One Day Humans Will Live On Another Earth-like Planet That Is Safe For Us.
One day humans will live on another earth-like planet that is safe for us.
A Space Odyssey: 21 Years of Searching for Another Earth
There are infinite worlds both like and unlike this world of ours. We must believe that in all worlds there are living creatures and plants and other things we see in this world. – Epicurus, c. 300 B.C.

Are we alone? Are there other planets like ours? Does life exist elsewhere in the universe?
These are questions mankind has been asking for years—since the time of Greek philosophers. But for years, those answers have been elusive, if not impossible to find.
The month of October marks the 21st anniversary of the discovery of the first planet orbiting another sun-like star (aka. an exoplanet), 51 Pegasi b or “Dimidium.” Its existence proved that there were other planets in the galaxy outside our solar system.*

Even more exciting is the fact that astronomers are in hot pursuit of the first discovery of an Earth-like exoplanet orbiting a star other than the sun. The discovery of the so-called “blue dot” could redefine our understanding of the universe and our place in it, especially if astronomers can also find signs that life exists on that planet’s surface.
Astronomy is entering a fascinating era where we’re beginning to answer tantalizing questions that people have pondered for thousands of years.

Are we alone?
In 1584, when the Catholic monk Giordano Bruno asserted that there were “countless suns and countless earths all rotating around their suns,” he was accused of heresy.

But even in Bruno’s time, the idea of a plurality of worlds wasn’t entirely new. As far back as ancient Greece, humankind has speculated that other solar systems might exist and that some would harbor other forms of life.
Still, centuries passed without convincing proof of planets around even the nearest stars.

Are there other planets like ours?
The first discovery of a planet orbiting a star similar to the sun came in 1995. The Swiss team of Michel Mayor and Didier Queloz of Geneva announced that they had found a rapidly orbiting gas world located blisteringly close to the star 51 Pegasi.

This announcement marked the beginning of a flood of discoveries. Exotic discoveries transformed science fiction into science fact:
a pink planet
worlds with two or even three suns
a gas giant as light as Styrofoam
a world in the shape of an egg
a lava planet

But what about another Earth?
Our first exoplanet mission**, Kepler, launched in 2009 and revolutionized how astronomers understand the universe and our place in it. Kepler was built to answer the question—how many habitable planets exist in our galaxy?

And it delivered: Thousands of planet discoveries poured in, providing statistical proof that one in five sun-like stars (yellow, main-sequence G type) harbor Earth-sized planets orbiting in their habitable zones– where it’s possible liquid water could exist on their surface.

Now, our other missions like the Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes point at promising planetary systems (TRAPPIST-1) to figure out whether they are suitable for life as we know it.

Does life exist elsewhere in the universe?
Now that exoplanet-hunting is a mainstream part of astronomy, the race is on to build instruments that can find more and more planets, especially worlds that could be like our own.

Our Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), set for launch in 2017-2018, will look for super-Earth and Earth-sized planets around stars much closer to home. TESS will find new planets the same way Kepler does—via the transit method—but will cover 400 times the sky area.

The James Webb Space Telescope, to launch in 2018, wil be our most powerful space telescope to date. Webb will use its spectrograph to look at exoplanet atmospheres, searching for signs of life.

We still don’t know where or which planets are in the habitable zones of the nearest stars to Earth. Searching out our nearest potentially habitable neighbors will be the next chapter in this unfolding story.

*The first true discovery of extrasolar planets was actually a triplet of dead worlds orbiting the remains of an exploded star, called a pulsar star. Two of three were found by Dr. Alexander Wolszczan in 1992– a full three years before Dimidium’s discovery. But because they are so strange, and can’t support life as we know it, most scientists would reserve the “first” designation for a planet orbiting a normal star.
** The French CoRoT mission, launched in 2006, was the first dedicated exoplanet space mission. It has contributed dozens of confirmed exoplanets to the ranks and boasts a roster of some of the most well-studied planets outside our solar system.
To stay up-to-date on our latest exoplanet discoveries, visit: https://exoplanets.nasa.gov
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Aliensteel23 and Others
Love it! More like the original version

