I Know It’s A Little Late, But Happy Valentine’s Day From The Tardigang! 💧 🐻❤️





I know it’s a little late, but happy Valentine’s Day from the tardigang! 💧 🐻❤️
More Posts from We-are-all-paranoid and Others

i got to work with some HeLa cells today!
as cool of an experience as this was and as interesting as these things are, it’s always important to acknowledge the bad along with the good. Henrietta Lacks’ cells revolutionized so many areas of research, but she deserved so much better.
working with these cells today just really reminded me of the duality of many scientific developments. many things have come with great cost and harm and i think that’s something important to keep in mind.
if you aren’t familiar with the story of Henrietta Lacks, i highly recommend looking her up. there’s a book about her live (the immortal life of henrietta lacks) that’s very illuminating.

The bacteria wars are coming. Researchers at Tel Aviv University have pitted “good” bacteria against “bad” bacteria and the good guys, it appears, are winning.
If the system can be scaled, this new approach could potentially replace antibiotics, which are increasingly struggling against antibiotic-resistant “superbugs.” For the TAU study, the researchers used a toxin injection system known as a “Type 6 Secretion System.” It’s usually deployed by pathogenic (“bad”) bacteria. They introduced the system into a “friendly” bacterium, Vibrio natriegens, which is not harmful to humans. The researchers described their technology as similar to a microscopic poison arrow shot from a good bacterium to eliminate a bad bacterium under specific conditions. “The system that we built allows us to engineer ‘good’ bacteria that can recognize pathogenic bacteria, attack them with toxins, and neutralize them,” explains Dr. Dor Salomon, who co-led the study. “We know how to change and control every component in the system and create a bacterium that neutralizes different strains of bacteria. This is proof of feasibility, showing that we have the knowledge and ability to create bacteria that take advantage of this killing system and may serve as antibiotic treatments. ”The current bacteria prototype is best suited for bugs that occur naturally in saltwater. This is a growing concern, as fish and seafood constitute a major food source in many regions of the world. “Their productivity is severely impaired as a result of bacteria-borne diseases,” Solomon notes, “and since we want to avoid pouring antibiotics into aquaculture farms, a biological solution such as the one we have developed is an effective alternative.” The system will eventually be adapted to treat pathogenic bacteria in humans, farm animals and plants. Tel Aviv University has filed a patent application through Ramot, the university’s technology-transfer company. In addition to Solomon, Dr. Biswanath Jana and Kinga Kappel of the department of clinical microbiology and immunology at TAU’s Sackler Faculty of Medicine participated in the research. The results were published this month in the scientific journal EMBO Reports.

Stop the ban on blood donation of gay men

Like humans, these big-brained birds may owe their smarts to long childhoods
Human beings typically don’t leave the nest until well into our teenage years—a relatively rare strategy among animals. But corvids—a group of birds that includes jays, ravens, and crows—also spend a lot of time under their parents’ wings. Now, in a parallel to humans, researchers have found that ongoing tutelage by patient parents may explain how corvids have managed to achieve their smarts.

