptizer in the Holy Ghost. In Romans, He is my justifier. In Corinthians, He is my sanctifier. In Galatians, He is the redeemer from the curse of the law. In Ephesians, He is the Christ of unsearchable riches. In Philippians, He is the God that supplies all my needs. In Colossians, He is the fullness of the godhead bodily. In I and II Thessalonians, He is my soon-coming King! In I and II Timothy, He is the mediator between God and man. In Tidus, He is my faithful pastor. In Philemon, He is the friend that sticketh closer than a brother. In Hebrews, He is the blood of the everlasting covenant. In James, He is our Great Physician, for “the prayer of faith shall save the sick.” In I and II Peter, He is my good shepherd. In I John, He is love. In II John, He is love. In III John, He is love. In Jude, He is the Lord coming with 10,000 of His saints. In Revelation, He is King of Kings and Lord of Lords.
HE IS THE WORD OF GOD.
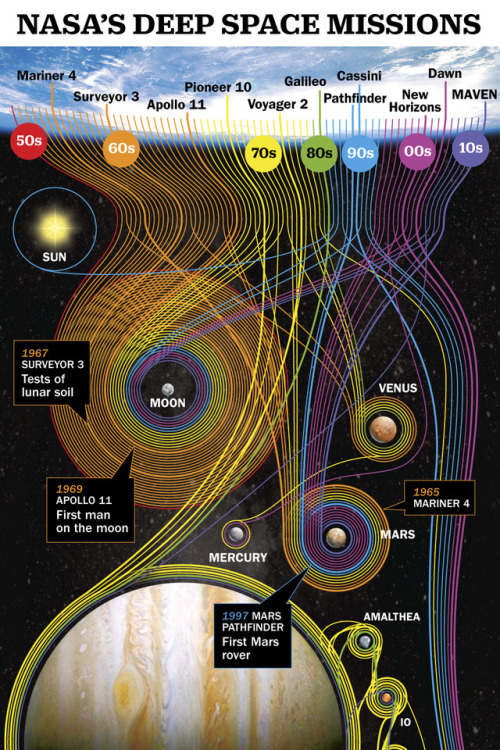
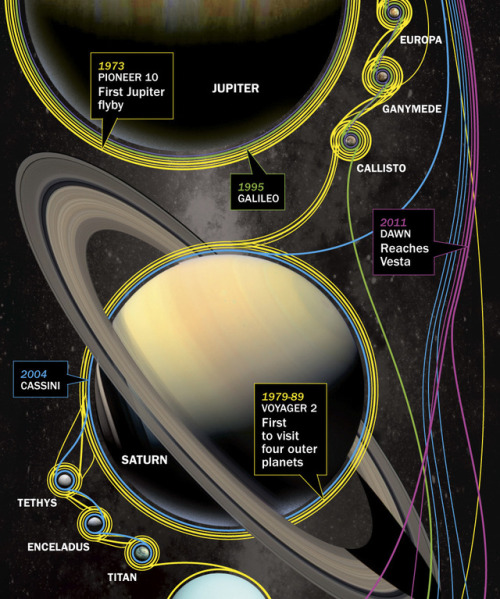
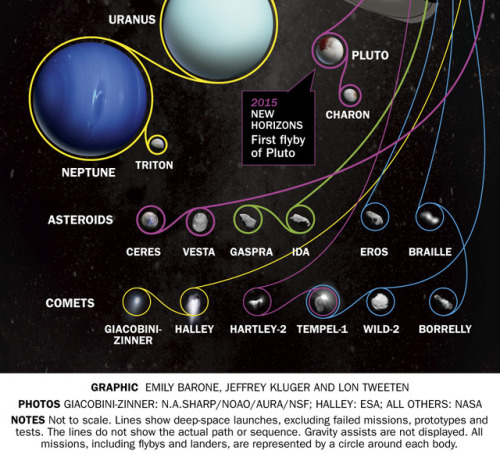
Deep Space Missions
Black Holes are NICER Than You Think!
We’re learning more every day about black holes thanks to one of the instruments aboard the International Space Station! Our Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) instrument is keeping an eye on some of the most mysterious cosmic phenomena.

