That Is One Amazing View
That is one amazing view

From the vantage point of the International Space Station, astronaut Shane Kimbrough (@astro_kimbrough) captured this image over the Earth, writing “Looking west over the Red Sea, Saudi Arabia and Egypt. #EarthArt from the amazing space station.”
The space station serves as the world’s laboratory for conducting cutting-edge microgravity research, and is the primary platform for technology development and testing in space to enable human and robotic exploration of destinations beyond low-Earth orbit, including asteroids and Mars.
More Posts from Aliensteel23 and Others
The wonders of Mars
1,000 Days in Orbit: MAVEN’s Top 10 Discoveries at Mars
On June 17, our MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution Mission) will celebrate 1,000 Earth days in orbit around the Red Planet.

Since its launch in November 2013 and its orbit insertion in September 2014, MAVEN has been exploring the upper atmosphere of Mars. MAVEN is bringing insight to how the sun stripped Mars of most of its atmosphere, turning a planet once possibly habitable to microbial life into a barren desert world.

Here’s a countdown of the top 10 discoveries from the mission so far:
10. Unprecedented Ultraviolet View of Mars

Revealing dynamic, previously invisible behavior, MAVEN was able to show the ultraviolet glow from the Martian atmosphere in unprecedented detail. Nightside images showed ultraviolet “nightglow” emission from nitric oxide. Nightglow is a common planetary phenomenon in which the sky faintly glows even in the complete absence of eternal light.
9. Key Features on the Loss of Atmosphere

Some particles from the solar wind are able to penetrate unexpectedly deep into the upper atmosphere, rather than being diverted around the planet by the Martian ionosphere. This penetration is allowed by chemical reactions in the ionosphere that turn the charged particles of the solar wind into neutral atoms that are then able to penetrate deeply.
8. Metal Ions

MAVEN made the first direct observations of a layer of metal ions in the Martian ionosphere, resulting from incoming interplanetary dust hitting the atmosphere. This layer is always present, but was enhanced dramatically by the close passage to Mars of Comet Siding Spring in October 2014.
7. Two New Types of Aurora

MAVEN has identified two new types of aurora, termed “diffuse” and “proton” aurora. Unlike how we think of most aurorae on Earth, these aurorae are unrelated to either a global or local magnetic field.
6. Cause of the Aurorae

These aurorae are caused by an influx of particles from the sun ejected by different types of solar storms. When particles from these storms hit the Martian atmosphere, they can also increase the rate of loss of gas to space, by a factor of ten or more.
5. Complex Interactions with Solar Wind

The interactions between the solar wind and the planet are unexpectedly complex. This results due to the lack of an intrinsic Martian magnetic field and the occurrence of small regions of magnetized crust that can affect the incoming solar wind on local and regional scales. The magnetosphere that results from the interactions varies on short timescales and is remarkably “lumpy” as a result.
4. Seasonal Hydrogen

After investigating the upper atmosphere of the Red Planet for a full Martian year, MAVEN determined that the escaping water does not always go gently into space. The spacecraft observed the full seasonal variation of hydrogen in the upper atmosphere, confirming that it varies by a factor of 10 throughout the year. The escape rate peaked when Mars was at its closest point to the sun and dropped off when the planet was farthest from the sun.
3. Gas Lost to Space

MAVEN has used measurements of the isotopes in the upper atmosphere (atoms of the same composition but having different mass) to determine how much gas has been lost through time. These measurements suggest that 2/3 or more of the gas has been lost to space.
2. Speed of Solar Wind Stripping Martian Atmosphere

MAVEN has measured the rate at which the sun and the solar wind are stripping gas from the top of the atmosphere to space today, along with details of the removal process. Extrapolation of the loss rates into the ancient past – when the solar ultraviolet light and the solar wind were more intense – indicates that large amounts of gas have been lost to space through time.
1. Martian Atmosphere Lost to Space

The Mars atmosphere has been stripped away by the sun and the solar wind over time, changing the climate from a warmer and wetter environment early in history to the cold, dry climate that we see today.
Maven will continue its observations and is now observing a second Martian year, looking at the ways that the seasonal cycles and the solar cycle affect the system.
For more information about MAVEN, visit: www.nasa.gov/maven
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Amazing.
The Moon Just Photobombed NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory
On May 25, 2017, the moon photobombed one of our sun-watching satellites by passing directly between the satellite and the sun.

The Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, orbits Earth and watches the sun nearly 24/7 — except when another body, like the moon, gets in the way. These lunar photobombs are called transits, the generic term for when any celestial body passes in front of another.
Transits are one way we detect distant worlds. When a planet in another star system passes in front of its host star, it blocks some of the star’s light so the star appears slightly dimmer. By monitoring changes in a star’s light over time, scientists can deduce the presence of a planet, and even determine what its atmosphere is like. This method has been used to discover thousands of planets, including the TRAPPIST-1 planets.

SDO sees lunar transits about twice a year, and this one lasted about an hour with the moon covering about 89 percent of the sun at the peak of its journey across the sun’s face.
When they’re seen from Earth, we call lunar transits by another name: eclipses.

Solar eclipses are just a special kind of transit where the moon blocks all or part of our view of the sun. Since SDO’s view of the sun was only partially blocked, it saw a partial eclipse. Later this year, on Aug. 21, a total eclipse will be observable from the ground: The moon will completely block the sun’s face in some parts of the US, creating a total solar eclipse on a 70-mile-wide stretch of land, called the path of totality, that runs from Oregon to South Carolina.
Throughout the rest of North America — and even in parts of South America, Africa, Europe and Asia — the moon will partially obscure the sun, creating a partial eclipse. SDO will also witness this partial eclipse.

Total solar eclipses are incredible, cosmic coincidences: The sun is about 400 times wider than the moon, but it also happens to be 400 times farther away, so the sun and moon appear to be the same size in our sky. This allows the moon to completely block the sun when they line up just right.

Within the path of totality, the moon completely obscures the sun’s bright face, revealing the comparatively faint corona — the sun’s pearly-white outer atmosphere.

It’s essential to observe eye safety during an eclipse. You must use proper eclipse glasses or an indirect viewing method when any part of the sun’s surface is exposed, whether during the partial phases of an eclipse, or just on a regular day. If you’re in the path of totality, you may look at the eclipse ONLY during the brief moments of totality.

A total solar eclipse is one of nature’s most awe-inspiring sights, so make your plans now for August 21! You’ll also be able to see the eclipse cross the country that day through the eyes of NASA – including views of the partial eclipse from SDO – on NASA TV and at nasa.gov.
Learn more about the August eclipse — including where, when, and how to safely see it — at eclipse2017.nasa.gov and follow along on Twitter @NASASun.
An amazing view of the cosmos.
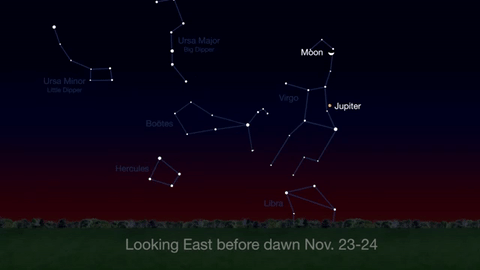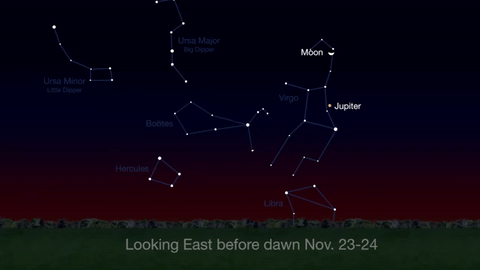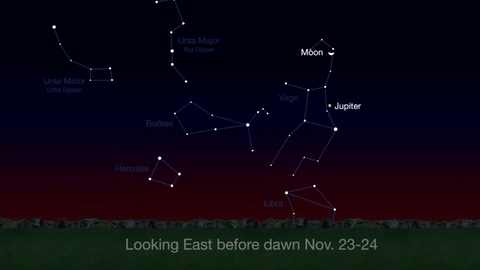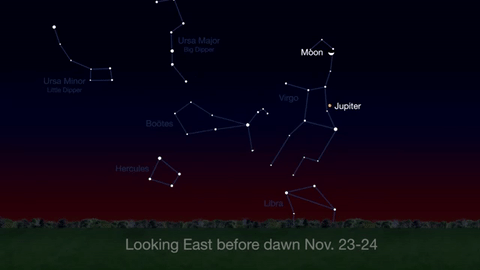
What’s Up for November 2016
What’s Up for November: Venus at sunset, Jupiter at dawn, your last evening glimpse of Saturn until spring, and more meteors!

Through November 3, catch glimpses of a gibbous Venus, a crescent moon and ringed Saturn in the southwest sky just after sunset.

