Merging Galaxies Have Enshrouded Black Holes
Merging Galaxies Have Enshrouded Black Holes
NASA - NuStar Mission patch. May 9, 2017 Black holes get a bad rap in popular culture for swallowing everything in their environments. In reality, stars, gas and dust can orbit black holes for long periods of time, until a major disruption pushes the material in. A merger of two galaxies is one such disruption. As the galaxies combine and their central black holes approach each other, gas and dust in the vicinity are pushed onto their respective black holes. An enormous amount of high-energy radiation is released as material spirals rapidly toward the hungry black hole, which becomes what astronomers call an active galactic nucleus (AGN). A study using NASA’s NuSTAR telescope shows that in the late stages of galaxy mergers, so much gas and dust falls toward a black hole that the extremely bright AGN is enshrouded. The combined effect of the gravity of the two galaxies slows the rotational speeds of gas and dust that would otherwise be orbiting freely. This loss of energy makes the material fall onto the black hole.
Image above: This illustration compares growing supermassive black holes in two different kinds of galaxies. A growing supermassive black hole in a normal galaxy would have a donut-shaped structure of gas and dust around it (left). In a merging galaxy, a sphere of material obscures the black hole (right). Image Credits: National Astronomical Observatory of Japan. “The further along the merger is, the more enshrouded the AGN will be,” said Claudio Ricci, lead author of the study published in the Monthly Notices Royal Astronomical Society. “Galaxies that are far along in the merging process are completely covered in a cocoon of gas and dust.” Ricci and colleagues observed the penetrating high-energy X-ray emission from 52 galaxies. About half of them were in the later stages of merging. Because NuSTAR is very sensitive to detecting the highest-energy X-rays, it was critical in establishing how much light escapes the sphere of gas and dust covering an AGN. The study was published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. Researchers compared NuSTAR observations of the galaxies with data from NASA’s Swift and Chandra and ESA’s XMM-Newton observatories, which look at lower energy components of the X-ray spectrum. If high-energy X-rays are detected from a galaxy, but low-energy X-rays are not, that is a sign that an AGN is heavily obscured.
NASA’s NuSTAR telescope. Image Credit: NASA
The study helps confirm the longstanding idea that an AGN’s black hole does most of its eating while enshrouded during the late stages of a merger. “A supermassive black hole grows rapidly during these mergers,” Ricci said. “The results further our understanding of the mysterious origins of the relationship between a black hole and its host galaxy.” NuSTAR is a Small Explorer mission led by Caltech and managed by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. NuSTAR was developed in partnership with the Danish Technical University and the Italian Space Agency (ASI). The spacecraft was built by Orbital Sciences Corp., Dulles, Virginia. NuSTAR’s mission operations center is at UC Berkeley, and the official data archive is at NASA’s High Energy Astrophysics Science Archive Research Center. ASI provides the mission’s ground station and a mirror archive. JPL is managed by Caltech for NASA. Related link: Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: https://academic.oup.com/mnras/article/468/2/1273/2939810/Growing-supermassive-black-holes-in-the-late For more information on NuSTAR, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/nustar http://www.nustar.caltech.edu Images (mentioned), Text, Credits: NASA/Tony Greicius/JPL/Elizabeth Landau. Greetings, Orbiter.ch Full article
More Posts from Fillthevoid-with-space and Others
Here’s a great example of the kinds of experiments astronauts perform on the International Space Station, just like I talked about in Episode 19! I absolutely want to high-five whoever called is ISS-CREAM.
From Frozen Antarctica to the Cold Vacuum of Space
A new experiment that will collect tiny charged particles known as galactic cosmic rays will soon be added to the International Space Station. The Cosmic Ray Energetics And Mass for the International Space Station payload, nicknamed ISS-CREAM, will soon be installed in its new home on the Station’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility. ISS-CREAM will help scientists understand more about galactic cosmic rays and the processes that produce them.

Wait, what are cosmic rays?
Cosmic rays are pieces of atoms that move through space at nearly the speed of light. Galactic cosmic rays come from beyond our solar system.

