Once Upon A Time T
Once Upon a Time t
Once upon the time t(0) there was a young buck named Butterbean who wanted nothing more than to know his ontological value. Being familiar with the concepts of quantum mechanics he was sadly aware that this was theoretically impossible, but remained unsatisfied with the notion.

In an undying effort to discover the nature of his own existence he set out on a journey to seek the answer from all those most wise and perceiving.
Clearly the first stop was at the front door of Glad the hippopotamus.
Glad was of the notion that all things are ultimately mundane and that it is simply a matter of time and “progress” before esoteric conundrums become simple everyday knowledge. Surely this most assured creature could derive an unknown variable to discover the true nature of Butterbean himself. They were both of the mind at this time t(realist) that all the probabilistic nonsense was clearly just a cop out for those ninnies who fancied themselves finished with discovering the universe.

Alas after decades, or maybe days (no one can be sure given that time itself is a construct commonly defined as the duration of 9,192,631,770 periods of the radiation corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the cesium 133 atom, and who can really say cesium 133 even exists… really), Glad was forced to admit that he could not tell Butterbean of his ontological state prior to Butterbean’s arrival on his doorstep, nor could he possibly without any reference to his own experience as a literalist hippo, and was forced to admit that this coveted obscure variable was beyond his abilities of perception.
With a sense of hopelessness Butterbean sought out the comfort and guidance of Ol’ Trusty, the Wire Stripper. They adventured together for t(hedonist) to t(fundamentalist) without ever committing to any defined notion as after all, how can you find the answer to a paradox, oxymoron much?

However comfort in ignorance becomes unsettling after you’ve had your fun and Butterbean became restless. There was one more known avenue he had not yet travelled…
With a renewed sense of wonder and determination Butterbean approached the Oak, which shook its branches excitedly upon Butterbean’s arrival to see such a valiant seeker of answers. “Oak, what can you tell me about my ontological value?” asked Butterbean humbly. The Oak remained silent, but a slight breeze rustled loose a few leaves from its massive head which fluttered to the ground and landed lightly at Butterbean’s feet, Butterbean faltered and then turned and retreated thoughtfully sensing that the conversation was over.

Upon further consideration over Δt(orthodox) Butterbean understood Oak’s lesson— the leaves could change position through many methods all resulting in different outcomes, however before any leaf falls, it has not fallen. Butterbean had discovered that no matter who or what observes him, there would be an outcome, but it could not be these interactions which defined the whole of himself, surely he must be something inherently like the leaves of Oak’s mane.
One day, a little time later at approximately t(decision), Butterbean decided to venture forth in search of a method of measurement that excluded observation. Knowing that the existence of alligators had long been debated among those with a higher understanding of the nature of things, he knew he should seek within the mind of that which may or may not exist; namely an alligator (though a unicorn or manticore could have sufficed, they are not quite as easy to find nowadays).

Unfortunately all alligators are actually just dead trees and Butterbean had to once again rethink his strategy.
It occurred to Butterbean, after his most recent experiences, that perhaps his disbelief in alligators had caused their value to be null, distracted in hoping that his mind was not quite that powerful Butterbean mistakenly stomped on a daisy which let out a loud squeal, “watch out dummy!” “OH!” replied Butterbean, “Sorry I didn’t see you there, though come to think of it I’m surprised you even exist as I hadn’t yet observed you my friend.” The daisy straightened herself and smoothing out her petals scoffed and said jeeringly, “you think that you are the only one who exists, eh?” “Well,” began Butterbean thoughtfully, “no, but I don’t understand how anything or anyone has any sort of defined nature without something else purposefully interacting with it, after all, how do you know that you exist?” “Oh for goodness sake,” exclaimed young Daisy, “Of course you’ll remain limited as long as you keep collapsing your wave function with all that introspection!” And she turned her face to the sun clearly dismissing Butterbean and all his angsty questions.

Butterbean, with all known theories exhausted, was still unsatisfied and longed to know the mystery of his own nature of being and the recent dismissal of the daisy weighed heavy on his soul. “Why can she be so satisfied just being,” he wondered, “when I spend all of my time dedicated to the mystery and nature of life but still feel so empty and unfulfilled?” And suddenly it struck him! It had been so obvious all along and basically verbatim the retorts he had only just received from the annoyed flower he had trod on, Butterbean ceased to observe himself and existed infinitely in all possible states of being.