Wake up before sunrise every day this month to see Jupiter just above Spica, the brightest star in the constellation Virgo, shining in the east-southeast sky.
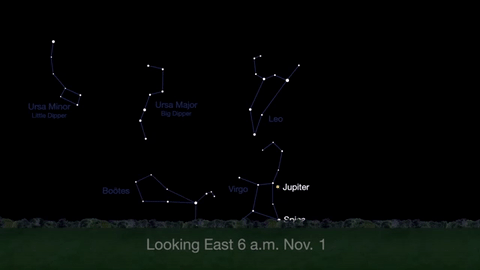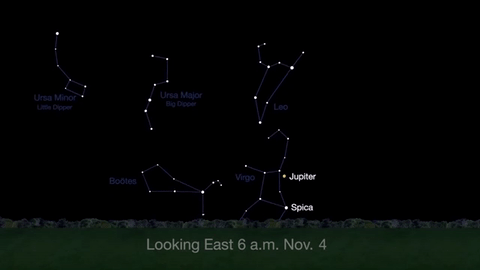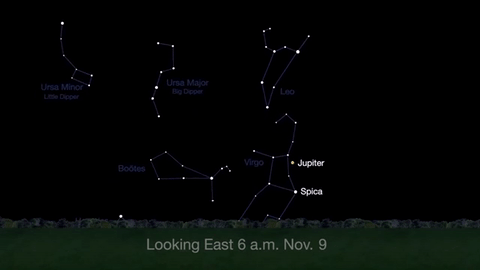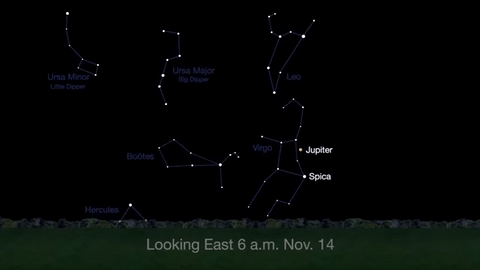
Just before dawn on November 23-24, see the waning crescent moon just above Jupiter.
November is a great time to see the constellation Ceres as it glides past Cetus, the Whale and you will be able to see the dwarf planet move relative to the background stars, but you’ll need a telescope for this one.
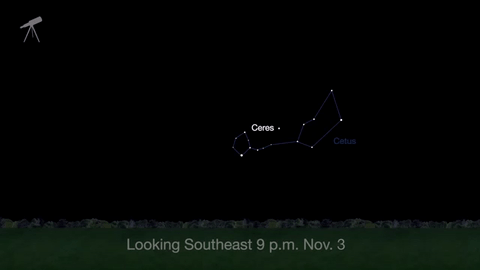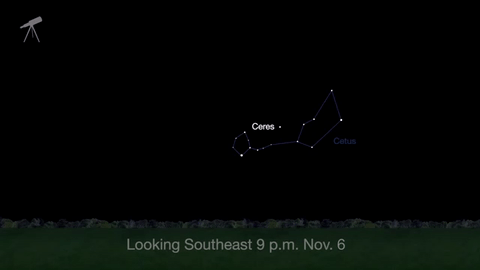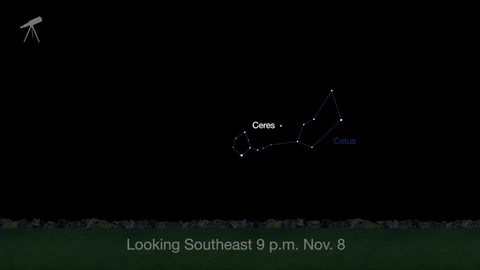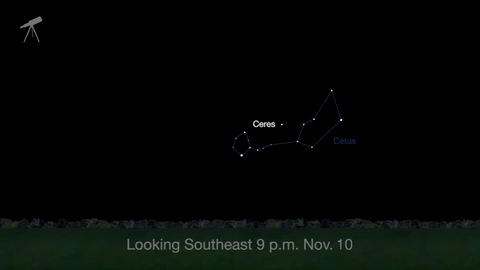
This month, just like last month, there will be three meteor showers–the Northern Tuarids, the Leonids and the November Orionids.

Watch the full November “What’s Up" video for more:
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
“blatherin blatherskite!”