NGL, Reboot Upgrade looks sick with normal colors.
You gotta love gem fusions.
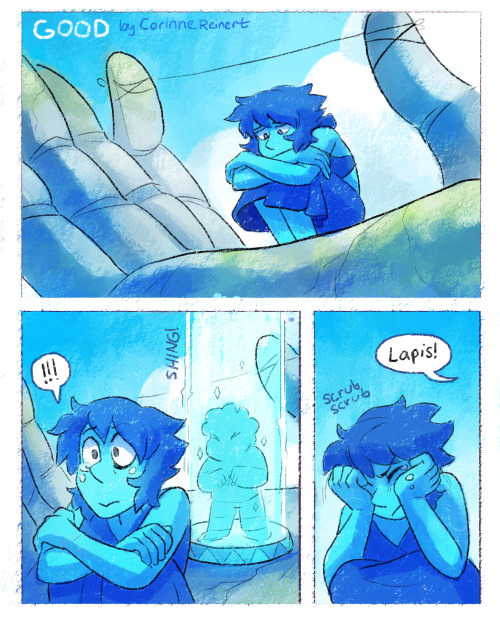











Chalcedony !
The wonders of Mars
1,000 Days in Orbit: MAVEN’s Top 10 Discoveries at Mars
On June 17, our MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution Mission) will celebrate 1,000 Earth days in orbit around the Red Planet.

Since its launch in November 2013 and its orbit insertion in September 2014, MAVEN has been exploring the upper atmosphere of Mars. MAVEN is bringing insight to how the sun stripped Mars of most of its atmosphere, turning a planet once possibly habitable to microbial life into a barren desert world.

Here’s a countdown of the top 10 discoveries from the mission so far:
10. Unprecedented Ultraviolet View of Mars

Revealing dynamic, previously invisible behavior, MAVEN was able to show the ultraviolet glow from the Martian atmosphere in unprecedented detail. Nightside images showed ultraviolet “nightglow” emission from nitric oxide. Nightglow is a common planetary phenomenon in which the sky faintly glows even in the complete absence of eternal light.
9. Key Features on the Loss of Atmosphere

Some particles from the solar wind are able to penetrate unexpectedly deep into the upper atmosphere, rather than being diverted around the planet by the Martian ionosphere. This penetration is allowed by chemical reactions in the ionosphere that turn the charged particles of the solar wind into neutral atoms that are then able to penetrate deeply.
8. Metal Ions

MAVEN made the first direct observations of a layer of metal ions in the Martian ionosphere, resulting from incoming interplanetary dust hitting the atmosphere. This layer is always present, but was enhanced dramatically by the close passage to Mars of Comet Siding Spring in October 2014.
7. Two New Types of Aurora

MAVEN has identified two new types of aurora, termed “diffuse” and “proton” aurora. Unlike how we think of most aurorae on Earth, these aurorae are unrelated to either a global or local magnetic field.
6. Cause of the Aurorae

These aurorae are caused by an influx of particles from the sun ejected by different types of solar storms. When particles from these storms hit the Martian atmosphere, they can also increase the rate of loss of gas to space, by a factor of ten or more.
5. Complex Interactions with Solar Wind

The interactions between the solar wind and the planet are unexpectedly complex. This results due to the lack of an intrinsic Martian magnetic field and the occurrence of small regions of magnetized crust that can affect the incoming solar wind on local and regional scales. The magnetosphere that results from the interactions varies on short timescales and is remarkably “lumpy” as a result.
4. Seasonal Hydrogen

After investigating the upper atmosphere of the Red Planet for a full Martian year, MAVEN determined that the escaping water does not always go gently into space. The spacecraft observed the full seasonal variation of hydrogen in the upper atmosphere, confirming that it varies by a factor of 10 throughout the year. The escape rate peaked when Mars was at its closest point to the sun and dropped off when the planet was farthest from the sun.
3. Gas Lost to Space

