Haaaaaay I’m On ITunes Now! Slightly More Convenient To Download Maybe!

Haaaaaay I’m on iTunes now! Slightly more convenient to download maybe!
More Posts from Fillthevoid-with-space and Others
How much of a daily threat is "Space junk"?
Good question, as this is a serious issue and one which we must monitor constantly in order to avoid harmful impacts on the International Space Station with objects in space. For example, the US Space Command in Colorado is monitoring all objects bigger than a few inches in order to assess any potential impact with the Space Station. We categorize the chance of impact and if there is a high probability, we will actually use thrusters to slightly change the position of the Space Station to avoid the impact. If it is something that we are unable to avoid, we will have the astronauts shelter in place in their spacecrafts and in case of a catastrophic impact, they will return to Earth.

Henges! What the heck are they? And why is the word for studying them (and various monuments around the world that serve a similar purpose) so friggin long? Archaeoastronomy? What even is that? I got quite a few requests for this one so hopefully I did it justice... in my own special, somewhat contrary way.
Below the cut is some elaboration on the episode itself, including my sources, music credits, a glossary, some Google Maps images of the locations I talk about, and a transcript (not an exact record of this episode, but it’s the loose, fairly conversational script I was working with). I mention a couple of books and quote a couple people in this episode so if you want to see that written down, those sources are there too. I’m also on Twitter at @HDandtheVoid.
Let me know what you think of this episode, let me know what you think I should research next*, tell me a fun space fact… anything’s helpful at this point!
*(My thoughts were planets or star classifications. Give me some feedback by May 25th so I can start working on it! The next episode will be on June 5th.)
Glossary:
archaeoastronomy - the study of the astronomical practices, celestial lore, mythologies, religions, and world-views of all ancient cultures. The anthropology of astronomy.
equinox - twice a year, in the spring (vernal equinox) and fall (autumnal equinox), the 23.5-degree tilt of the Earth’s axis and Earth’s orbit around the sun combine in such a way that the axis is inclined neither away from nor toward the sun. The day and night are of equal length.
henge - a prehistoric monument consisting of a circle of stone or wooden uprights.
kiva - a room used for rituals and political meetings for many Southwest American Indian tribes.
petroglyph - rock carvings made by pecking directly on the rock surface using a stone chisel and a hammerstone. The desert varnish on the surface of the rock is chipped off, exposing the lighter rock underneath.
solstice - twice a year, in the summer (Midsummer) and winter (Midwinter), the 23.5-degree tilt of the Earth’s axis and Earth’s orbit around the sun mean that the axis is inclined away from or toward the sun. In Midsummer, the day is longest; in Midwinter, the day is shortest.
Script/Transcript (I do tend to embellish in the moment of recording so it’s not exact, but all the facts are there and I can’t know a fact and not talk about it so trust me, all you’re missing is probably another swear word or two)
Chaco Canyon, New Mexico, United States of America