Stop the ban on blood donation of gay men


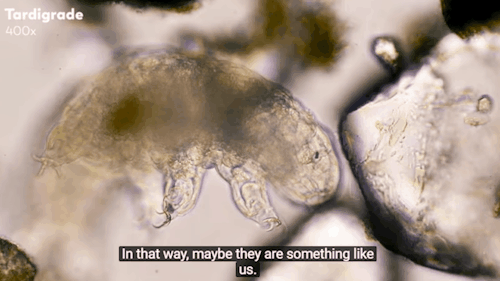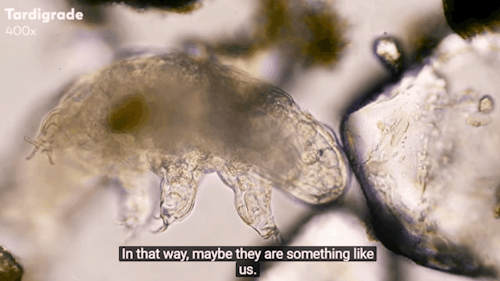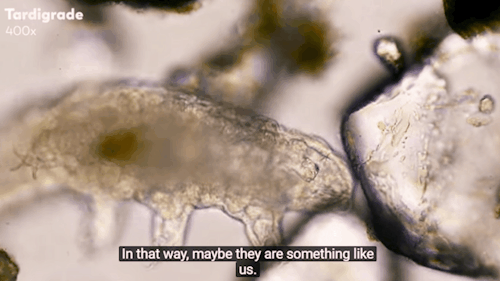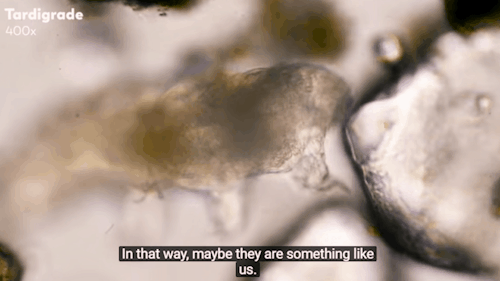


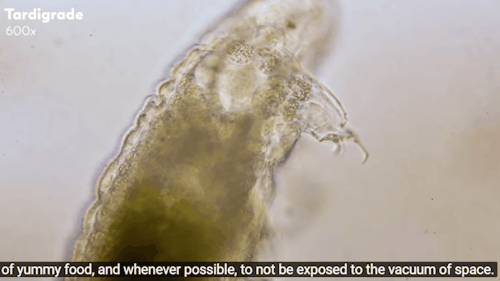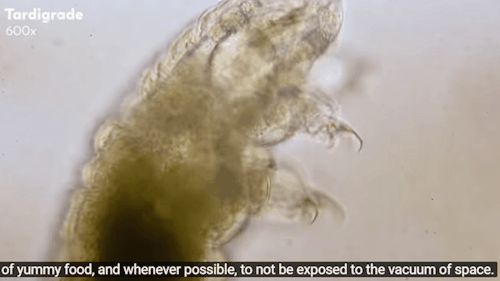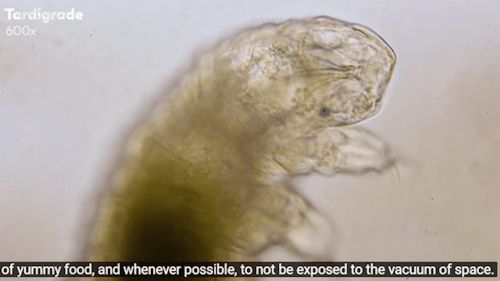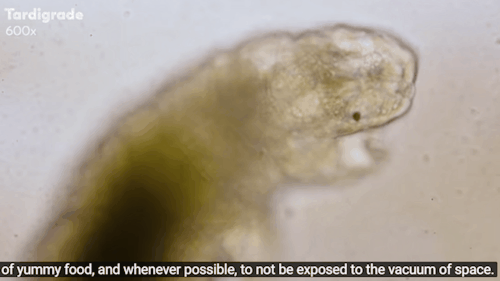
Journey to the Microcosmos: Tardigrades: Chubby, Misunderstood, & Not Immortal
Images originally captured by Jam’s Germs
Thank you @airyearthgirl for inspiring me to gif these amazing lines


Fun fact: my dad, after being a surgeon for 25 years, no longer has fingerprints. The sponge he uses to wash his hands several times a day is so harsh that it’s rubbed off his fingerprints throughout the years. Sometimes he can’t get into our building because the biometric uses a fingerprint scanner 😭