We’re going to talk about some of the amazing new things NICER is showing us about black holes. But first, let’s talk about black holes — how do they work, and where do they come from? There are two important types of black holes we’ll talk about here: stellar and supermassive. Stellar mass black holes are three to dozens of times as massive as our Sun while supermassive black holes can be billions of times as massive!

Stellar black holes begin with a bang — literally! They are one of the possible objects left over after a large star dies in a supernova explosion. Scientists think there are as many as a billion stellar mass black holes in our Milky Way galaxy alone!
Supermassive black holes have remained rather mysterious in comparison. Data suggest that supermassive black holes could be created when multiple black holes merge and make a bigger one. Or that these black holes formed during the early stages of galaxy formation, born when massive clouds of gas collapsed billions of years ago. There is very strong evidence that a supermassive black hole lies at the center of all large galaxies, as in our Milky Way.

Imagine an object 10 times more massive than the Sun squeezed into a sphere approximately the diameter of New York City — or cramming a billion trillion people into a car! These two examples give a sense of how incredibly compact and dense black holes can be.
Because so much stuff is squished into such a relatively small volume, a black hole’s gravity is strong enough that nothing — not even light — can escape from it. But if light can’t escape a dark fate when it encounters a black hole, how can we “see” black holes?

Scientists can’t observe black holes directly, because light can’t escape to bring us information about what’s going on inside them. Instead, they detect the presence of black holes indirectly — by looking for their effects on the cosmic objects around them. We see stars orbiting something massive but invisible to our telescopes, or even disappearing entirely!
When a star approaches a black hole’s event horizon — the point of no return — it’s torn apart. A technical term for this is “spaghettification” — we’re not kidding! Cosmic objects that go through the process of spaghettification become vertically stretched and horizontally compressed into thin, long shapes like noodles.

Scientists can also look for accretion disks when searching for black holes. These disks are relatively flat sheets of gas and dust that surround a cosmic object such as a star or black hole. The material in the disk swirls around and around, until it falls into the black hole. And because of the friction created by the constant movement, the material becomes super hot and emits light, including X-rays.
At last — light! Different wavelengths of light coming from accretion disks are something we can see with our instruments. This reveals important information about black holes, even though we can’t see them directly.

So what has NICER helped us learn about black holes? One of the objects this instrument has studied during its time aboard the International Space Station is the ever-so-forgettably-named black hole GRS 1915+105, which lies nearly 36,000 light-years — or 200 million billion miles — away, in the direction of the constellation Aquila.
Scientists have found disk winds — fast streams of gas created by heat or pressure — near this black hole. Disk winds are pretty peculiar, and we still have a lot of questions about them. Where do they come from? And do they change the shape of the accretion disk?

It’s been difficult to answer these questions, but NICER is more sensitive than previous missions designed to return similar science data. Plus NICER often looks at GRS 1915+105 so it can see changes over time.
NICER’s observations of GRS 1915+105 have provided astronomers a prime example of disk wind patterns, allowing scientists to construct models that can help us better understand how accretion disks and their outflows around black holes work.

NICER has also collected data on a stellar mass black hole with another long name — MAXI J1535-571 (we can call it J1535 for short) — adding to information provided by NuSTAR, Chandra, and MAXI. Even though these are all X-ray detectors, their observations tell us something slightly different about J1535, complementing each other’s data!
This rapidly spinning black hole is part of a binary system, slurping material off its partner, a star. A thin halo of hot gas above the disk illuminates the accretion disk and causes it to glow in X-ray light, which reveals still more information about the shape, temperature, and even the chemical content of the disk. And it turns out that J1535’s disk may be warped!