Chichen Itza, Yucutan, Mexico

Stonehenge, Salisbury, England

Newgrange, County Meath, Republic of Ireland

Sources:
The definition of ‘henge’
A slightly more exciting definition of ‘henge,’ with pictures
Classifications of henges in the British Isles
The definition of a petroglyph, with pictures
A 3-minute video about solstices and equinoxes that has images of Chichen Itza and Stonehenge as well as Macchu Picchu, via National Geographic
Another explanation of the equinoxes and solstices; no video, though
The great Stonehenge Purchase!
More on the great Stonehenge Purchase!
Neil deGrasse Tyson writes about Manhattanhenge
Find your own city’s henge!
Burl, Aubrey. The Stone Circles of Britain, Ireland, and Brittany. Yale UP: New Haven, CT, 2000. Located on Google Books.
Crouper, Heather and Nigel Henbest. The History of Astronomy. Firefly Books: Buffalo, NY, 2007.
Clive Ruggles quote: “Generally people in indigenous cultures in the past tried to make sense of the cosmos—of the world around them—by drawing links between things; things in the sky, things around them in the landscape, and social things too—all mixed in” (14).
G.B. Cornucopia quote: “One of the Chacoan people’s tools was certainly astronomy, and they were interested in astronomy because anyone living in this harsh environment who does not understand their environment will not survive” (11).
Ed Krupp quote: “Usually monumental architecture isn’t dedicated to observing the sky. It’s a way that people express how they feel at home in the universe; but also how they control the universe” (21).
Glowacki, Donna M. Living and Leaving: A Social History of Regional Depopulation in Thirteenth-Century Mesa Verde. U of AZ P: Tucson, AZ, 2015. Located on Google Books.
McCluskey, S. C. “Historical Archaeoastronomy: The Hopi Example.” Archaeoastronomy in the New World. Ed. A. F. Aveni. London: Cambridge UP, 1982 (31-58).
McCluskey quote: “began watching when the sun ‘went in’ near the cultural center and motel on Second Mesa” (38).
Williamson, R. A. et al. “Anasazi Solar Observatories.” Native American Astronomy. Ed. A. F. Aveni. Austin: U Texas P, 1977 (203-218).
Intro Music: ‘Better Times Will Come’ by No Luck Club off their album Prosperity
Filler Music: ‘Leaves’ by Patients aka Ben Cooper, who primarily releases music as Radical Face but also has at least three other bands or band names he’s working with/has released music as.
Outro Music: ‘Fields of Russia’ by Mutefish off their album On Draught
Merging Galaxies Have Enshrouded Black Holes
NASA - NuStar Mission patch. May 9, 2017 Black holes get a bad rap in popular culture for swallowing everything in their environments. In reality, stars, gas and dust can orbit black holes for long periods of time, until a major disruption pushes the material in. A merger of two galaxies is one such disruption. As the galaxies combine and their central black holes approach each other, gas and dust in the vicinity are pushed onto their respective black holes. An enormous amount of high-energy radiation is released as material spirals rapidly toward the hungry black hole, which becomes what astronomers call an active galactic nucleus (AGN). A study using NASA’s NuSTAR telescope shows that in the late stages of galaxy mergers, so much gas and dust falls toward a black hole that the extremely bright AGN is enshrouded. The combined effect of the gravity of the two galaxies slows the rotational speeds of gas and dust that would otherwise be orbiting freely. This loss of energy makes the material fall onto the black hole.
Image above: This illustration compares growing supermassive black holes in two different kinds of galaxies. A growing supermassive black hole in a normal galaxy would have a donut-shaped structure of gas and dust around it (left). In a merging galaxy, a sphere of material obscures the black hole (right). Image Credits: National Astronomical Observatory of Japan. “The further along the merger is, the more enshrouded the AGN will be,” said Claudio Ricci, lead author of the study published in the Monthly Notices Royal Astronomical Society. “Galaxies that are far along in the merging process are completely covered in a cocoon of gas and dust.” Ricci and colleagues observed the penetrating high-energy X-ray emission from 52 galaxies. About half of them were in the later stages of merging. Because NuSTAR is very sensitive to detecting the highest-energy X-rays, it was critical in establishing how much light escapes the sphere of gas and dust covering an AGN. The study was published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. Researchers compared NuSTAR observations of the galaxies with data from NASA’s Swift and Chandra and ESA’s XMM-Newton observatories, which look at lower energy components of the X-ray spectrum. If high-energy X-rays are detected from a galaxy, but low-energy X-rays are not, that is a sign that an AGN is heavily obscured.
NASA’s NuSTAR telescope. Image Credit: NASA
The study helps confirm the longstanding idea that an AGN’s black hole does most of its eating while enshrouded during the late stages of a merger. “A supermassive black hole grows rapidly during these mergers,” Ricci said. “The results further our understanding of the mysterious origins of the relationship between a black hole and its host galaxy.” NuSTAR is a Small Explorer mission led by Caltech and managed by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. NuSTAR was developed in partnership with the Danish Technical University and the Italian Space Agency (ASI). The spacecraft was built by Orbital Sciences Corp., Dulles, Virginia. NuSTAR’s mission operations center is at UC Berkeley, and the official data archive is at NASA’s High Energy Astrophysics Science Archive Research Center. ASI provides the mission’s ground station and a mirror archive. JPL is managed by Caltech for NASA. Related link: Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: https://academic.oup.com/mnras/article/468/2/1273/2939810/Growing-supermassive-black-holes-in-the-late For more information on NuSTAR, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/nustar http://www.nustar.caltech.edu Images (mentioned), Text, Credits: NASA/Tony Greicius/JPL/Elizabeth Landau. Greetings, Orbiter.ch Full article
I still highly recommend this good, beautiful web comic about love in space, and now it's all done! You can read it all.