More Posts from Philosophical-amoeba and Others



David Bowie (1947-2016) at Kyoto - Japan - 1980
Photos by Sukita Masayoshi 鋤田 正義
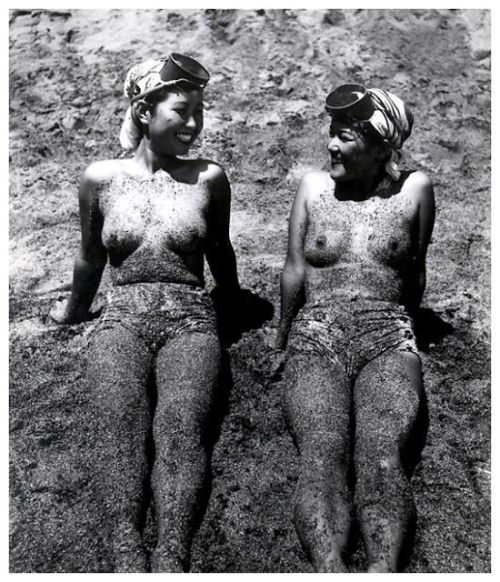
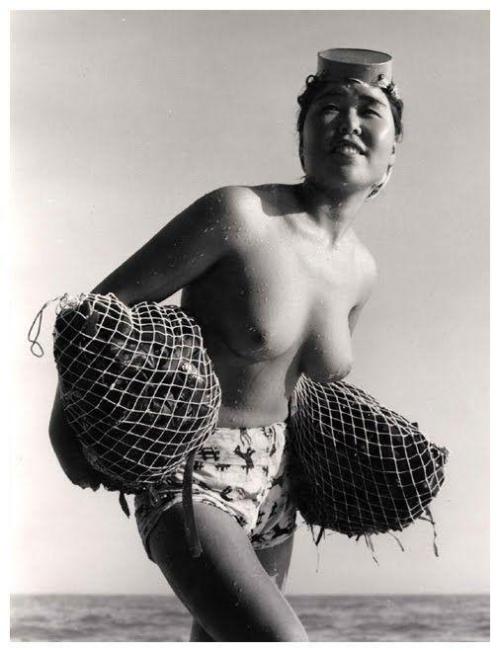
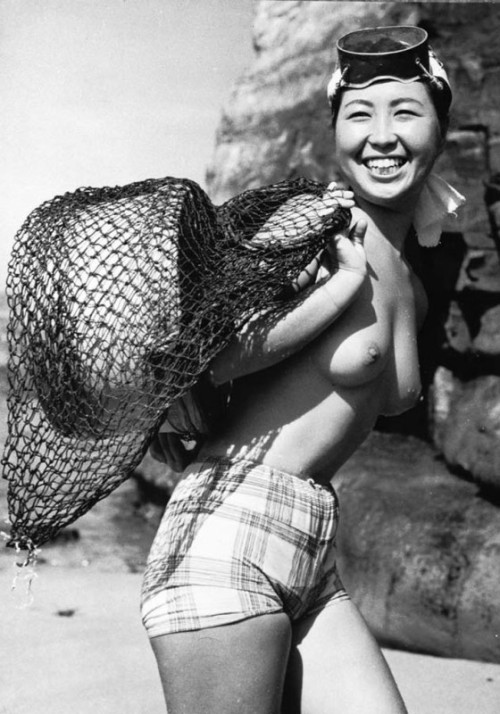
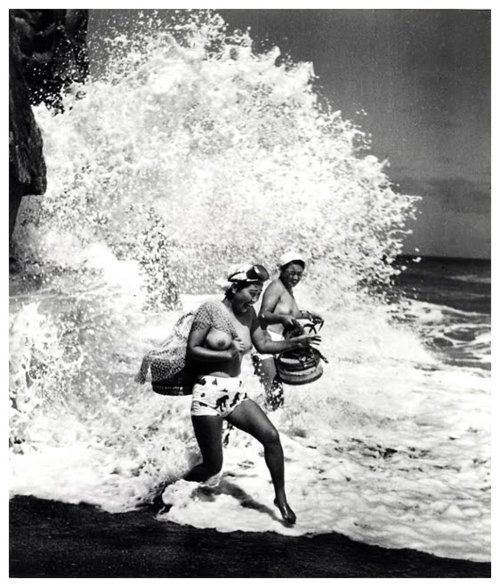
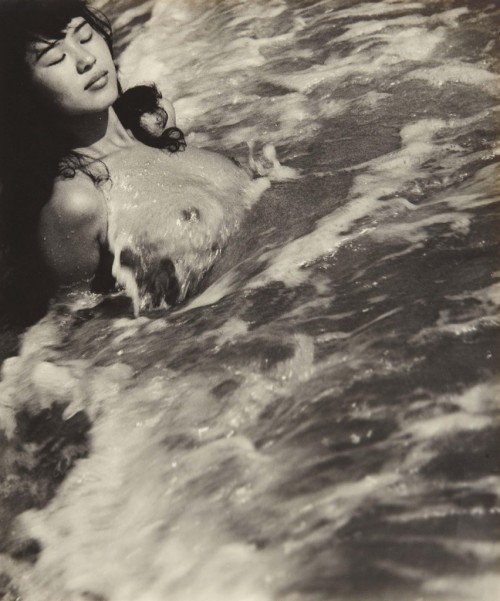