Image courtesy of NRAO/AUI and Artist: John Kagaya (Hoshi No Techou)
This isn’t the first time we have seen evidence for a warped disk, but J1535’s disk can help us learn more about stellar black holes in binary systems, such as how they feed off their companions and how the accretion disks around black holes are structured.
NICER primarily studies neutron stars — it’s in the name! These are lighter-weight relatives of black holes that can be formed when stars explode. But NICER is also changing what we know about many types of X-ray sources. Thanks to NICER’s efforts, we are one step closer to a complete picture of black holes. And hey, that’s pretty nice!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Black holes
A black hole is a region of spacetime exhibiting such strong gravitational effects that nothing—not even particles and electromagnetic radiation such as light—can escape from inside it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can deform spacetime to form a black hole. The boundary of the region from which no escape is possible is called the event horizon. Although the event horizon has an enormous effect on the fate and circumstances of an object crossing it, no locally detectable features appear to be observed. In many ways a black hole acts like an ideal black body, as it reflects no light.

The idea of a body so massive that even light could not escape was briefly proposed by astronomical pioneer and English clergyman John Michell in a letter published in November 1784. Michell’s simplistic calculations assumed that such a body might have the same density as the Sun, and concluded that such a body would form when a star’s diameter exceeds the Sun’s by a factor of 500, and the surface escape velocity exceeds the usual speed of light.

At the center of a black hole, as described by general relativity, lies a gravitational singularity, a region where the spacetime curvature becomes infinite. For a non-rotating black hole, this region takes the shape of a single point and for a rotating black hole, it is smeared out to form a ring singularity that lies in the plane of rotation. In both cases, the singular region has zero volume. It can also be shown that the singular region contains all the mass of the black hole solution. The singular region can thus be thought of as having infinite density.

How Do Black Holes Form?
Scientists think the smallest black holes formed when the universe began.
Stellar black holes are made when the center of a very big star falls in upon itself, or collapses. When this happens, it causes a supernova. A supernova is an exploding star that blasts part of the star into space.

Scientists think supermassive black holes were made at the same time as the galaxy they are in.
Supermassive black holes, which can have a mass equivalent to billions of suns, likely exist in the centers of most galaxies, including our own galaxy, the Milky Way. We don’t know exactly how supermassive black holes form, but it’s likely that they’re a byproduct of galaxy formation. Because of their location in the centers of galaxies, close to many tightly packed stars and gas clouds, supermassive black holes continue to grow on a steady diet of matter.

If Black Holes Are “Black,” How Do Scientists Know They Are There?
A black hole can not be seen because strong gravity pulls all of the light into the middle of the black hole. But scientists can see how the strong gravity affects the stars and gas around the black hole.
Scientists can study stars to find out if they are flying around, or orbiting, a black hole.

When a black hole and a star are close together, high-energy light is made. This kind of light can not be seen with human eyes. Scientists use satellites and telescopes in space to see the high-energy light.

On 11 February 2016, the LIGO collaboration announced the first observation of gravitational waves; because these waves were generated from a black hole merger it was the first ever direct detection of a binary black hole merger. On 15 June 2016, a second detection of a gravitational wave event from colliding black holes was announced.

Simulation of gravitational lensing by a black hole, which distorts the image of a galaxy in the background
Animated simulation of gravitational lensing caused by a black hole going past a background galaxy. A secondary image of the galaxy can be seen within the black hole Einstein ring on the opposite direction of that of the galaxy. The secondary image grows (remaining within the Einstein ring) as the primary image approaches the black hole. The surface brightness of the two images remains constant, but their angular size varies, hence producing an amplification of the galaxy luminosity as seen from a distant observer. The maximum amplification occurs when the background galaxy (or in the present case a bright part of it) is exactly behind the black hole.
Could a Black Hole Destroy Earth?
Black holes do not go around in space eating stars, moons and planets. Earth will not fall into a black hole because no black hole is close enough to the solar system for Earth to do that.