Gizmoduck is on the town! Love the Ducktales reboot, the designs, the production quality, and the AMAZING voice cast!!!
One day humans will live on another earth-like planet that is safe for us.
A Space Odyssey: 21 Years of Searching for Another Earth
There are infinite worlds both like and unlike this world of ours. We must believe that in all worlds there are living creatures and plants and other things we see in this world. – Epicurus, c. 300 B.C.

Are we alone? Are there other planets like ours? Does life exist elsewhere in the universe?
These are questions mankind has been asking for years—since the time of Greek philosophers. But for years, those answers have been elusive, if not impossible to find.
The month of October marks the 21st anniversary of the discovery of the first planet orbiting another sun-like star (aka. an exoplanet), 51 Pegasi b or “Dimidium.” Its existence proved that there were other planets in the galaxy outside our solar system.*

Even more exciting is the fact that astronomers are in hot pursuit of the first discovery of an Earth-like exoplanet orbiting a star other than the sun. The discovery of the so-called “blue dot” could redefine our understanding of the universe and our place in it, especially if astronomers can also find signs that life exists on that planet’s surface.
Astronomy is entering a fascinating era where we’re beginning to answer tantalizing questions that people have pondered for thousands of years.

Are we alone?
In 1584, when the Catholic monk Giordano Bruno asserted that there were “countless suns and countless earths all rotating around their suns,” he was accused of heresy.

But even in Bruno’s time, the idea of a plurality of worlds wasn’t entirely new. As far back as ancient Greece, humankind has speculated that other solar systems might exist and that some would harbor other forms of life.
Still, centuries passed without convincing proof of planets around even the nearest stars.

Are there other planets like ours?
The first discovery of a planet orbiting a star similar to the sun came in 1995. The Swiss team of Michel Mayor and Didier Queloz of Geneva announced that they had found a rapidly orbiting gas world located blisteringly close to the star 51 Pegasi.

This announcement marked the beginning of a flood of discoveries. Exotic discoveries transformed science fiction into science fact:
a pink planet
worlds with two or even three suns
a gas giant as light as Styrofoam
a world in the shape of an egg
a lava planet

But what about another Earth?
Our first exoplanet mission**, Kepler, launched in 2009 and revolutionized how astronomers understand the universe and our place in it. Kepler was built to answer the question—how many habitable planets exist in our galaxy?

And it delivered: Thousands of planet discoveries poured in, providing statistical proof that one in five sun-like stars (yellow, main-sequence G type) harbor Earth-sized planets orbiting in their habitable zones– where it’s possible liquid water could exist on their surface.

Now, our other missions like the Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes point at promising planetary systems (TRAPPIST-1) to figure out whether they are suitable for life as we know it.

Does life exist elsewhere in the universe?
Now that exoplanet-hunting is a mainstream part of astronomy, the race is on to build instruments that can find more and more planets, especially worlds that could be like our own.

Our Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), set for launch in 2017-2018, will look for super-Earth and Earth-sized planets around stars much closer to home. TESS will find new planets the same way Kepler does—via the transit method—but will cover 400 times the sky area.

The James Webb Space Telescope, to launch in 2018, wil be our most powerful space telescope to date. Webb will use its spectrograph to look at exoplanet atmospheres, searching for signs of life.

We still don’t know where or which planets are in the habitable zones of the nearest stars to Earth. Searching out our nearest potentially habitable neighbors will be the next chapter in this unfolding story.

*The first true discovery of extrasolar planets was actually a triplet of dead worlds orbiting the remains of an exploded star, called a pulsar star. Two of three were found by Dr. Alexander Wolszczan in 1992– a full three years before Dimidium’s discovery. But because they are so strange, and can’t support life as we know it, most scientists would reserve the “first” designation for a planet orbiting a normal star.
** The French CoRoT mission, launched in 2006, was the first dedicated exoplanet space mission. It has contributed dozens of confirmed exoplanets to the ranks and boasts a roster of some of the most well-studied planets outside our solar system.
To stay up-to-date on our latest exoplanet discoveries, visit: https://exoplanets.nasa.gov
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
New things in space
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Our Dawn mission to the asteroid belt is no ordinary deep space expedition.
Instead of traditional chemical rockets, the spacecraft uses sophisticated ion engines for propulsion. This enabled Dawn to become the first mission to orbit not one, but two different worlds — first the giant asteroid Vesta and now the dwarf planet Ceres. Vesta and Ceres formed early in the solar system’s history, and by studying them, the mission is helping scientists go back in time to the dawn of the planets. To mark a decade since Dawn was launched on Sept. 27, 2007, here are 10 things to know about this trailblazing mission.
1. Ion Engines: Not Just for Sci-Fi Anymore