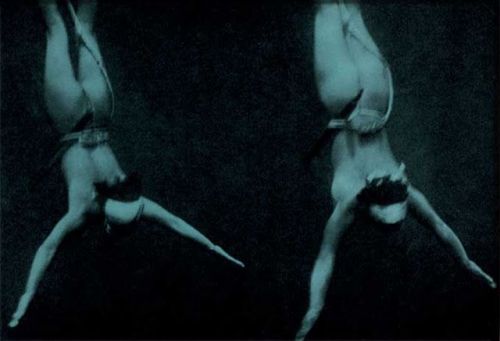
The Last Japanese Mermaids
For nearly two thousand years, Japanese women living in coastal fishing villages made a remarkable livelihood hunting the ocean for oysters and abalone, a sea snail that produces pearls. They are known as Ama. The few women left still make their living by filling their lungs with air and diving for long periods of time deep into the Pacific ocean, with nothing more than a mask and flippers.
In the mid 20th century, Iwase Yoshiyuki returned to the fishing village where he grew up and photographed these women when the unusual profession was still very much alive. After graduating from law school, Yoshiyuki had been given an early Kodak camera and found himself drawn to the ancient tradition of the ama divers in his hometown. His photographs are thought to be the only comprehensive documentation of the near-extinct tradition in existence
Word of the Day: philodox
n. A person who loves or vehemently propounds his or her own opinions; a dogmatic or argumentative person

Image: “Savonarola Preaching Against Prodigality” by Ludwig von Langenmantel. Public Domain via Wikimedia Commons










Fairyland, or, Through the Enchanted Forest.
[Gloucester, England], [Roberts Brothers], [ca. 1890-1915].
Bryn Mawr College Special Collections GV1469.F221 T4 1890z
This whimsical board game, with its blinding powder, cabbage, meat, and cake tokens, has it all! Wild two-headed animals ravage the forest and hapless children must make it through armed only with odd grocery items! The game is a new addition to the Bryn Mawr College Special Collections as part of the Ellery Yale Wood Collection of Children’s Books.