Even if a black hole the same mass as the sun were to take the place of the sun, Earth still would not fall in. The black hole would have the same gravity as the sun. Earth and the other planets would orbit the black hole as they orbit the sun now.
The sun will never turn into a black hole. The sun is not a big enough star to make a black hole.
More posts about black holes
Source 1, 2 & 3
NASA Science Show & Tell
This week, we’re at one of the biggest science conferences in the country, where our scientists are presenting new results from our missions and projects. It’s called the American Geophysical Union’s Fall Meeting.
Here are a few of the things we shared this week…

The Sun
A few months into its seven-year mission, Parker Solar Probe has already flown far closer to the Sun than any spacecraft has ever gone. The data from this visit to the Sun has just started to come back to Earth, and scientists are hard at work on their analysis.

Parker Solar Probe sent us this new view of the Sun’s outer atmosphere, the corona. The image was taken by the mission’s WISPR instrument on Nov. 8, 2018, and shows a coronal streamer seen over the east limb of the Sun. Coronal streamers are structures of solar material within the Sun’s atmosphere, the corona, that usually overlie regions of increased solar activity. The fine structure of the streamer is very clear, with at least two rays visible. Parker Solar Probe was about 16.9 million miles from the Sun’s surface when this image was taken. The bright object near the center of the image is Mercury, and the dark spots are a result of background correction.
Hurricane Maria
Using a satellite view of human lights, our scientists watched the lights go out in Puerto Rico after Hurricane Maria. They could see the slow return of electricity to the island, and track how rural and mountainous regions took longer to regain power.

In the spring, a team of scientists flew a plane over Puerto Rico’s forests, using a laser instrument to measure how trees were damaged and how the overall structure of the forests had changed.

Earth’s Ice
Our scientists who study Antarctica saw some surprising changes to East Antarctica. Until now, most of the continent’s melting has been on the peninsula and West Antarctica, but our scientists have seen glaciers in East Antarctica lose lots of ice in the last few years.


Our ICESat-2 team showed some of their brand new data. From the changing height of Antarctic ice to lagoons off the coast of Mexico, the little satellite has spent its first few months measuring our planet in 3D. The laser pulses even see individual ocean waves, in this graph.

Scientists are using our satellite data to track Adélie penguin populations, by using an unusual proxy – pictures of their poop! Penguins are too small to be seen by satellites, but they can see large amounts of their poop (which is pink!) and use that as a proxy for penguin populations.

Asteroid Bennu
Our OSIRIS-REx mission recently arrived at its destination, asteroid Bennu. On approach, data from the spacecraft’s spectrometers revealed chemical signatures of water trapped in clay minerals. While Bennu itself is too small to have ever hosted liquid water, the finding indicates that liquid water was present at some time on Bennu’s parent body, a much larger asteroid.
We also released a new, detailed shape model of Bennu, which is very similar to our ground-based observations of Bennu’s shape. This is a boon to ground-based radar astronomy since this is our first validation of the accuracy of the method for an asteroid! One change from the original shape model is the size of the large boulder near Bennu’s south pole, nicknamed “Benben.” The boulder is much bigger than we thought and overall, the quantity of boulders on the surface is higher than expected. Now the team will make further observations at closer ranges to more accurately assess where a sample can be taken on Bennu to later be returned to Earth.

Jupiter
The Juno mission celebrated it’s 16th science pass of #Jupiter, marking the halfway point in data collection of the prime mission. Over the second half of the prime mission — science flybys 17 through 32 — the spacecraft will split the difference, flying exactly halfway between each previous orbit. This will provide coverage of the planet every 11.25 degrees of longitude, providing a more detailed picture of what makes the whole of Jupiter tick.

Mars
The Mars 2020 team had a workshop to discuss the newly announced landing site for our next rover on the Red Planet. The landing site…Jezero Crater! The goal of Mars 2020 is to learn whether life ever existed on Mars. It’s too cold and dry for life to exist on the Martian surface today. But after Jezero Crater formed billions of years ago, water filled it to form a deep lake about the same size as Lake Tahoe. Eventually, as Mars’ climate changed, Lake Jezero dried up. And surface water disappeared from the planet.
Interstellar Space
Humanity now has two interstellar ambassadors. On Nov. 5, 2018, our Voyager 2 spacecraft left the heliosphere — the bubble of the Sun’s magnetic influence formed by the solar wind. It’s only the second-ever human-made object to enter interstellar space, following its twin, Voyager 1, that left the heliosphere in 2012.