MAVEN has used measurements of the isotopes in the upper atmosphere (atoms of the same composition but having different mass) to determine how much gas has been lost through time. These measurements suggest that 2/3 or more of the gas has been lost to space.
2. Speed of Solar Wind Stripping Martian Atmosphere

MAVEN has measured the rate at which the sun and the solar wind are stripping gas from the top of the atmosphere to space today, along with details of the removal process. Extrapolation of the loss rates into the ancient past – when the solar ultraviolet light and the solar wind were more intense – indicates that large amounts of gas have been lost to space through time.
1. Martian Atmosphere Lost to Space

The Mars atmosphere has been stripped away by the sun and the solar wind over time, changing the climate from a warmer and wetter environment early in history to the cold, dry climate that we see today.
Maven will continue its observations and is now observing a second Martian year, looking at the ways that the seasonal cycles and the solar cycle affect the system.
For more information about MAVEN, visit: www.nasa.gov/maven
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Amazing.
The Moon Just Photobombed NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory
On May 25, 2017, the moon photobombed one of our sun-watching satellites by passing directly between the satellite and the sun.

The Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, orbits Earth and watches the sun nearly 24/7 — except when another body, like the moon, gets in the way. These lunar photobombs are called transits, the generic term for when any celestial body passes in front of another.
Transits are one way we detect distant worlds. When a planet in another star system passes in front of its host star, it blocks some of the star’s light so the star appears slightly dimmer. By monitoring changes in a star’s light over time, scientists can deduce the presence of a planet, and even determine what its atmosphere is like. This method has been used to discover thousands of planets, including the TRAPPIST-1 planets.

SDO sees lunar transits about twice a year, and this one lasted about an hour with the moon covering about 89 percent of the sun at the peak of its journey across the sun’s face.
When they’re seen from Earth, we call lunar transits by another name: eclipses.

Solar eclipses are just a special kind of transit where the moon blocks all or part of our view of the sun. Since SDO’s view of the sun was only partially blocked, it saw a partial eclipse. Later this year, on Aug. 21, a total eclipse will be observable from the ground: The moon will completely block the sun’s face in some parts of the US, creating a total solar eclipse on a 70-mile-wide stretch of land, called the path of totality, that runs from Oregon to South Carolina.
Throughout the rest of North America — and even in parts of South America, Africa, Europe and Asia — the moon will partially obscure the sun, creating a partial eclipse. SDO will also witness this partial eclipse.

Total solar eclipses are incredible, cosmic coincidences: The sun is about 400 times wider than the moon, but it also happens to be 400 times farther away, so the sun and moon appear to be the same size in our sky. This allows the moon to completely block the sun when they line up just right.

Within the path of totality, the moon completely obscures the sun’s bright face, revealing the comparatively faint corona — the sun’s pearly-white outer atmosphere.

It’s essential to observe eye safety during an eclipse. You must use proper eclipse glasses or an indirect viewing method when any part of the sun’s surface is exposed, whether during the partial phases of an eclipse, or just on a regular day. If you’re in the path of totality, you may look at the eclipse ONLY during the brief moments of totality.

A total solar eclipse is one of nature’s most awe-inspiring sights, so make your plans now for August 21! You’ll also be able to see the eclipse cross the country that day through the eyes of NASA – including views of the partial eclipse from SDO – on NASA TV and at nasa.gov.
Learn more about the August eclipse — including where, when, and how to safely see it — at eclipse2017.nasa.gov and follow along on Twitter @NASASun.
Galacticly awesome
Living and Working Aboard Station
Join us on Facebook Live for a conversation with astronaut Kate Rubins and the director of the National Institutes for Health on Tuesday, October 18 at 11:15 a.m. ET.
Astronaut Kate Rubins has conducted out of this world research aboard Earth’s only orbiting laboratory. During her time aboard the International Space Station, she became the first person to sequence DNA in space. On Tuesday, she’ll be live on Facebook with National Institute of Health director Francis Collins, who led the effort to map the human genome. You can submit questions for Kate using the hashtag #SpaceChat on Twitter, or during the live event. Here’s a primer on the science this PhD astronaut has been conducting to help inspire your questions:

Kate has a background in genomics (a branch of molecular genetics that deals with the study of genomes,specifically the identification and sequencing of their constituent genes and the application of this knowledge in medicine, pharmacy,agriculture, and other fields). When she began her tenure on the station, zero base pairs of DNA had been sequenced in space. Within just a few weeks, she and the Biomolecule Sequencer team had sequenced their one billionth base of DNA aboard the orbital platform.
“I [have a] genomics background, [so] I get really excited about that kind of stuff,” Rubins said in a downlink shortly after reaching the one billion base pairs sequenced goal.
Learn more about this achievement:
+First DNA Sequencing in Space a Game Changer
+Science in Short: One Billion Base Pairs Sequenced
Why is DNA Sequencing in Space a Big Deal?
A space-based DNA sequencer could identify microbes, diagnose diseases and understand crew member health, and potentially help detect DNA-based life elsewhere in the solar system.
+Why Sequencing DNA in Space is a Big Deal
https://youtu.be/1N0qm8HcFRI
Miss the Reddit AMA on the subject? Here’s a transcript:
+NASA AMA: We just sequenced DNA in space for the first time. Ask us anything!
NASA and Its Partnerships

We’re not doing this alone. Just like the DNA sequencing was a collaborative project with industry, so is the Eli Lilly Hard to Wet Surfaces investigation, which is a partnership between CASIS and Eli Lilly Co. In this experiment aboard the station, astronauts will study how certain materials used in the pharmaceutical industry dissolve in water while in microgravity. Results from this investigation could help improve the design of tablets that dissolve in the body to deliver drugs, thereby improving drug design for medicines used in space and on Earth. Learn more about what we and our partners are doing:
+Eli Lilly Hard to Wet Surfaces – been happening the last week and a half or so
Researchers to Test How Solids Dissolve in Space to Design Better Tablets and Pills on Earth
With our colleagues at the Stanford University School of Medicine, we’re also investigating the effects of spaceflight on stem cell-derived heart cells, specifically how heart muscle tissue, contracts, grows and changes in microgravity and how those changes vary between subjects. Understanding how heart muscle cells change in space improves efforts for studying disease, screening drugs and conducting cell replacement therapy for future space missions. Learn more:
+Heart Cells
+Weekly Recap From the Expedition Lead Scientist for Aug. 18, 2016
It’s Not Just Medicine

Kate and her crew mates have also worked on the combustion experiments.
Kate has also worked on the Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM), an experimental expandable capsule that docks with the station. As we work on our Journey to Mars, future space habitats are a necessity. BEAM, designed for Mars or other destinations, is a lightweight and relatively simple to construct solution. Kate has recently examined BEAM, currently attached to the station, to take measurements and install sensors.

Kate recently performed a harvest of the Plant RNA Regulation experiment, by removing seed cassettes and stowing them in cold stowage.

The Plant RNA Regulation investigation studies the first steps of gene expression involved in development of roots and shoots. Scientists expect to find new molecules that play a role in how plants adapt and respond to the microgravity environment of space, which provides new insight into growing plants for food and oxygen supplies on long-duration missions. Read more about the experiment:
+Plant RNA Harvest
NASA Astronaut Kate Rubins is participating in several investigations examining changes in her body as a result of living in space. Some of these changes are similar to issues experienced by our elderly on Earth; for example, bone loss (osteoporosis), cardiovascular deconditioning, immune dysfunction, and muscle atrophy. Understanding these changes and how to prevent them in astronauts off the Earth may help improve health for all of us on the Earth. In additional, the crew aboard station is also working on more generalized studies of aging.
+ Study of the effects of aging on C. elegans, a model organism for a range of biological studies.
Now I've seen everything
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Making every night science movie night with these amazing videos.

