Thumbs Up For Science

Thumbs Up For Science
The cover of the legendary journal Nature from February 1879, featuring this thumb microscope, yours for the low, low price of three pounds.
(via Ptak Science Books, which you should really check out)
More Posts from Thejoyofscience and Others
Sanity check
Hi everyone, I overheard a very troubling conversation between a neighboring grad student and my PI. In this conversation, the neighboring grad student said the following:
She has no work-life balance. Most of the times, she comes in very early in the morning (before 7 or 8 AM) and leaves very late (after 10 PM).
She says she’s fine with this but also says she’s under constant state of stress because of her PI’s expectations, and my labmate and I have actually ran into her crying in the stairwell.
She’s actually concerned about her peers when they can relax in the evenings instead of being in lab or at least working from home, or when they get to do things on the weekends.
I just want to see how other PhD students are handling their work-life balance after hearing this conversation just to make sure I’m not slacking off.
For me, I come in 9 AM - 5 PM (sometimes staying later depending on experiments, but this is NOT the norm). Sometimes, I come in for a few hours on the weekends to speed things up or if need be (also not the norm). After dinner, I usually do homework, prepare powerpoints for journal clubs or seminar presentations and other non-lab related things, but sometimes I do some work (interneuron quantifying, schedule and plan experiments for the next day/week, etc). I do want to incorporate more literature reading in the evenings or mornings. Regardless, the majority of my work is done on the weekdays 9 AM - 5 PM.
My reasoning is that I’d rather go “normal” pace and steady since I’ll be here for 3+ years to avoid burning out. I want to enjoy my work, and that’s not happening if I feel like I NEED to be here and NEED to do all these things on this impossible schedule. I have been having thoughts of mastering out in the back of my mind, but at the end of the day, I do enjoy my work and my PI’s mentorship and I think I can learn a lot more being here for 3+ years of my PhD.
In addition, we get paid barely above minimum wage as a grad student if we work 40 hours a week. During crazy weeks (which everyone has), that increases by a lot, which means we get paid less than minimum wage, for very specialized and skilled works. Yes, we are in training as PhD students, but if the expectation is for us to work all day, all night, all week, then the PhD feels less like training and more like slave labor disguised as training.
How are your schedules like as PhD students? @cancerbiophd @queenofthebench @whitecoatjourney @adorable-amygdala and many others!
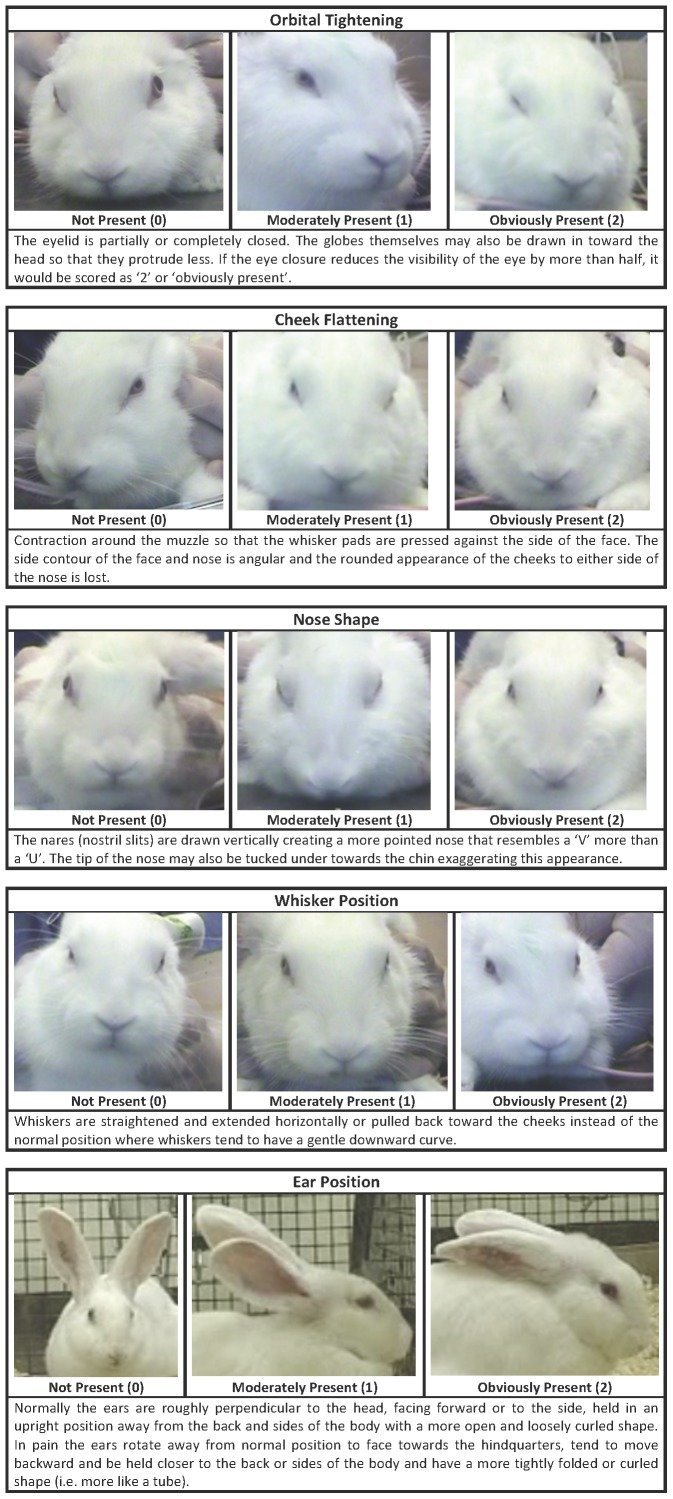



