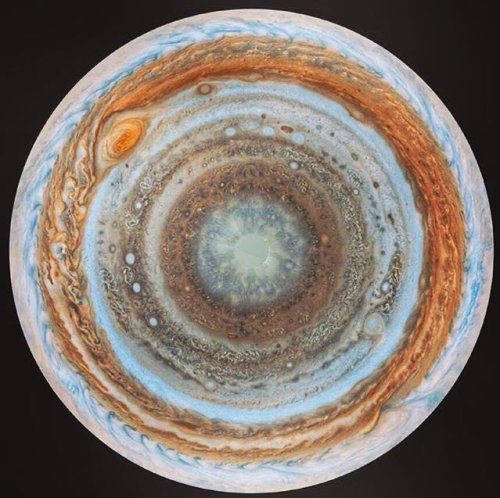
Jupiter’s Moon, Callisto.
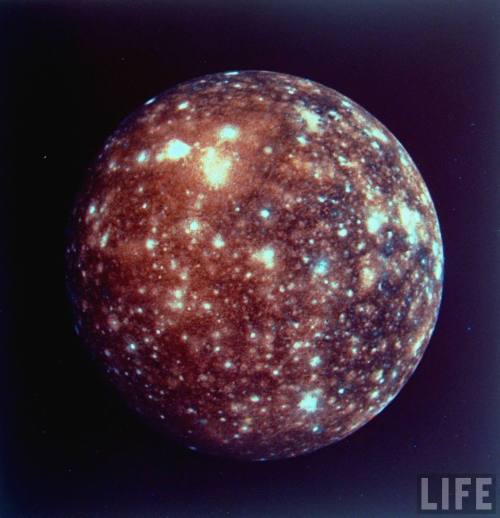
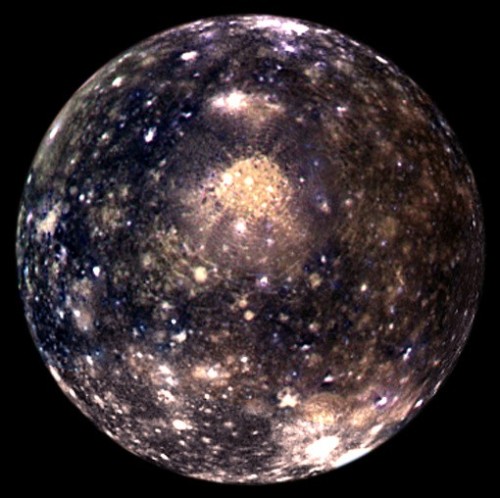
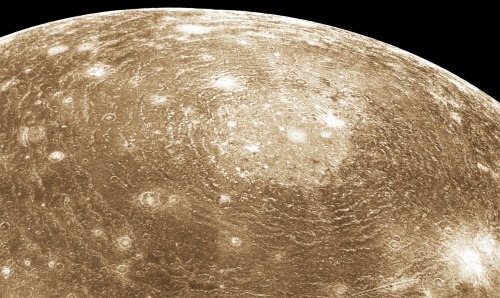
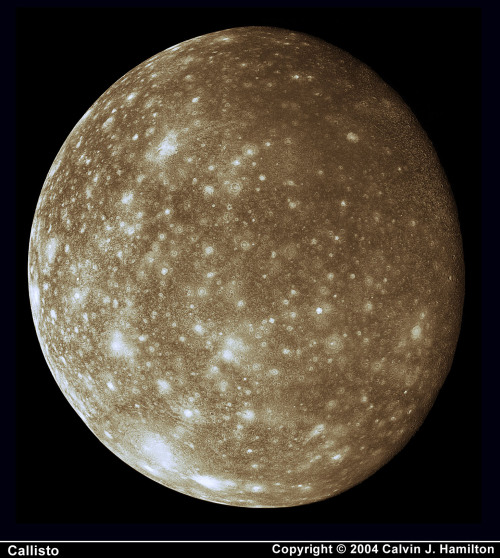
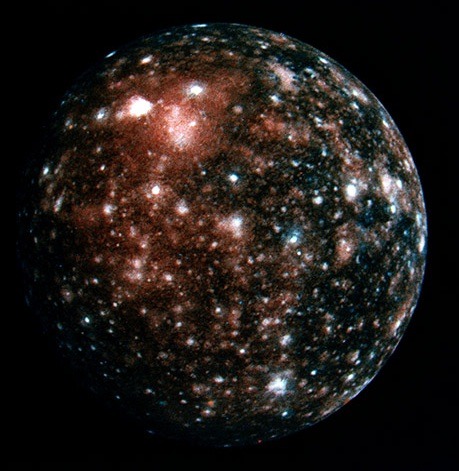




Jupiter’s moon, Callisto.
More Posts from Xnzda and Others

Beware of the Big, Bad Wolf
Visible within the center of the Crescent nebula is what’s classified as a Wolf-Rayet star. This star is a staggering 250,000 times brighter than the Sun, 15 times more massive, and 3.3 times larger. Its surface temperature is nearly 70,000° C/ 125,000° F. At just 4.7 million years old, it is already toward the end of it’s life and is shedding its outer envelope, ejecting the equivalent of the Sun’s mass every 10,000 years. Within a few hundred thousand years, it is expected to explode as a supernova. (Image Credit: Michael Miller, Jimmy Walker)
Charting the slow death of the Universe
Paris (SPX) Aug 12, 2015 The study, which is part of the Galaxy And Mass Assembly (GAMA) project, the largest multi-wavelength survey ever put together, involved many of the world’s most powerful telescopes [1]. “We used as many space and ground-based telescopes as we could get our hands on to measure the energy output of over 200 000 galaxies across as broad a wavelength range as possible,” says Simon Driver ICRA Full article

Cygnus entering the atmosphere, photographed by Alexander Gerst on the ISS.

