Close-up Of M27, The Dumbbell Nebula

Close-up of M27, the Dumbbell Nebula
Credit: NASA/ESA, Hubble
More Posts from Xnzda and Others
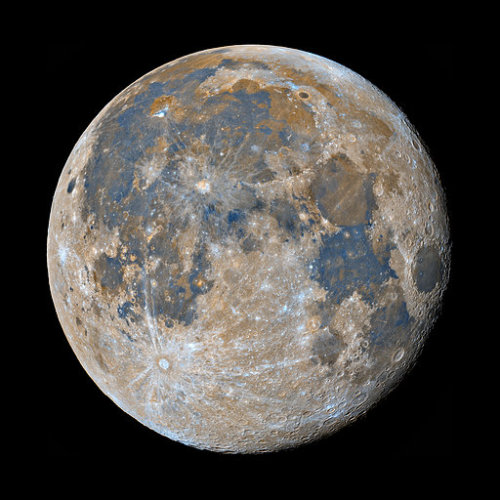
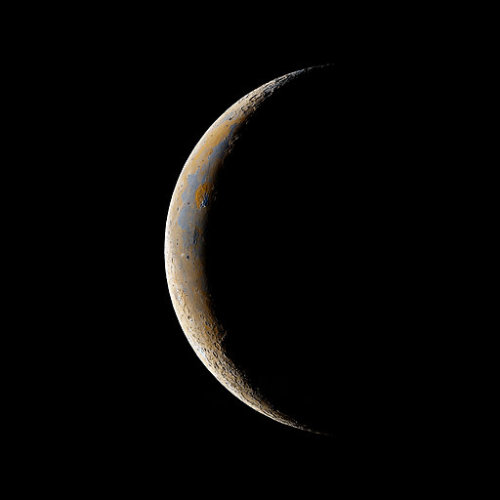


98% waning gibbous Moon | 11% waning crescent Moon
by Bartosz Wojczyński
Remember kids: Pluto is not a planet, WAS never a planet, and any acknowledgement of Pluto as a planet was an error of assumption

Image of Messier 81 (M81). Located about 12 million light-years away in the Ursa Major constellation, M81 is among the brightest of the galaxies visible by telescope from Earth.
Image credit:NASA/JPL-Caltech/ESA/Harvard-Smithsonian CfA

The Spanish Dancer and her supernova by strongmanmike2002 on Flickr.










Where Could Life Exist?
When NASA scientists announced earlier this year that they had found evidence of liquid water on Mars, imaginations ran wild with the possibility that life could exist somewhere other than here on Earth.
Scientists continue to explore the possibility that Mars once looked a lot like Earth — salty oceans, fresh water lakes, and a water cycle to go with it. That’s exciting stuff.
So where else are they looking? What exactly are they looking for?
There are nine places in our universe where scientists say life is a possibility. The locations range from a smoking hot planet like Venus to a moon that orbits Saturn called Enceladus, which looks a lot like a massive, tightly-packed ball of ice.
All of these places show signs that water is, or at least was, a possibility. They also appear to feature some kind of energy that could produce heat.
full resolution
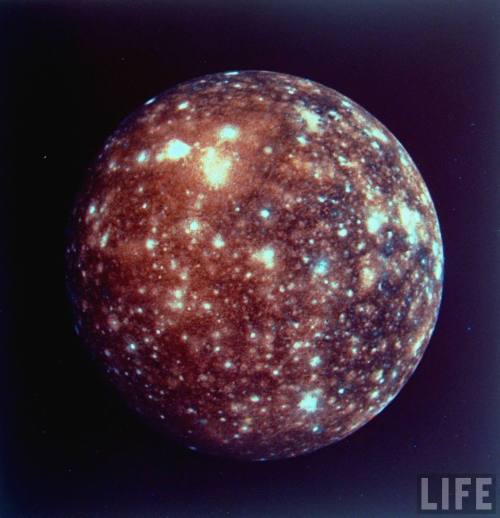
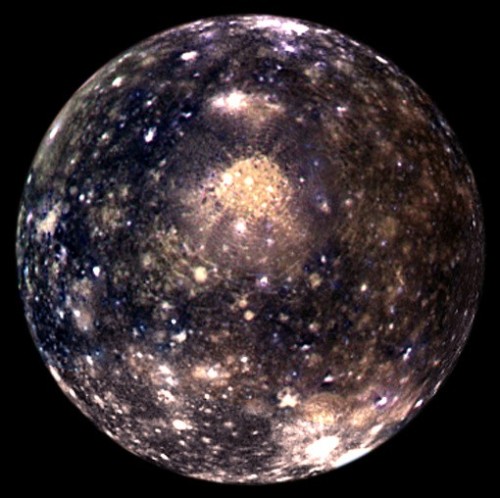
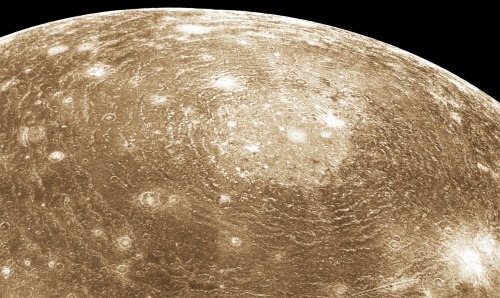
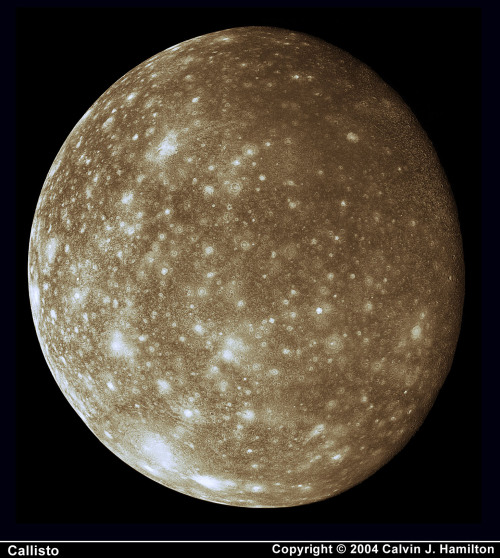
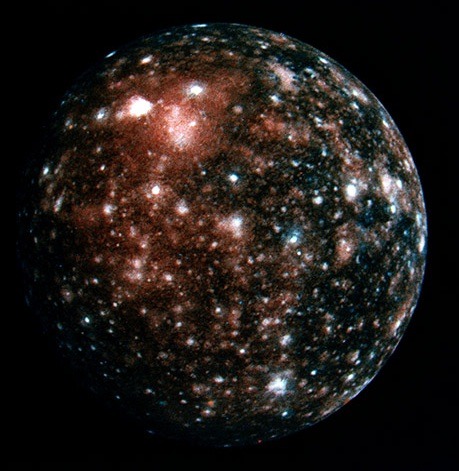