They provide us with direct samples of matter from distant places in our galaxy.
Why do these things go so fast?
Galactic cosmic rays have been sped up by extreme processes. When massive stars die, they explode as supernovas. The explosion’s blast wave expands into space along with a cloud of debris.

Particles caught up in this blast wave can bounce around in it and slowly pick up speed. Eventually they move so fast they can escape the blast wave and race away as a cosmic ray.
Where can we catch cosmic rays?
Cosmic rays are constantly zipping through space at these super-fast speeds, running into whatever is in their path – including Earth.

But Earth’s atmosphere is a great shield, protecting us from 99.9 percent of the radiation coming from space, including most cosmic rays. This is good news for life on Earth, but bad news for scientists studying cosmic rays.
So… how do you deal with that?
Because Earth has such an effective shield against cosmic rays, the best place for scientists to study them is above our atmosphere – in space. Since the 1920s, scientists have tried to get their instruments as close to space as possible. One of the simplest ways to do this is to send these instruments up on balloons the size of football stadiums. These balloons are so large because they have to be able to both lift their own weight and that of their cargo, which can be heavier than a car. Scientific balloons fly to 120,000 feet or more above the ground – that’s at least three times higher than you might fly in a commercial airplane!

Credit: Isaac Mognet (Pennsylvania State University)
Earlier versions of ISS-CREAM’s instruments were launched on these giant balloons from McMurdo Station in Antarctica seven times, starting in 2004, for a total of 191 days near the top of the atmosphere. Each of these flights helped the team test their hardware and work towards sending a cutting-edge cosmic ray detector into space!
How is going to space different than flying balloons?
Balloon flights allowed the team to collect a lot of cosmic rays, but even at 120,000 feet, a lot of the particles are still blocked. Scientists at the University of Maryland, College Park, who operate ISS-CREAM, expect to get about 10 times as much data from their new home on the International Space Station.

That’s because it will be both above the atmosphere and fly far longer than is possible with a balloon. As you might imagine, there are large differences between flying something on a balloon and launching it into space. The science instruments and other systems had to be changed so ISS-CREAM could safely launch on a rocket and work in space.
What will ISS-CREAM do?
While on the space station, ISS-CREAM will collect millions of cosmic rays – electrons, protons and atomic nuclei representing the elements found in the solar system. These results will help us understand why cosmic rays reach the wicked-fast speeds they do and, most important, what limits those speeds.
ISS-CREAM launches to the International Space Station aboard the latest SpaceX Dragon spacecraft, targeted to launch August 14. Want to learn more about ISS-CREAM and some of our scientific balloons? Check out our recent feature, NASA’s Scientific Balloon Program Reaches New Heights.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
New Horizons Flyover of Pluto
Using actual New Horizons data and digital elevation models of Pluto and its largest moon Charon, mission scientists have created flyover movies that offer spectacular new perspectives of the many unusual features that were discovered and which have reshaped our views of the Pluto system – from a vantage point even closer than the spacecraft itself. This dramatic Pluto flyover begins over the highlands to the southwest of the great expanse of nitrogen ice plain informally named Sputnik Planitia. The viewer first passes over the western margin of Sputnik, where it borders the dark, cratered terrain of Cthulhu Macula, with the blocky mountain ranges located within the plains seen on the right. The tour moves north past the rugged and fractured highlands of Voyager Terra and then turns southward over Pioneer Terra – which exhibits deep and wide pits – before concluding over the bladed terrain of Tartarus Dorsa in the far east of the encounter hemisphere. Digital mapping and rendering were performed by Paul Schenk and John Blackwell of the Lunar and Planetary Institute in Houston.