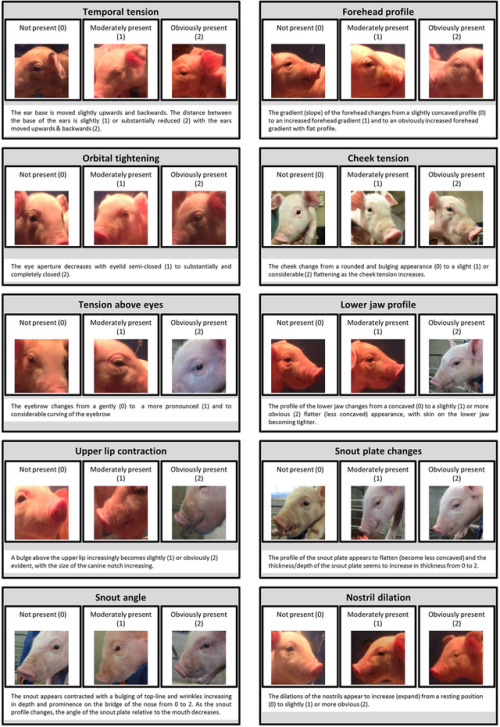





Recognising silent acute pain in animals - assorted species grimace scales:
Development of the Horse Grimace Scale (HGS) as a Pain Assessment Tool in Horses Undergoing Routine Castration
The composition and initial evaluation of a grimace scale in ferrets after surgical implantation of a telemetry probe
The Assessment of Facial Expressions in Piglets Undergoing Tail Docking and Castration: Toward the Development of the Piglet Grimace Scale
The Sheep Grimace Scale as an indicator of post-operative distress and pain in laboratory sheep and the Coding and quantification of a facial expression for pain in lambs
Mouse - How to be a pain management advocate for exotic and zoo animals (full text available - includes additional species)
The Rat Grimace Scale: A partially automated method for quantifying pain in the laboratory rat via facial expressions
Evaluation of EMLA Cream for Preventing Pain during Tattooing of Rabbits: Changes in Physiological, Behavioural and Facial Expression Responses
Pain evaluation in dairy cattle
Pain is subtle - we cannot depend on vocalisations or extreme abnormal behaviour to determine if an animal is on pain - animals can cover up pain while going about their daily life. Grimace scales have been found to be reliable indicators of pain (full text available)
Unfortunately, I could not find a clear visual grimace scale for dogs, cats or birds :(
Which is a shame, because perhaps I could have recognised my own dog’s discomfort for the acute pain it was sooner:

(left: dog in pain. See eyes, tension, cheeks, whiskers, ears compared to the multiple species grimace charts above. right: tired but not in pain dog)
Perhaps my new books that arrived today might have some on dogs at least. There’s this visual blog post of a stressed dog at the vet - stress in the absence of a trigger looks very much like pain.
Here is a small comparative cats, with the link going into more detail. Not a scale but better than nothing:


Bonus round - you can get free A3 posters on recognising pain for Rabbits, Mice and Rats from the National Centre for the Replacement, Refinement and Reduction of Animals in Research. My rabbit specialist vet has the rabbit one!