David in Singapore, Serious Moonlight Tour 1983
Photo © Denis O’Regan

The late effects of stress: New insights into how the brain responds to trauma
Mrs. M would never forget that day. She was walking along a busy road next to the vegetable market when two goons zipped past on a bike. One man’s hand shot out and grabbed the chain around her neck. The next instant, she had stumbled to her knees, and was dragged along in the wake of the bike. Thankfully, the chain snapped, and she got away with a mildly bruised neck. Though dazed by the incident, Mrs. M was fine until a week after the incident.
Then, the nightmares began.
She would struggle and yell and fight in her sleep every night with phantom chain snatchers. Every bout left her charged with anger and often left her depressed. The episodes continued for several months until they finally stopped. How could a single stressful event have such extended consequences?
A new study by Indian scientists has gained insights into how a single instance of severe stress can lead to delayed and long-term psychological trauma. The work pinpoints key molecular and physiological processes that could be driving changes in brain architecture.
The team, led by Sumantra Chattarji from the National Centre for Biological Sciences (NCBS) and the Institute for Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine (inStem), Bangalore, have shown that a single stressful incident can lead to increased electrical activity in a brain region known as the amygdala. This activity sets in late, occurring ten days after a single stressful episode, and is dependent on a molecule known as the N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor (NMDA-R), an ion channel protein on nerve cells known to be crucial for memory functions.
The amygdala is a small, almond-shaped groups of nerve cells that is located deep within the temporal lobe of the brain. This region of the brain is known to play key roles in emotional reactions, memory and making decisions. Changes in the amygdala are linked to the development of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), a mental condition that develops in a delayed fashion after a harrowing experience.
Previously, Chattarji’s group had shown that a single instance of acute stress had no immediate effects on the amygdala of rats. But ten days later, these animals began to show increased anxiety, and delayed changes in the architecture of their brains, especially the amygdala.
“We showed that our study system is applicable to PTSD. This delayed effect after a single episode of stress was reminiscent of what happens in PTSD patients,” says Chattarji. “We know that the amygdala is hyperactive in PTSD patients. But no one knows as of now, what is going on in there,” he adds.
Investigations revealed major changes in the microscopic structure of the nerve cells in the amygdala. Stress seems to have caused the formation of new nerve connections called synapses in this region of the brain. However, until now, the physiological effects of these new connections were unknown.
In their recent study, Chattarji’s team has established that the new nerve connections in the amygdala lead to heightened electrical activity in this region of the brain.
“Most studies on stress are done on a chronic stress paradigm with repeated stress, or with a single stress episode where changes are looked at immediately afterwards – like a day after the stress,” says Farhana Yasmin, one of the Chattarji’s students. “So, our work is unique in that we show a reaction to a single instance of stress, but at a delayed time point,” she adds.
Furthermore, a well-known protein involved in memory and learning, called NMDA-R has been recognised as one of the agents that bring about these changes. Blocking the NMDA-R during the stressful period not only stopped the formation of new synapses, it also blocked the increase in electrical activity at these synapses.
“So we have for the first time, a molecular mechanism that shows what is required for the culmination of events ten days after a single stress,” says Chattarji. “In this study, we have blocked the NMDA Receptor during stress. But we would like to know if blocking the molecule after stress can also block the delayed effects of the stress. And if so, how long after the stress can we block the receptor to define a window for therapy,” he adds.
Chattarji’s group first began their investigations into how stress affects the amygdala and other regions of the brain around ten years ago. The work has required the team to employ an array of highly specialised and diverse procedures that range from observing behaviour to recording electrical signals from single brain cells and using an assortment of microscopy techniques. “To do this, we have needed to use a variety of techniques, for which we required collaborations with people who have expertise in such techniques,” says Chattarji. “And the glue for such collaborations especially in terms of training is vital. We are very grateful to the Wadhwani Foundation that supports our collaborative efforts and to the DBT and DAE for funding this work,” he adds.











Singapore Food (in Manga/Anime) Appreciation Post!
(Also: Onion Chopping Ninja Reveals Her Timezone!)
It’s Singapore’s National Day today (9th Aug) and I was going to do a Singaporean-based Recipe, (like Hayama’s Curry Fish Head), but didn’t have time to, so here’s a Singapore Food in Manga/Anime Appreciation Post - from Kuragehime, Shokugeki no Souma, and Addicted to Curry!
The Singaporean food that is usually shown in manga/anime is usually either curry-based or chicken rice. And of course, I don’t usually make them at home because: 1. They’re easier to make in bulk 2. You can get them cheaper outside 3. My version would pale in comparison to the masters’ 4. It requires hours of preparation, except for some of the easier curry dishes in Addicted to Curry. (A manga cap of the recipe is above!)
Addicted to Curry lists Singapore as Curry Central, and I never realized how true that was until I went abroad for a couple of years and missed how we would just drown everything in curry, especially for mixed rice dishes like Chap Chye Png and Nasi Briyani. There was also a huge uproar when McDonald’s ran out of Curry Sauce for McNuggets (they have since started selling it in bottles), and a near-riot when a neighbour complained about the smell of another neighbour cooking curry. Also, Gordon Ramsay can’t beat our laksa, even though I think that particular store he challenged isn’t the best one.
(Not everything is curry, of course, but if there’s no curry, generally, there must be chili. And woe betide those who eat the wrong kind of chili with the wrong kind of food. And here’s a PSA for foreigners - Chili Crab is largely for tourists. Take Black Pepper Crab or Salted Egg Crab instead. It’s possible to live as a weak sauce who can’t take spicy foods here, but less exciting. )
Happy 51st Birthday, Singapore! Here’s to the spread of our food all over the world! And a birthday wish would be for more kinds of our food to be shown in manga/anime. :D - O.C.N.