(I broke the last link, whoops)
Another week of theory, but no fun new particles. Instead, hear me try to say a lot of names of scientists or their eponymous equations as I talk about dark energy in the universe! Learn what some astronomers think it is and why other astronomers think there are better explanations for certain nutty galactic phenomena.
Below the cut are my sources, music credits, a vocab list, and the transcript of this episode. Let your voice be heard and tell me what you think I should research next by messaging me here, tweeting at me at @HDandtheVoid, or asking me to my face if you know me in real life. And please subscribe to the podcast on iTunes, rate it and maybe review it, and tell friends if you think they’d like to listen!
(If anything about dark matter or dark energy or cosmic microwave background radiation confused you over the past few podcasts, for sure send me your questions so I can ask someone more qualified than me—my doctorate student friend! My thoughts on the next episode are still the Voyager golden records, space race history, the transit of Venus, the Moon landing, Edmond Halley, or Dark Sky Preserves and it will be up on November 20th.)
Glossary
baryons - heaviest particles. Ex. Protons, neutrons. In astroparticle physics, electrons are included in baryonic matter.
cosmic microwave background radiation - the electromagnetic radiation left over from the time of recombination in Big Bang cosmology.
dark energy - a theoretical force made up of unknown, undetectable energy. It is used to explain why the universe is expanding more rapidly over time instead of slowing its expansion.
dark matter - a theoretical mass made up of unknown particles that have not been created on Earth. It is used to explain why galaxy clusters have 10x the mass that their light output suggests they would have; why distant stars on the edges of spiral galaxies orbit at the same speed as stars near the center of the galaxy; and the accretion of gases that created galaxies at the beginning of the universe.
fundamental forces - four fundamental forces in our current model of the universe: the strong and weak nuclear forces, the electromagnetic force, and gravity.
gravitational lensing - when light from more distant sources passes near a massive star, galaxy, or galaxy cluster and the object’s gravity bends the light like a lens to provide a warped angle view of space.
Transcript
Sources
Dark energy via NASA
Dark energy via Hubble
“The strangeness of dark energy is thrilling.”
Fundamental forces via Georgia State University
Dark energy via Science Magazine (April 2017)
László Dobos: “We assume that every region of the universe determines its expansion rate itself.”
Dark energy and the South Pole Telescope via Smithsonian Magazine (April 2010)
“Knowing what dark matter is would help scientists think about how the structure of the universe forms. Knowing what dark energy does would help scientists think about how that structure has evolved over time—and how it will continue to evolve.”
Intro Music: ‘Better Times Will Come’ by No Luck Club off their album Prosperity
Filler Music: ‘Even The Darkness Has Arms’ by The Barr Brothers off their album The Sleeping Operator
Outro Music: ‘Fields of Russia’ by Mutefish off their album On Draught

Its pretty incredible how accurate the science of astrophysics has gotten. New Horizons actually arrived 72 seconds early after travelling for almost 10 years straight to its destination.

One-year countdown to solar eclipse, August 21, 2017: path of totality overlaid on U.S. population density and interstate map.