The final three chapters are up. Read it now.
That’s it folks, On A Sunbeam is over. Though I am pondering a sequel.
Thank you all so much for following along.
Shooting for an April first post date! I just started researching and hooboy, I am going to go way way way way down the rabbit hole of tangents. I think everything is interesting and cool.
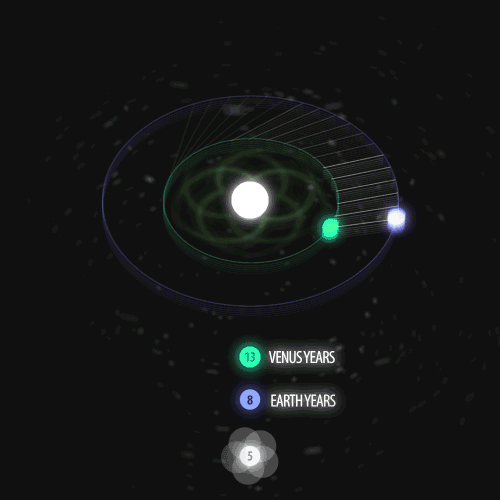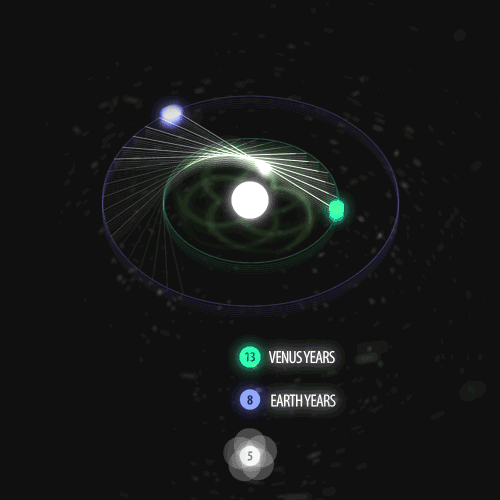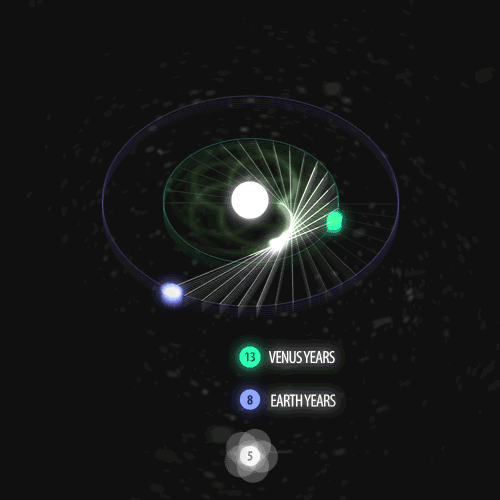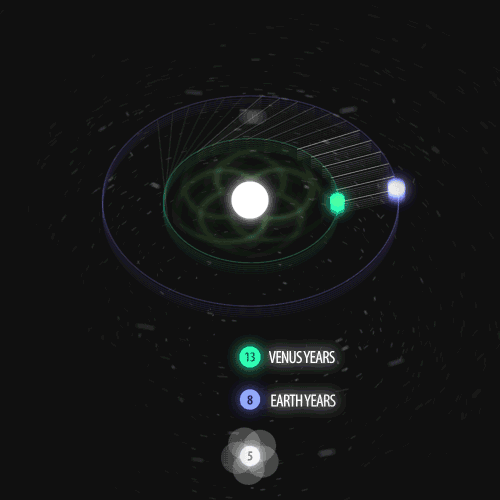
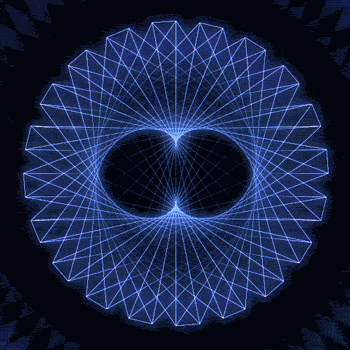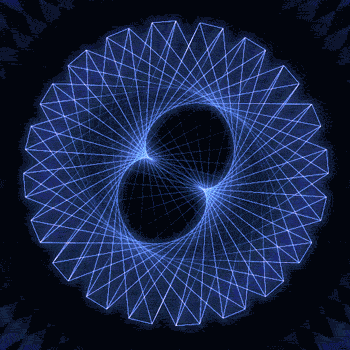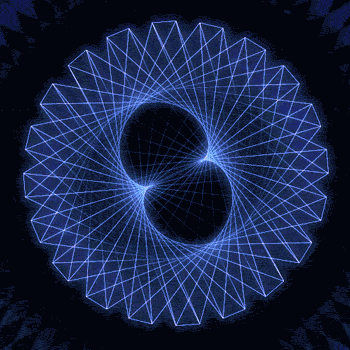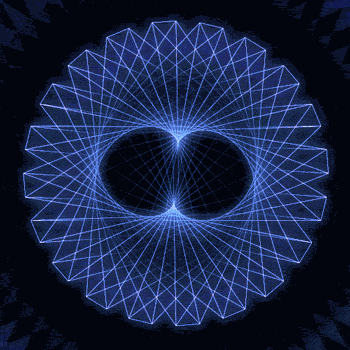
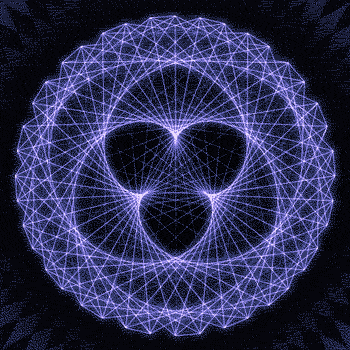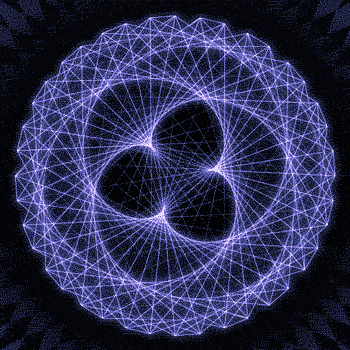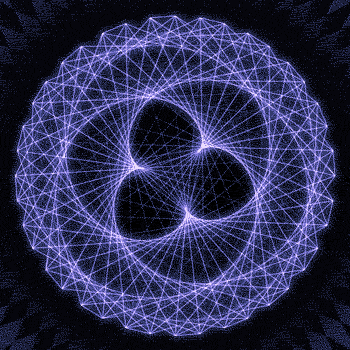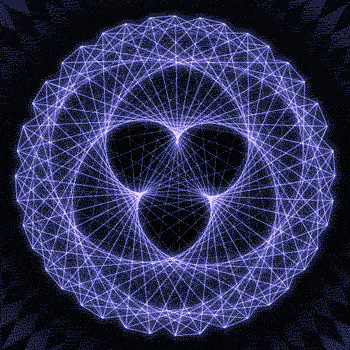