Jupiter’s moon, Callisto.

The Carina Nebula - A Birthplace Of Stars
The Carina Nebula lies at an estimated distance of 6,500 to 10,000 light years away from Earth in the constellation Carina. This nebula is one of the most well studied in astrophysics and has a high rate of star formation. The star-burst in the Carina region started around three million years ago when the nebula’s first generation of newborn stars condensed and ignited in the middle of a huge cloud of cold molecular hydrogen. Radiation from these stars carved out an expanding bubble of hot gas. The island-like clumps of dark clouds scattered across the nebula are nodules of dust and gas that are resisting being eaten away by photons (particles of light) that are ionizing the surrounding gas (giving it an electrical charge).
Credit: NASA/Hubble
Charting the slow death of the Universe
Paris (SPX) Aug 12, 2015 The study, which is part of the Galaxy And Mass Assembly (GAMA) project, the largest multi-wavelength survey ever put together, involved many of the world’s most powerful telescopes [1]. “We used as many space and ground-based telescopes as we could get our hands on to measure the energy output of over 200 000 galaxies across as broad a wavelength range as possible,” says Simon Driver ICRA Full article
-
 noura-099 liked this · 1 month ago
noura-099 liked this · 1 month ago -
 dotglobal liked this · 10 months ago
dotglobal liked this · 10 months ago -
 zurgy-space reblogged this · 11 months ago
zurgy-space reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 zurgy liked this · 11 months ago
zurgy liked this · 11 months ago -
 kamamo1 liked this · 2 years ago
kamamo1 liked this · 2 years ago -
 windyocinspo reblogged this · 2 years ago
windyocinspo reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 neonomens liked this · 2 years ago
neonomens liked this · 2 years ago -
 furyroadsux liked this · 3 years ago
furyroadsux liked this · 3 years ago -
 sheliesshattered reblogged this · 3 years ago
sheliesshattered reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 laurelintengel reblogged this · 3 years ago
laurelintengel reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 eternallyrisen reblogged this · 3 years ago
eternallyrisen reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 komala-scientist-archived reblogged this · 3 years ago
komala-scientist-archived reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 squidrolls360 liked this · 3 years ago
squidrolls360 liked this · 3 years ago -
 iiapple reblogged this · 3 years ago
iiapple reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 giulla reblogged this · 3 years ago
giulla reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 dildoteamtaskforce reblogged this · 3 years ago
dildoteamtaskforce reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 justangrygirl reblogged this · 3 years ago
justangrygirl reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 nintendofreaks reblogged this · 3 years ago
nintendofreaks reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 nintendofreaks liked this · 3 years ago
nintendofreaks liked this · 3 years ago -
 asocialpessimist reblogged this · 3 years ago
asocialpessimist reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 estrelya reblogged this · 3 years ago
estrelya reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 milkshake-fries reblogged this · 3 years ago
milkshake-fries reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 milkshake-fries liked this · 3 years ago
milkshake-fries liked this · 3 years ago -
 milkywayan reblogged this · 3 years ago
milkywayan reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 rabbithaver reblogged this · 3 years ago
rabbithaver reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 heathen-beast reblogged this · 3 years ago
heathen-beast reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 princessbootys reblogged this · 3 years ago
princessbootys reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 aarontaman reblogged this · 3 years ago
aarontaman reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 riphuntertimemasterlegend reblogged this · 3 years ago
riphuntertimemasterlegend reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 riphuntertimemasterlegend liked this · 3 years ago
riphuntertimemasterlegend liked this · 3 years ago -
 sheliesshattered liked this · 3 years ago
sheliesshattered liked this · 3 years ago -
 marivela14 liked this · 3 years ago
marivela14 liked this · 3 years ago -
 sinister--potato reblogged this · 3 years ago
sinister--potato reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 camalyng reblogged this · 3 years ago
camalyng reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 theoriginalladya reblogged this · 3 years ago
theoriginalladya reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 a-little-star-adrift reblogged this · 3 years ago
a-little-star-adrift reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 blogshowhost reblogged this · 3 years ago
blogshowhost reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 einesnachts reblogged this · 3 years ago
einesnachts reblogged this · 3 years ago