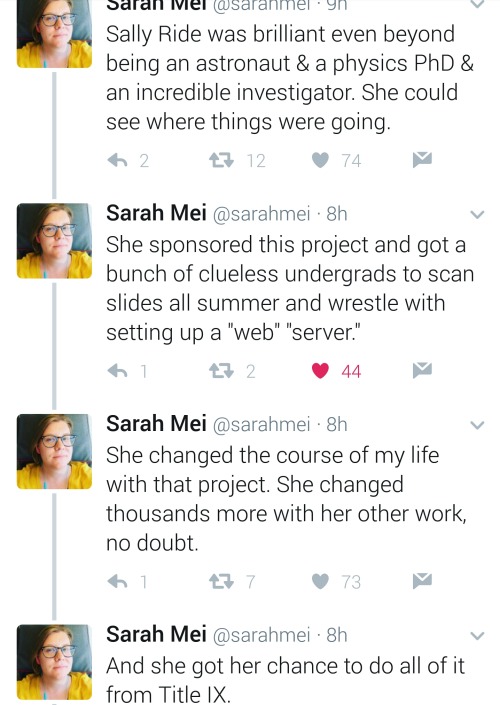
Equal opportunity benefits can be far-reaching
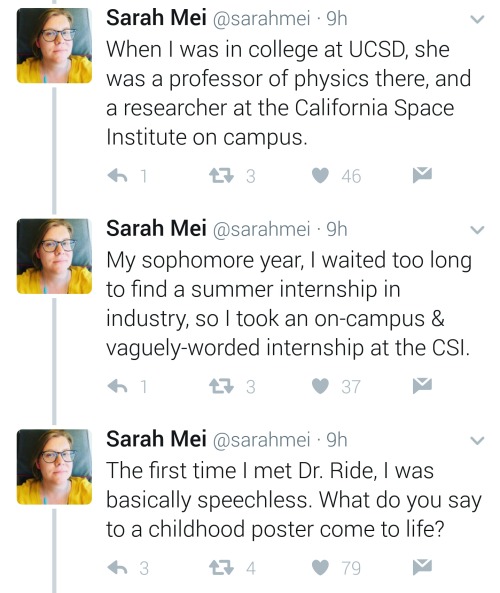
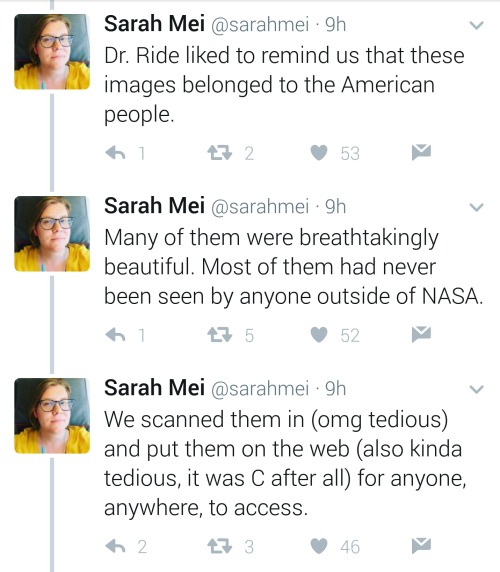
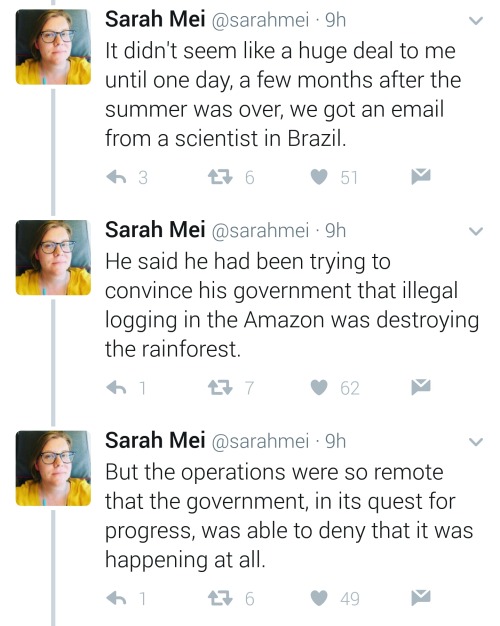
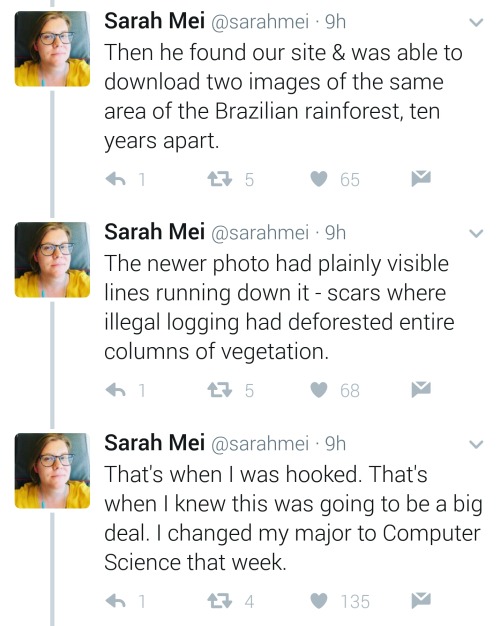
https://twitter.com/sarahmei/status/818682610712866817