Fibonacci you crazy bastard….
As seen in the solar system (by no ridiculous coincidence), Earth orbits the Sun 8 times in the same period that Venus orbits the Sun 13 times! Drawing a line between Earth & Venus every week results in a spectacular FIVE side symmetry!!
Lets bring up those Fibonacci numbers again: 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34..
So if we imagine planets with Fibonacci orbits, do they create Fibonacci symmetries?!
You bet!! Depicted here is a:
2 sided symmetry (5 orbits x 3 orbits)
3 sided symmetry (8 orbits x 5 orbits)
5 sided symmetry (13 orbits x 8 orbits) - like Earth & Venus
8 sided symmetry (21 orbits x 13 orbits)
I wonder if relationships like this exist somewhere in the universe….
Read the Book | Follow | Hi-Res -2- -3- -5- -8-
In Conversation with the Sun: Parker Solar Probe Communications
Our Sun powers life on Earth. It defines our days, nourishes our crops and even fuels our electrical grids. In our pursuit of knowledge about the universe, we’ve learned so much about the Sun, but in many ways we’re still in conversation with it, curious about its mysteries.

Parker Solar Probe will advance this conversation, flying through the Sun’s atmosphere as close as 3.8 million miles from our star’s surface, more than seven times closer to it than any previous spacecraft. If space were a football field, with Earth at one end and the Sun at the other, Parker would be at the four-yard line, just steps away from the Sun! This journey will revolutionize our understanding of the Sun, its surface and solar winds.

Supporting Parker on its journey to the Sun are our communications networks. Three networks, the Near Earth Network, the Space Network and the Deep Space Network, provide our spacecraft with their communications, delivering their data to mission operations centers. Their services ensure that missions like Parker have communications support from launch through the mission.

For Parker’s launch on Aug. 12, the Delta IV Heavy rocket that sent Parker skyward relied on the Space Network. A team at Goddard Space Flight Center’s Networks Integration Center monitored the launch, ensuring that we maintained tracking and communications data between the rocket and the ground. This data is vital, allowing engineers to make certain that Parker stays on the right path towards its orbit around the Sun.