Most rocket engines use chemical reactions for propulsion, which tend to be powerful but short-lived. Dawn’s futuristic, hyper-efficient ion propulsion system works by using electricity to accelerate ions (charged particles) from xenon fuel to a speed seven to 10 times that of chemical engines. Ion engines accelerate the spacecraft slowly, but they’re very thrifty with fuel, using just milligrams of xenon per second (about 10 ounces over 24 hours) at maximum thrust. Without its ion engines, Dawn could not have carried enough fuel to go into orbit around two different solar system bodies. Try your hand at an interactive ion engine simulation.
2. Time Capsules

Scientists have long wanted to study Vesta and Ceres up close. Vesta is a large, complex and intriguing asteroid. Ceres is the largest object in the entire asteroid belt, and was once considered a planet in its own right after it was discovered in 1801. Vesta and Ceres have significant differences, but both are thought to have formed very early in the history of the solar system, harboring clues about how planets are constructed. Learn more about Ceres and Vesta—including why we have pieces of Vesta here on Earth.
3. Portrait of a Dwarf Planet

This view of Ceres built from Dawn photos is centered on Occator Crater, home of the famous “bright spots.” The image resolution is about 460 feet (140 meters) per pixel.
Take a closer look.
4. What’s in a Name?
Craters on Ceres are named for agricultural deities from all over the world, and other features carry the names of agricultural festivals. Ceres itself was named after the Roman goddess of corn and harvests (that’s also where the word “cereal” comes from). The International Astronomical Union recently approved 25 new Ceres feature names tied to the theme of agricultural deities. Jumi, for example, is the Latvian god of fertility of the field. Study the full-size map.
5. Landslides or Ice Slides?

Thanks to Dawn, evidence is mounting that Ceres hides a significant amount of water ice. A recent study adds to this picture, showing how ice may have shaped the variety of landslides seen on Ceres today.
6. The Lonely Mountain

Ahuna Mons, a 3-mile-high (5-kilometer-high) mountain, puzzled Ceres explorers when they first found it. It rises all alone above the surrounding plains. Now scientists think it is likely a cryovolcano — one that erupts a liquid made of volatiles such as water, instead of rock. “This is the only known example of a cryovolcano that potentially formed from a salty mud mix, and that formed in the geologically recent past,” one researcher said. Learn more.
7. Shining a Light on the Bright Spots

The brightest area on Ceres, located in the mysterious Occator Crater, has the highest concentration of carbonate minerals ever seen outside Earth, according to studies from Dawn scientists. Occator is 57 miles (92 kilometers) wide, with a central pit about 6 miles (10 kilometers) wide. The dominant mineral of this bright area is sodium carbonate, a kind of salt found on Earth in hydrothermal environments. This material appears to have come from inside Ceres, and this upwelling suggests that temperatures inside Ceres are warmer than previously believed. Even more intriguingly, the results suggest that liquid water may have existed beneath the surface of Ceres in recent geological time. The salts could be remnants of an ocean, or localized bodies of water, that reached the surface and then froze millions of years ago. See more details.
8. Captain’s Log
Dawn’s chief engineer and mission director, Marc Rayman, provides regular dispatches about Dawn’s work in the asteroid belt. Catch the latest updates here.
9. Eyes on Dawn
Another cool way to retrace Dawn’s decade-long flight is to download NASA’s free Eyes on the Solar System app, which uses real data to let you go to any point in the solar system, or ride along with any spacecraft, at any point in time—all in 3-D.
10. No Stamp Required

Send a postcard from one of these three sets of images that tell the story of dwarf planet Ceres, protoplanet Vesta, and the Dawn mission overall.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Awesome
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Learn the latest on Cassini’s Grand Finale, Pluto, Hubble Space Telescope and the Red Planet.
1. Cassini’s Grand Finale

After more than 12 years at Saturn, our Cassini mission has entered the final year of its epic voyage to the giant planet and its family of moons. But the journey isn’t over. The upcoming months will be like a whole new mission, with lots of new science and a truly thrilling ride in the unexplored space near the rings. Later this year, the spacecraft will fly repeatedly just outside the rings, capturing the closest views ever. Then, it will actually orbit inside the gap between the rings and the planet’s cloud tops.
Get details on Cassini’s final mission
The von Kármán Lecture Series: 2016
2. Chandra X-Rays Pluto