Scientists Discover The Oldest, Largest Body Of Water In Existence–In Space
Scientists have found the biggest and oldest reservoir of water ever–so large and so old, it’s almost impossible to describe.
The water is out in space, a place we used to think of as desolate and desert dry, but it’s turning out to be pretty lush.
Researchers found a lake of water so large that it could provide each person on Earth an entire planet’s worth of water–20,000 times over. Yes, so much water out there in space that it could supply each one of us all the water on Earth–Niagara Falls, the Pacific Ocean, the polar ice caps, the puddle in the bottom of the canoe you forgot to flip over–20,000 times over.
The water is in a cloud around a huge black hole that is in the process of sucking in matter and spraying out energy (such an active black hole is called a quasar), and the waves of energy the black hole releases make water by literally knocking hydrogen and oxygen atoms together.
The official NASA news release describes the amount of water as “140 trillion times all the water in the world’s oceans,“ which isn’t particularly helpful, except if you think about it like this.
That one cloud of newly discovered space water vapor could supply 140 trillion planets that are just as wet as Earth is.
Mind you, our own galaxy, the Milky Way, has about 400 billion stars, so if every one of those stars has 10 planets, each as wet as Earth, that’s only 4 trillion planets worth of water.
The new cloud of water is enough to supply 28 galaxies with water.
Truly, that is one swampy patch of intergalactic space.
Equally stunning is the age of the water factory. The two teams of astrophysicists that found the quasar were looking out in space a distance of 12 billion light years. That means they were also looking back in time 12 billion years, to when the universe itself was just 1.6 billion years old. They were watching water being formed at the very start of the known universe, which is to say, water was one of the first substances formed, created in galactic volumes from the earliest time. Given water’s creative power to shape geology, climate and biology, that’s dramatic.
“It’s another demonstration that water is pervasive throughout the universe, even at the very earliest times,” says Matt Bradford, an astrophysicist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory and leader of one of the teams that made the discovery. (The journal article reporting the discovery is titled, without drama, “The Water Vapor Spectrum of APM 08279+5255: X-Ray Heating and Infrared Pumping over Hundreds of Parsecs.”)
It is not as if you’d have to wear foul-weather gear if you could visit this place in space, however. The distances are as mind-bogglingly large as the amount of water being created, so the water vapor is the finest mist–300 trillion times less dense than the air in a typical room.
And it’s not as if this intergalactic water can be of any use to us here on Earth, of course, at least not in the immediate sense. Indeed, the discovery comes as a devastating drought across eastern Africa is endangering the lives of 10 million people in Somalia, Kenya, and Ethiopia. NASA’s water discovery should be a reminder that if we have the sophistication to discover galaxies full of water 12 billion light years away, we should be able to save people just an ocean away from drought-induced starvation.
The NASA announcement is also a reminder how quickly our understanding of the universe is evolving and how much capacity for surprise nature still has for us. There’s water on Mars, there’s water jetting hundreds of miles into space from Enceladus, one of Saturn’s moons, there are icebergs of water hidden in the polar craters of our own Moon. And now it turns out that a single quasar has the ability to manufacture galaxies full of water.
But it was only 40 years ago, in 1969, that scientists first confirmed that water existed anywhere besides Earth.
September 15
This one is technically not yet history, because at the time of posting, the little craft has about half an hour left to go. That said, let’s proceed.
In 2017, NASA’s Cassini space probe ended its twenty-year mission at Saturn. After a nearly-seven-year-long journey there, it orbited the ringed planet for 13 years and just over two months, gathering copious amounts of information about the planet, said rings, and many of its moons. It landed an ESA probe called Huygens on Titan, the first-ever soft landing in the outer Solar System. It discovered lakes, seas, and rivers of methane on Titan, geysers of water erupting from Enceladus (and passed within 50 miles of that moon’s surface), and found gigantic, raging hurricanes at both of Saturn’s poles.
And the images it returned are beautiful enough to make you weep.
On this day in 2017, with the fuel for Cassini’s directional thrusters running low, the probe was de-orbited into the Saturnian atmosphere to prevent any possibility of any contamination of possible biotic environments on Titan or Enceladus. The remaining thruster fuel was used to keep the radio dish pointed towards Earth so the probe could transmit information about the upper atmosphere of Saturn while it was burning up due to atmospheric friction.
This is us at our best. We spent no small amount of money on a nuclear-powered robot, launched it into space, sent it a billion miles away, and worked with it for two decades just to learn about another planet. And when the repeatedly-extended missions were through, we made the little craft sacrifice itself like a samurai, performing its duty as long as it could while it became a shooting star in the Saturnian sky.