The Space Network’s constellation of Tracking and Data Relay Satellites (TDRS) enabled constant communications coverage for the rocket as Parker made its way out of Earth’s atmosphere. These satellites fly in geosynchronous orbit, circling Earth in step with its rotation, relaying data from spacecraft at lower altitudes to the ground. The network’s three collections of TDRS over the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian oceans provide enough coverage for continuous communications for satellites in low-Earth orbit.

The Near Earth Network’s Launch Communications Segment tracked early stages of Parker’s launch, testing our brand new ground stations’ ability to provide crucial information about the rocket’s initial velocity (speed) and trajectory (path). When fully operational, it will support launches from the Kennedy spaceport, including upcoming Orion missions. The Launch Communications Segment’s three ground stations are located at Kennedy Space Center; Ponce De Leon, Florida; and Bermuda.

When Parker separated from the Delta IV Heavy, the Deep Space Network took over. Antennas up to 230 feet in diameter at ground stations in California, Australia and Spain are supporting Parker for its 24 orbits around the Sun and the seven Venus flybys that gradually shrink its orbit, bringing it closer and closer to the Sun. The Deep Space Network is delivering data to mission operations centers and will continue to do so as long as Parker is operational.
Near the Sun, radio interference and the heat load on the spacecraft’s antenna makes communicating with Parker a challenge that we must plan for. Parker has three distinct communications phases, each corresponding to a different part of its orbit.
When Parker comes closest to the Sun, the spacecraft will emit a beacon tone that tells engineers on the ground about its health and status, but there will be very little opportunity to command the spacecraft and downlink data. High data rate transmission will only occur during a portion of Parker’s orbit, far from the Sun. The rest of the time, Parker will be in cruise mode, taking measurements and being commanded through a low data rate connection with Earth.

Communications infrastructure is vital to any mission. As Parker journeys ever closer to the center of our solar system, each byte of downlinked data will provide new insight into our Sun. It’s a mission that continues a conversation between us and our star that has lasted many millions of years and will continue for many millions more.
For more information about NASA’s mission to touch the Sun: https://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/parker-solar-probe
For more information about our satellite communications check out: http://nasa.gov/SCaN
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

TODAY IN HISTORY: The first-ever color image of Mars, taken by NASA’s Viking 1 lander on July 21, 1976. (San Diego Air & Space Museum)










Cassini prepares for final orbital “Grand Finale” at Saturn.
Erik Wernquist, the same filmmaker who created 2014’s “Wanderers” and a stunning New Horizons promotional film in 2015, has created a new video highlighting NASA’s Cassini mission’s final days at Saturn. The Cassini spacecraft will begin its final series of orbits to cap a 13-year groundbreaking science mission known as the Grand Finale. For the first time ever in Cassini’s time at Saturn, the spacecraft will fly in between the planet’s rings and atmosphere. No spacecraft has ever before flown in this region of any of the solar system’s ringed planets. After 20 orbits, Cassini will dive into Saturn’s upper atmosphere September 15 where it will be destroyed. In 2008, mission managers explored a range of End of Mission scenarios that would protect Saturn’s moon’s from Earthly contaminants before ultimately deciding on atmospheric reentry. Cassini began her End of Mission manoeuvres on November 26, 2016, when it began the first of 20 ring-grazing orbits. A close flyby of Titan April 22 will alter the spacecraft’s trajectory to begin the first of 23 orbits in the Grand Finale, which will begin April 26.

Cassini launched from Earth on October 20, 1997, and entered Saturn orbit July 1, 2004. 16 days later, the European-built Huygens probe attached to the spacecraft landed on Titan, becoming the first probe to land in the outer solar system. Originally scheduled for a four-year mission ending in 2008, Cassini received two mission extensions in 2008 and 2010, with the latter ending in 2017. With the spacecraft’s fuel reserves low, the Cassini team decided to end the mission. P/C: JPL/Erik Wernquist
-
 letsfollowthesedays liked this · 8 years ago
letsfollowthesedays liked this · 8 years ago -
 fillthevoid-with-space reblogged this · 8 years ago
fillthevoid-with-space reblogged this · 8 years ago
A podcast project to fill the space in my heart and my time that used to be filled with academic research. In 2018, that space gets filled with... MORE SPACE! Cheerfully researched, painstakingly edited, informal as hell, definitely worth everyone's time.
243 posts