As the New Horizon’s mission headed to Pluto, our Chandra X-Ray Observatory made the first detection of the planet in X-rays. Chandra’s observations offer new insight into the space environment surrounding the largest and best-known object in the solar system’s outermost regions.
See Pluto’s X-Ray
3. … And Then Pluto Painted the Town Red

When the cameras on our approaching New Horizons spacecraft first spotted the large reddish polar region on Pluto’s largest moon, Charon, mission scientists knew two things: they’d never seen anything like it before, and they couldn’t wait to get the story behind it. After analyzing the images and other data that New Horizons has sent back from its July 2015 flight through the Pluto system, scientists think they’ve solved the mystery. Charon’s polar coloring comes from Pluto itself—as methane gas that escapes from Pluto’s atmosphere and becomes trapped by the moon’s gravity and freezes to the cold, icy surface at Charon’s pole.
Get the details
4. Pretty as a Postcard

The famed red-rock deserts of the American Southwest and recent images of Mars bear a striking similarity. New color images returned by our Curiosity Mars rover reveal the layered geologic past of the Red Planet in stunning detail.
More images
5. Things Fall Apart

Our Hubble Space Telescope recently observed a comet breaking apart. In a series of images taken over a three-day span in January 2016, Hubble captured images of 25 building-size blocks made of a mixture of ice and dust drifting away from the comet. The resulting debris is now scattered along a 3,000-mile-long trail, larger than the width of the continental U.S.
Learn more
Discover the full list of 10 things to know about our solar system this week HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
-
 boldog-tudatlansag liked this · 4 years ago
boldog-tudatlansag liked this · 4 years ago -
 weirywolf liked this · 5 years ago
weirywolf liked this · 5 years ago -
 galestral liked this · 6 years ago
galestral liked this · 6 years ago -
 jadeblackwellsblog reblogged this · 6 years ago
jadeblackwellsblog reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 swrilofsummerbreeze-realitycheck reblogged this · 7 years ago
swrilofsummerbreeze-realitycheck reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 marko-man reblogged this · 7 years ago
marko-man reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 artimies6 reblogged this · 7 years ago
artimies6 reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 colorfulbirdtree-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
colorfulbirdtree-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 colorfulbirdtree-blog liked this · 7 years ago
colorfulbirdtree-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 holometabolism reblogged this · 7 years ago
holometabolism reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 24h7 reblogged this · 7 years ago
24h7 reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 acommonanomaly reblogged this · 8 years ago
acommonanomaly reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 acommonanomaly liked this · 8 years ago
acommonanomaly liked this · 8 years ago -
 across-the-cypress-trees reblogged this · 8 years ago
across-the-cypress-trees reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 wanderontherocks reblogged this · 8 years ago
wanderontherocks reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 h0miecidal reblogged this · 8 years ago
h0miecidal reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 clairvoyant-fry-cook reblogged this · 8 years ago
clairvoyant-fry-cook reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 crawfordtheturtle reblogged this · 8 years ago
crawfordtheturtle reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 tumbleweed-chaser liked this · 8 years ago
tumbleweed-chaser liked this · 8 years ago -
 spuddymuffin liked this · 8 years ago
spuddymuffin liked this · 8 years ago -
 sylvermyth reblogged this · 8 years ago
sylvermyth reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 xpertghosts liked this · 8 years ago
xpertghosts liked this · 8 years ago -
 incessantthinkingkid-blog liked this · 8 years ago
incessantthinkingkid-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 unclaimed-username reblogged this · 8 years ago
unclaimed-username reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 always-smi1e reblogged this · 8 years ago
always-smi1e reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 24h7 liked this · 8 years ago
24h7 liked this · 8 years ago -
 jeza-jezaro reblogged this · 8 years ago
jeza-jezaro reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 g00dg0lliemissm0llie liked this · 8 years ago
g00dg0lliemissm0llie liked this · 8 years ago -
 ileref reblogged this · 8 years ago
ileref reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 coeluscoeli liked this · 8 years ago
coeluscoeli liked this · 8 years ago -
 ca00-blog liked this · 8 years ago
ca00-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 but-dont-we-all-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
but-dont-we-all-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 tchintchun reblogged this · 8 years ago
tchintchun reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 solrift reblogged this · 8 years ago
solrift reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 maybecomedy liked this · 8 years ago
maybecomedy liked this · 8 years ago -
 themapletreesremember reblogged this · 8 years ago
themapletreesremember reblogged this · 8 years ago