NASA’s planet-hunting Kepler Telescope has spotted the first roughly Earth-sized world orbiting in the “Goldilocks zone” of another star – offering perhaps the best bet so far for life elsewhere in the universe.
A year on Kepler 452b, which is about 1,400 light years from us in the constellation Cygnus, is 385 days, meaning its orbit is just a bit farther away from its star than the Earth is from the sun. That places it squarely within what planetary scientists call the habitable zone, or “Goldilocks” zone — not too cold and not too hot.
“In my mind, this is the closest planet indeed to Earth,” Jon Jenkins, Kepler data analysis lead at NASA’s Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, Calif, said at a media briefing. “The star is a little bit older and a little bit bigger and brighter, so it’s good that it’s a bit farther from its star.”
Kepler Telescope Introduces Earth To A Very Distant Cousin
Image: Artist’s concept compares Earth (left) to the new planet, called Kepler-452b, which is about 60 percent larger in diameter. Courtesy of NASA/JPL-Caltech/T. Pyle
-
 the-real-pink-ninja liked this · 2 weeks ago
the-real-pink-ninja liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 midnight-reader-morning-sleeper liked this · 3 weeks ago
midnight-reader-morning-sleeper liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 worldweaverofmediocrity reblogged this · 4 weeks ago
worldweaverofmediocrity reblogged this · 4 weeks ago -
 catkin-morgs-kookaburralover liked this · 4 weeks ago
catkin-morgs-kookaburralover liked this · 4 weeks ago -
 the-land-of-eternal-winter-novel reblogged this · 4 weeks ago
the-land-of-eternal-winter-novel reblogged this · 4 weeks ago -
 jellycaustic reblogged this · 1 month ago
jellycaustic reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 blade-liger-4ever liked this · 1 month ago
blade-liger-4ever liked this · 1 month ago -
 vitamaeternum reblogged this · 1 month ago
vitamaeternum reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 vitamaeternum liked this · 1 month ago
vitamaeternum liked this · 1 month ago -
 lenjaminmacbuttons liked this · 1 month ago
lenjaminmacbuttons liked this · 1 month ago -
 polyglot-thought-2 liked this · 1 month ago
polyglot-thought-2 liked this · 1 month ago -
 scribbly-bear liked this · 1 month ago
scribbly-bear liked this · 1 month ago -
 pensandsliverswords reblogged this · 1 month ago
pensandsliverswords reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 pensandsliverswords liked this · 1 month ago
pensandsliverswords liked this · 1 month ago -
 herebesherlocks reblogged this · 1 month ago
herebesherlocks reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 professor-cold-ramen liked this · 1 month ago
professor-cold-ramen liked this · 1 month ago -
 learlir liked this · 1 month ago
learlir liked this · 1 month ago -
 thejonderettegirl liked this · 1 month ago
thejonderettegirl liked this · 1 month ago -
 tzarina-alexandra reblogged this · 1 month ago
tzarina-alexandra reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 angelbornaltruist liked this · 1 month ago
angelbornaltruist liked this · 1 month ago -
 liamins liked this · 1 month ago
liamins liked this · 1 month ago -
 greengrace reblogged this · 1 month ago
greengrace reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 alchemisticramblings reblogged this · 1 month ago
alchemisticramblings reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 alchemisticramblings liked this · 1 month ago
alchemisticramblings liked this · 1 month ago -
 inkyrainstorms liked this · 1 month ago
inkyrainstorms liked this · 1 month ago -
 fancytomato reblogged this · 1 month ago
fancytomato reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 fancytomato liked this · 1 month ago
fancytomato liked this · 1 month ago -
 alcadanon reblogged this · 1 month ago
alcadanon reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 alcadanon liked this · 1 month ago
alcadanon liked this · 1 month ago -
 marie-pippins liked this · 1 month ago
marie-pippins liked this · 1 month ago -
 indynerdgirl reblogged this · 1 month ago
indynerdgirl reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 starfayy liked this · 1 month ago
starfayy liked this · 1 month ago -
 livingandthriving liked this · 1 month ago
livingandthriving liked this · 1 month ago -
 aevarswall reblogged this · 1 month ago
aevarswall reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 aevarswall liked this · 1 month ago
aevarswall liked this · 1 month ago -
 screwtornadowarningsimsouthern reblogged this · 1 month ago
screwtornadowarningsimsouthern reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 argen-lobo-ridder reblogged this · 1 month ago
argen-lobo-ridder reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 banana-with-a-bow-tie reblogged this · 1 month ago
banana-with-a-bow-tie reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 ladypyewacket reblogged this · 1 month ago
ladypyewacket reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 noelia-diaz06 liked this · 1 month ago
noelia-diaz06 liked this · 1 month ago -
 strawberry-muffin-crisis liked this · 1 month ago
strawberry-muffin-crisis liked this · 1 month ago -
 tealfoxarts liked this · 1 month ago
tealfoxarts liked this · 1 month ago -
 vio1315 liked this · 1 month ago
vio1315 liked this · 1 month ago -
 jacepi-time reblogged this · 1 month ago
jacepi-time reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 toothpaste-dragon liked this · 1 month ago
toothpaste-dragon liked this · 1 month ago -
 theworldoffandoming reblogged this · 1 month ago
theworldoffandoming reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 kazeharuhime liked this · 1 month ago
kazeharuhime liked this · 1 month ago -
 banana-with-a-bow-tie liked this · 1 month ago
banana-with-a-bow-tie liked this · 1 month ago -
 thegreatclowncat reblogged this · 1 month ago
thegreatclowncat reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 firefletch liked this · 1 month ago
firefletch liked this · 1 month ago