Rhea occulting Saturn

Water geysers on Enceladus

Strange Iapetus

Look at this gorgeousness

A gigantic motherfucking storm in Saturn’s northern hemisphere

Tethys

This image is from the surface of a moon of a planet at least 746 million miles away. Sweet lord

Mimas

Vertical structures in the rings. Holy shit

Titan and Dione occulting Saturn, rings visible

Little Daphnis making gravitational ripples in the rings

That’s here. That’s home. That’s all of us that ever lived.

Saturn, backlit

A polar vortex on the gas giant

Icy Enceladus
(All images from NASA/JPL)
-
 miisthios reblogged this · 8 years ago
miisthios reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 hades-huntress liked this · 8 years ago
hades-huntress liked this · 8 years ago -
 spacetimewithstuartgary reblogged this · 8 years ago
spacetimewithstuartgary reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 burninginahellishwonderland-blog liked this · 8 years ago
burninginahellishwonderland-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 catshapeddarkness liked this · 8 years ago
catshapeddarkness liked this · 8 years ago -
 southtxgainer liked this · 8 years ago
southtxgainer liked this · 8 years ago -
 brightmane57 reblogged this · 8 years ago
brightmane57 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 brightmane57 liked this · 8 years ago
brightmane57 liked this · 8 years ago -
 fillthevoid-with-space reblogged this · 8 years ago
fillthevoid-with-space reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 venusian-8 liked this · 8 years ago
venusian-8 liked this · 8 years ago -
 foundbutforeverlost reblogged this · 8 years ago
foundbutforeverlost reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 ikumi-roronoa liked this · 8 years ago
ikumi-roronoa liked this · 8 years ago -
 vastormrunner reblogged this · 8 years ago
vastormrunner reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 aejrogota-infodump reblogged this · 8 years ago
aejrogota-infodump reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 arctic-hands reblogged this · 8 years ago
arctic-hands reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 zivas13-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
zivas13-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 tomcat6335 liked this · 8 years ago
tomcat6335 liked this · 8 years ago -
 sgl14167-blog liked this · 8 years ago
sgl14167-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 i-normally-dont reblogged this · 8 years ago
i-normally-dont reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 i-normally-dont liked this · 8 years ago
i-normally-dont liked this · 8 years ago -
 johnnyreyna liked this · 8 years ago
johnnyreyna liked this · 8 years ago -
 stretchmarx reblogged this · 8 years ago
stretchmarx reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 pprismo liked this · 8 years ago
pprismo liked this · 8 years ago -
 nottagirl liked this · 8 years ago
nottagirl liked this · 8 years ago -
 jenna-dilemme reblogged this · 8 years ago
jenna-dilemme reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 jenna-dilemme liked this · 8 years ago
jenna-dilemme liked this · 8 years ago -
 myceliumnb liked this · 8 years ago
myceliumnb liked this · 8 years ago -
 vidaamorosa-aion reblogged this · 8 years ago
vidaamorosa-aion reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 thestarmystic reblogged this · 8 years ago
thestarmystic reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 transgaygender liked this · 8 years ago
transgaygender liked this · 8 years ago -
 prnh reblogged this · 8 years ago
prnh reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 prnh liked this · 8 years ago
prnh liked this · 8 years ago -
 spaceexp reblogged this · 8 years ago
spaceexp reblogged this · 8 years ago
A podcast project to fill the space in my heart and my time that used to be filled with academic research. In 2018, that space gets filled with... MORE SPACE! Cheerfully researched, painstakingly edited, informal as hell, definitely worth everyone's time.
243 posts