1. Pure Beauty
Our star sprouting coronal loops courtesy of the NASA sun team. See the full video: https://go.nasa.gov/2p47Lt2

2. Where’s the last place you’d expect to find enough ice to bury a city?
Answer: Mercury, the closest planet to the sun. Watch the video: https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/11184

3. The Mars Fleet
Only Earth has more satellites studying it. Full video: https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/4414

4. A Star-Studded Cast
Check out NASA’s satellite fleet of Earth observers. See the video: https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/12586

5. Jupiter in Ultra HD
Thanks, Hubble Space Telescope! See the video: https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/12021

6. A Tear Jerker
Our Cassini spacecraft starts her 4.5-month Grand Finale this week. Full video: https://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov/resources/7628

7. Faster Than the Speed of Sound
Winds on Neptune travel faster than the speed of sound. Full video: https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/11349

8. A Musical Number
This one features the planet Uranus doing pop and lock. Full video: https://youtu.be/CWuWoiHmXUs

9. Up Close and Personal
Thanks to our New Horizons mission, we’ve been able to get up close and with Pluto. Full video: https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/12080

10: The Treasure Trove
TRAPPIST-1 is a treasure trove of seven Earth-sized planets orbiting a distant star. Full video: https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/video/details.php?id=1459
Discover more lists of 10 things to know about our solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
An amazing view of the cosmos.
What’s Up for November 2016
What’s Up for November: Venus at sunset, Jupiter at dawn, your last evening glimpse of Saturn until spring, and more meteors!

Through November 3, catch glimpses of a gibbous Venus, a crescent moon and ringed Saturn in the southwest sky just after sunset.