PS: By the way, Eizan Senpai, you can get Hainanese Chicken Rice for $3, and it is considered Street Food even though there are $30+ versions at hotels. Never eaten one with Jidori Chicken, though.
-
 hhhhhhhh-hhhhhhh liked this · 8 years ago
hhhhhhhh-hhhhhhh liked this · 8 years ago -
 theweezbeez reblogged this · 8 years ago
theweezbeez reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 theweezbeez liked this · 8 years ago
theweezbeez liked this · 8 years ago -
 morethananswers liked this · 8 years ago
morethananswers liked this · 8 years ago -
 two-randomwords liked this · 8 years ago
two-randomwords liked this · 8 years ago -
 thetacopanda liked this · 8 years ago
thetacopanda liked this · 8 years ago -
 photonic-pulsar reblogged this · 8 years ago
photonic-pulsar reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 discoverysciencecentre reblogged this · 8 years ago
discoverysciencecentre reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 drzaa liked this · 8 years ago
drzaa liked this · 8 years ago -
 mav3rick413 liked this · 8 years ago
mav3rick413 liked this · 8 years ago -
 ajapamworld reblogged this · 8 years ago
ajapamworld reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 ajapamworld liked this · 8 years ago
ajapamworld liked this · 8 years ago -
 tangereendream liked this · 8 years ago
tangereendream liked this · 8 years ago -
 cruisininfinity-blog1 liked this · 8 years ago
cruisininfinity-blog1 liked this · 8 years ago -
 comfortablysharedsilence reblogged this · 8 years ago
comfortablysharedsilence reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 forevermorous reblogged this · 8 years ago
forevermorous reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 usernamegeneric55-blog liked this · 8 years ago
usernamegeneric55-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 philosophical-amoeba reblogged this · 8 years ago
philosophical-amoeba reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 forgetful-amoeba liked this · 8 years ago
forgetful-amoeba liked this · 8 years ago -
 uinen2-blog liked this · 8 years ago
uinen2-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 myvampirepuppy reblogged this · 8 years ago
myvampirepuppy reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 photonic-pulsar liked this · 8 years ago
photonic-pulsar liked this · 8 years ago -
 sonmojo reblogged this · 8 years ago
sonmojo reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 new-omen liked this · 8 years ago
new-omen liked this · 8 years ago -
 neuro-slut liked this · 8 years ago
neuro-slut liked this · 8 years ago -
 thecrowpenguinzombie liked this · 8 years ago
thecrowpenguinzombie liked this · 8 years ago -
 aggrovigliamento-blog liked this · 8 years ago
aggrovigliamento-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 dragonium7 liked this · 8 years ago
dragonium7 liked this · 8 years ago -
 joejoat reblogged this · 8 years ago
joejoat reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 joejoat liked this · 8 years ago
joejoat liked this · 8 years ago -
 anticorn-lawleag-ue reblogged this · 8 years ago
anticorn-lawleag-ue reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 psychologist54 liked this · 8 years ago
psychologist54 liked this · 8 years ago -
 apintofstarstuff liked this · 8 years ago
apintofstarstuff liked this · 8 years ago -
 physicsforbunnies reblogged this · 8 years ago
physicsforbunnies reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 theogonia liked this · 8 years ago
theogonia liked this · 8 years ago -
 siderealcalendars reblogged this · 9 years ago
siderealcalendars reblogged this · 9 years ago
A reblog of nerdy and quirky stuff that pique my interest.
291 posts