-
 alychampignon reblogged this · 2 years ago
alychampignon reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 jojogigi liked this · 2 years ago
jojogigi liked this · 2 years ago -
 zoexqsblog liked this · 2 years ago
zoexqsblog liked this · 2 years ago -
 bees-eat-rocks liked this · 2 years ago
bees-eat-rocks liked this · 2 years ago -
 theone-eyedowl liked this · 2 years ago
theone-eyedowl liked this · 2 years ago -
 mushruvi liked this · 3 years ago
mushruvi liked this · 3 years ago -
 polygodnal liked this · 3 years ago
polygodnal liked this · 3 years ago -
 wingedcloudfun liked this · 3 years ago
wingedcloudfun liked this · 3 years ago -
 warios-worl liked this · 3 years ago
warios-worl liked this · 3 years ago -
 bardificer reblogged this · 3 years ago
bardificer reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 bardificer liked this · 3 years ago
bardificer liked this · 3 years ago -
 laarkspurr liked this · 3 years ago
laarkspurr liked this · 3 years ago -
 lxremipsumm reblogged this · 3 years ago
lxremipsumm reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 lxremipsumm liked this · 3 years ago
lxremipsumm liked this · 3 years ago -
 voiidfriend reblogged this · 3 years ago
voiidfriend reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 voiidfriend liked this · 3 years ago
voiidfriend liked this · 3 years ago -
 xieled4377 liked this · 3 years ago
xieled4377 liked this · 3 years ago -
 maximumsouldragon liked this · 3 years ago
maximumsouldragon liked this · 3 years ago -
 formideable liked this · 3 years ago
formideable liked this · 3 years ago -
 differentfacestranger liked this · 3 years ago
differentfacestranger liked this · 3 years ago -
 malew11fe reblogged this · 3 years ago
malew11fe reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 malew11fe liked this · 3 years ago
malew11fe liked this · 3 years ago -
 yakexiasworld liked this · 3 years ago
yakexiasworld liked this · 3 years ago -
 eeveestoneson reblogged this · 3 years ago
eeveestoneson reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 endress-knight-the-drokain liked this · 3 years ago
endress-knight-the-drokain liked this · 3 years ago -
 horizon32 liked this · 3 years ago
horizon32 liked this · 3 years ago -
 chaoticfurysheep liked this · 3 years ago
chaoticfurysheep liked this · 3 years ago -
 jifxxk20 liked this · 3 years ago
jifxxk20 liked this · 3 years ago -
 yami-no-kokoro liked this · 3 years ago
yami-no-kokoro liked this · 3 years ago -
 crystalqueerenby liked this · 3 years ago
crystalqueerenby liked this · 3 years ago -
 notawriter liked this · 3 years ago
notawriter liked this · 3 years ago -
 alexackrman liked this · 3 years ago
alexackrman liked this · 3 years ago -
 myriapodmarshmello liked this · 3 years ago
myriapodmarshmello liked this · 3 years ago -
 enrothsky liked this · 3 years ago
enrothsky liked this · 3 years ago -
 thelumpiestpotato liked this · 3 years ago
thelumpiestpotato liked this · 3 years ago -
 cattfig liked this · 3 years ago
cattfig liked this · 3 years ago -
 transcendinding-g liked this · 3 years ago
transcendinding-g liked this · 3 years ago -
 kindofdreamcatcher liked this · 3 years ago
kindofdreamcatcher liked this · 3 years ago -
 mercuryferns liked this · 3 years ago
mercuryferns liked this · 3 years ago -
 queersicles liked this · 3 years ago
queersicles liked this · 3 years ago -
 mecha-droid liked this · 3 years ago
mecha-droid liked this · 3 years ago -
 terminally-spooked liked this · 3 years ago
terminally-spooked liked this · 3 years ago -
 overly-emotional-bisexual liked this · 3 years ago
overly-emotional-bisexual liked this · 3 years ago -
 indignantbarista reblogged this · 3 years ago
indignantbarista reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 indignantbarista liked this · 3 years ago
indignantbarista liked this · 3 years ago -
 happy-asparagus liked this · 3 years ago
happy-asparagus liked this · 3 years ago -
 casperb000 liked this · 3 years ago
casperb000 liked this · 3 years ago