Wake up before sunrise every day this month to see Jupiter just above Spica, the brightest star in the constellation Virgo, shining in the east-southeast sky.
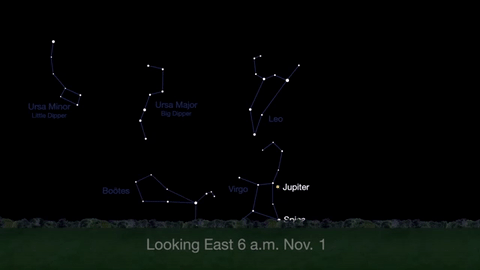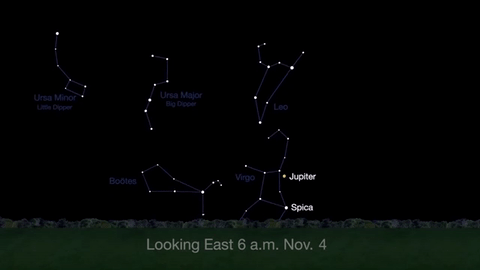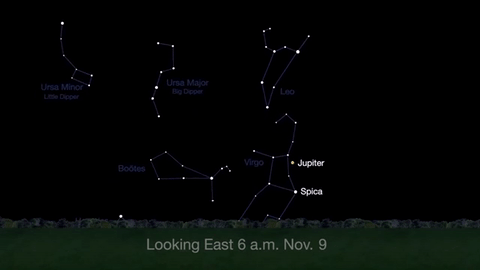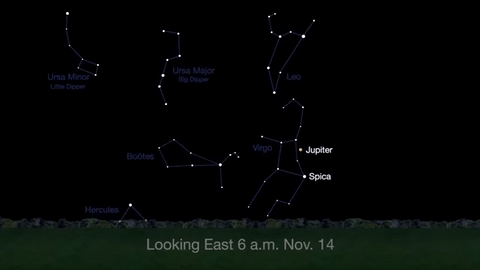
Just before dawn on November 23-24, see the waning crescent moon just above Jupiter.
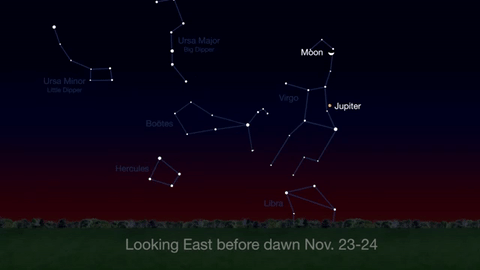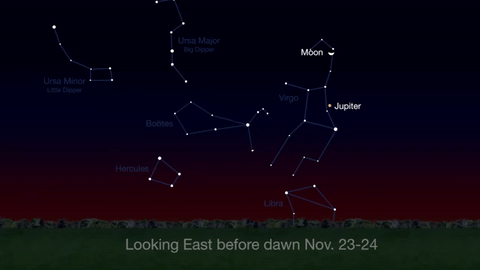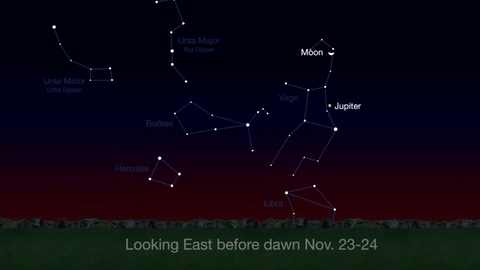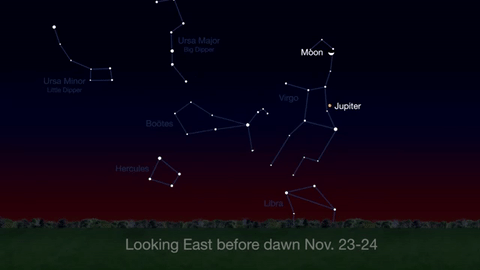
November is a great time to see the constellation Ceres as it glides past Cetus, the Whale and you will be able to see the dwarf planet move relative to the background stars, but you’ll need a telescope for this one.
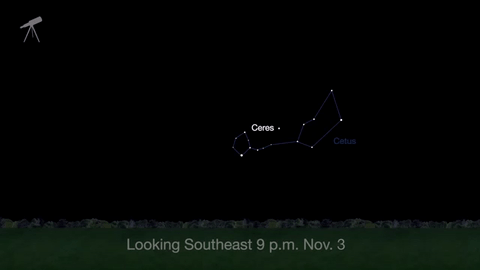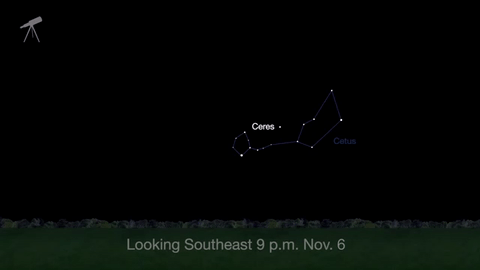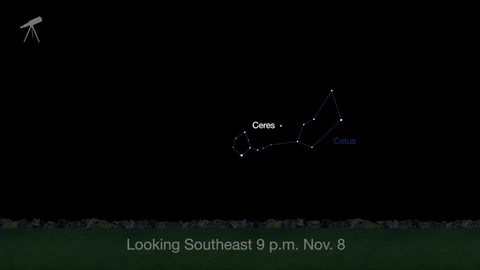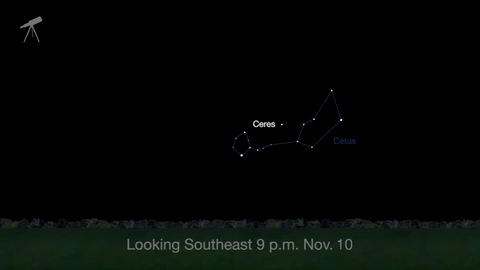
This month, just like last month, there will be three meteor showers–the Northern Tuarids, the Leonids and the November Orionids.