Scientists are especially excited to keep receiving data from Voyager 2, because — unlike Voyager 1 — its plasma science instrument is still working. That means we’ll learn brand-new information about what fills the space between the stars.
Learn more about NASA Science at science.nasa.gov.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com


Image Credit:NASA/JPL-Caltech
In this large celestial mosaic, our Spitzer Space Telescope captured a stellar family portrait! You can find infants, parents and grandparents of star-forming regions all in this generational photo. There’s a lot to see in this image, including multiple clusters of stars born from the same dense clumps of gas and dust – some older and more evolved than others. Dive deeper into its intricacies by visiting https://go.nasa.gov/2XpiWLf
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
-
 interstellarstorms reblogged this · 5 months ago
interstellarstorms reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 annita89z038o4h liked this · 7 months ago
annita89z038o4h liked this · 7 months ago -
 kawiza reblogged this · 8 months ago
kawiza reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 gueule-de-contact liked this · 9 months ago
gueule-de-contact liked this · 9 months ago -
 crucrionnia reblogged this · 11 months ago
crucrionnia reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 revolverthemes liked this · 1 year ago
revolverthemes liked this · 1 year ago -
 sumechiayuu reblogged this · 1 year ago
sumechiayuu reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 ocularskewer liked this · 1 year ago
ocularskewer liked this · 1 year ago -
 brokenimageswherethesunbeats liked this · 1 year ago
brokenimageswherethesunbeats liked this · 1 year ago -
 anpaintsthemoon liked this · 1 year ago
anpaintsthemoon liked this · 1 year ago -
 estefanyailen liked this · 1 year ago
estefanyailen liked this · 1 year ago -
 cosmic-shark reblogged this · 1 year ago
cosmic-shark reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 thankyoufortheadventure liked this · 2 years ago
thankyoufortheadventure liked this · 2 years ago -
 draghes liked this · 2 years ago
draghes liked this · 2 years ago -
 writingfish reblogged this · 2 years ago
writingfish reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 dani-pants reblogged this · 2 years ago
dani-pants reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 sisterzoned reblogged this · 2 years ago
sisterzoned reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 wings-scales-fire reblogged this · 2 years ago
wings-scales-fire reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 the-fresh-prince-of-busan reblogged this · 2 years ago
the-fresh-prince-of-busan reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 heresjeonny liked this · 2 years ago
heresjeonny liked this · 2 years ago -
 agamenon-11 liked this · 2 years ago
agamenon-11 liked this · 2 years ago -
 dani-pants liked this · 2 years ago
dani-pants liked this · 2 years ago -
 ichigorosedoll reblogged this · 2 years ago
ichigorosedoll reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 satellitesempreinorbita liked this · 2 years ago
satellitesempreinorbita liked this · 2 years ago -
 younghologramdreamsworld reblogged this · 2 years ago
younghologramdreamsworld reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 younghologramdreamsworld liked this · 2 years ago
younghologramdreamsworld liked this · 2 years ago -
 byebyeuf0 liked this · 2 years ago
byebyeuf0 liked this · 2 years ago -
 tsuchiman reblogged this · 2 years ago
tsuchiman reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 saint-lucas liked this · 2 years ago
saint-lucas liked this · 2 years ago -
 thatswhatheavenfeelslike reblogged this · 2 years ago
thatswhatheavenfeelslike reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 the-widow-hazard reblogged this · 2 years ago
the-widow-hazard reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 paladinsandruffians liked this · 2 years ago
paladinsandruffians liked this · 2 years ago -
 rainstormraider reblogged this · 2 years ago
rainstormraider reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 the-widow-hazard liked this · 2 years ago
the-widow-hazard liked this · 2 years ago -
 kaliyera liked this · 2 years ago
kaliyera liked this · 2 years ago