Watch the full November “What’s Up" video for more:
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Now those are 5 great heroes.
![Voltron: Legendary Defender Season 2 Now Streaming [x]](https://64.media.tumblr.com/39070de2b5836ba0f4a3295933bd60b8/tumblr_ok39yrTfcw1u3bhkao1_500.gif)
![Voltron: Legendary Defender Season 2 Now Streaming [x]](https://64.media.tumblr.com/05ee5b724c2559b61592a1e980ea3e58/tumblr_ok39yrTfcw1u3bhkao2_500.gif)
![Voltron: Legendary Defender Season 2 Now Streaming [x]](https://64.media.tumblr.com/f8b5fc0bbb8f59880da3c874c00c543d/tumblr_ok39yrTfcw1u3bhkao3_500.gif)
![Voltron: Legendary Defender Season 2 Now Streaming [x]](https://64.media.tumblr.com/9d5afbb305763028c401efd4d18d020f/tumblr_ok39yrTfcw1u3bhkao4_500.gif)
![Voltron: Legendary Defender Season 2 Now Streaming [x]](https://64.media.tumblr.com/2790f57379e82ac4cdcfc34111e8c869/tumblr_ok39yrTfcw1u3bhkao5_500.gif)
![Voltron: Legendary Defender Season 2 Now Streaming [x]](https://64.media.tumblr.com/5a237dac7ed2253983e28cc819c2f18c/tumblr_ok39yrTfcw1u3bhkao6_500.gif)
Voltron: Legendary Defender Season 2 Now Streaming [x]
A tribute to every brave men and women who rise their lives for our free country.
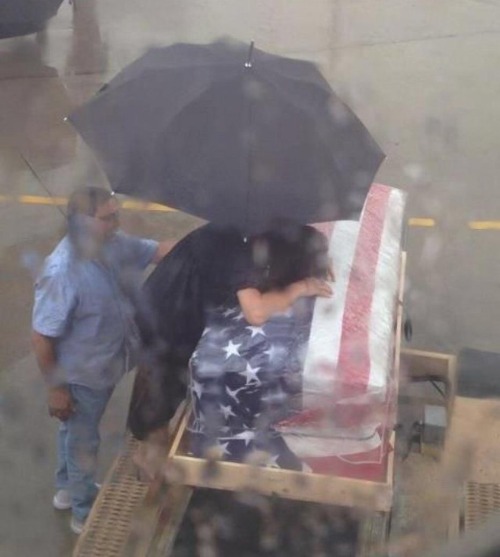
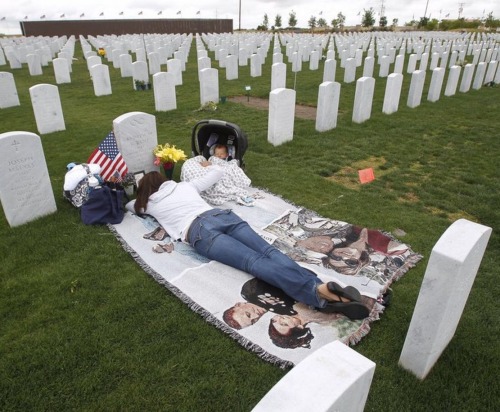










RIP to all the Men and Women who gave their lives for us to be able to be “Free”
This is the beauty of space
Holiday Lights from the Universe
Although there are no seasons in space, some cosmic vistas invoke thoughts of a frosty winter landscape. Here are a few stellar images of holiday wonderlands from across the galaxy…

Located in our galaxy about 5,500 light years from Earth, this region is actually a “cluster of clusters,” containing at least three clusters of young stars, including many hot, massive, luminous stars.

The outstretched “wings” of this nebula looks like a soaring, celestial snow angel. Twin lobes of super-hot gas, glowing blue in this image, stretch outward from the central star. This hot gas creates the “wings” of our angel. A ring of dust and gas orbiting the star acts like a belt, clinching the expanding nebula into an “hourglass” shape.

At this time of year, holiday parties often include festive lights. When galaxies get together, they also may be surrounded by a spectacular light show. This pair of spiral galaxies has been caught in a grazing encounter. This region has hosted three supernova explosions in the past 15 years and has produced one of the most bountiful collections of super-bright X-ray lights known.

What do the following things have in common: a cone, the fur of a fox and a Christmas tree? Answer: they all occur in the constellation of the unicorn (Monoceros). Pictured as a star forming region, the complex jumble of cosmic gas and dust is about 2,700 light-years away.

Resembling festive lights on a holiday wreath, this Hubble Space Telescope image of a nearby spiral galaxy is an iconic reminder of the impending season. Bright knots of glowing gas light up the spiral arms, indicating a rich environment of star formation.

The Hubble Space Telescope captured two festive-looking nebulas, situated so as to appear as one. Intense radiation from the brilliant central stars is heating hydrogen in each of the nebulas, causing them to glow red…like a holiday light.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
-
 saphicspacesociety19 reblogged this · 1 year ago
saphicspacesociety19 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 aspergers1044 liked this · 2 years ago
aspergers1044 liked this · 2 years ago -
 shovel0 reblogged this · 3 years ago
shovel0 reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 shovel0 liked this · 3 years ago
shovel0 liked this · 3 years ago -
 pinkypie1209 liked this · 3 years ago
pinkypie1209 liked this · 3 years ago -
 porcelainrobot liked this · 4 years ago
porcelainrobot liked this · 4 years ago -
 perkiejazz-2132 liked this · 7 years ago
perkiejazz-2132 liked this · 7 years ago -
 ubebear liked this · 7 years ago
ubebear liked this · 7 years ago -
 jamlessyuki liked this · 7 years ago
jamlessyuki liked this · 7 years ago -
 lucky7saint liked this · 7 years ago
lucky7saint liked this · 7 years ago -
 celina1617 liked this · 7 years ago
celina1617 liked this · 7 years ago -
 araloran liked this · 7 years ago
araloran liked this · 7 years ago -
 thestarspangledman reblogged this · 7 years ago
thestarspangledman reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 potatobatteries reblogged this · 7 years ago
potatobatteries reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 jellybrigade liked this · 7 years ago
jellybrigade liked this · 7 years ago -
 witch-gamer liked this · 7 years ago
witch-gamer liked this · 7 years ago -
 pluviinthestars liked this · 7 years ago
pluviinthestars liked this · 7 years ago -
 swifty--wish liked this · 7 years ago
swifty--wish liked this · 7 years ago -
 dougdimmadildo reblogged this · 7 years ago
dougdimmadildo reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 avi-availys liked this · 7 years ago
avi-availys liked this · 7 years ago -
 avi-availys reblogged this · 7 years ago
avi-availys reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 andromeda-gay reblogged this · 7 years ago
andromeda-gay reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 andromeda-gay liked this · 7 years ago
andromeda-gay liked this · 7 years ago -
 bramblestein reblogged this · 7 years ago
bramblestein reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 bramblestein liked this · 7 years ago
bramblestein liked this · 7 years ago -
 artblart-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
artblart-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 1337samtheman liked this · 7 years ago
1337samtheman liked this · 7 years ago -
 hyliankalmo liked this · 7 years ago
hyliankalmo liked this · 7 years ago -
 cityofglitches liked this · 7 years ago
cityofglitches liked this · 7 years ago -
 catodotexe liked this · 7 years ago
catodotexe liked this · 7 years ago -
 redvioletz liked this · 7 years ago
redvioletz liked this · 7 years ago -
 casuallyserious liked this · 7 years ago
casuallyserious liked this · 7 years ago -
 wemblingfool reblogged this · 7 years ago
wemblingfool reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 ihavenoshane reblogged this · 7 years ago
ihavenoshane reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 destrudovassago liked this · 7 years ago
destrudovassago liked this · 7 years ago -
 mobiustwixt liked this · 7 years ago
mobiustwixt liked this · 7 years ago -
 ayleidwell reblogged this · 7 years ago
ayleidwell reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 ayleidwell liked this · 7 years ago
ayleidwell liked this · 7 years ago -
 msmothra liked this · 7 years ago
msmothra liked this · 7 years ago -
 eversame liked this · 7 years ago
eversame liked this · 7 years ago -
 its-sophia-jane-blog liked this · 7 years ago
its-sophia-jane-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 420turbovicki liked this · 7 years ago
420turbovicki liked this · 7 years ago -
 dasflauschy liked this · 7 years ago
dasflauschy liked this · 7 years ago