Aspirate of a mammary mass from a 8 year-old, female-intact, Yorkshire Terrier. The patient was found wondering in a field by a good Samaritan-turned-owner over the 4th of July weekend. Although she was acting normally, the owner brought the little dog in for a ‘look over.’ On physical examination a 2cm mass was felt in the left mammary chain. No obvious spay scar was present.
*
On cytology there were copious clusters of epithelial cells. These epithelial cells (top picture) were very non-descript, making for large, jumbled piles of cells. Notice how you cannot see any well-defined cell borders between them?? Just a ton of nuclei (and nucleoli) blending in together! That’s a sign of cell craziness! Many clusters were surrounded by this gorgeous, pink-magenta material. Likely secretory product or matrix.
*
Cytologic diagnosis: Mammary tumor! Although the cells look quite malignant on cytology, many studies have shown you cannot reliably determine malignancy with cytology alone. Thus, you NEED a biopsy to determine if a mammary tumor is malignant or benign in a dog. And flip a coin on that - about 50% are malignant and 50% are benign. Intact female dogs have an almost 35% lifetime chance of developing one of these beasts!

Thunderstorm from space
This photo was taken from the International Space Station during a project to capture photos of clouds. Here a large anvil supercell (some 200 km across) is silhouetted against the limb of our blue orb, revealing clearly the layers of the atmosphere somewhere over northern Australia around 1,500 km from the station, which was then flying over Papua New Guinea.
Keep reading

drowning in that lovin gendrya and braime juice
Hitchhiking bacteria might help their host navigate via magnetic fields
Deep in the mud of the Mediterranean Sea, scientists have caught microscopic protists dancing to a strange beat—the beat of Earth’s magnetic fields. Now, a new study reveals how these tiny clusters of cells orient themselves along those fields: by letting magneto-sensing bacteria hitch a ride on their outer membranes.
Researchers used microscopes to examine protist-packed sediment taken from the bottom of the Mediterranean Sea near Carry-le-Rouet, France. When they placed a magnet with its north pole facing a water droplet from the sediment, the hundreds of protists inside immediately began to swim toward the droplet’s edge. When the researchers reversed the magnet so its south pole was facing the droplet, the protists fled in the other direction (above).

Monochrome image of a victorian butterfly tongue captured by Gregg Kleinberg with a Paxcam microscope camera under the microscope at 400x.


Right lateral thoracic wall mass from a 10 year-old, female-spayed, Golden Retriever. Approximately six months ago the owner noticed a small, firm swelling on the patient’s right chest. No doubt it grew with time, as it finally got large enough for the owner to become truly concerned! The patient is clinically healthy otherwise.
*
The most prominent feature on the cytology were these gorgeous globules of magenta, streaming material! In fact, the entire slide was imbued with this color when you looked at it without a microscope. The substance is most likely matrix produced by cancer cells. Matrix of this color is commonly observed in chrondrosarcomas. Occasional malignant spindle-shaped cells were found imbedded in the matrix.
*
Diagnosis: Chondrosarcoma. Well , that’s the most likely diagnosis given the location and appearance of the neoplastic cells and matrix! Other possibilities include a myxosarcoma (which produces a mucous like material!) or osteosarcoma (malignant primary bone tumor). Chondrosarcomas are often regionally invasive but rarely metastasize. If the owner is on board with a chest wall resection, the patient will have a good prognosis :-)
I just read that bees don't have lungs how do their respiratory system works??
Correct. Insects do not have lungs they breathe through spiracles (tiny openings) that can open and close, as well as having filters to keep dust and other external contaminants out.

The spiracles run across their abdomen connecting to tracheae which is where oxygen exchange takes place (In mammals this happens in the blood), that then connect to tracheole. The air sacs expand and collapse so force the air in the spiracles and into the trachea and almost function in that they can reserve air in them so insects can conserve water.

Honey bees have 10 pairs of spiracles, 3 pairs on the thorax and 7 pairs on the abdomen. Bees can use and accelerate the passage of air in their bodies via their air sacs, contacting them and increasing their respiration rate.
This adaptive function of their respiratory system actually helps them to fly and the first few spiracles are used for air to exit while the others for air entering, they also have valves to prevent backflow. This also allows the bee to cool down or heat up if it needs to, which is why you’ll see bees abdomens wiggling while they’re resting. They’re forcing air in and out of their bodies in order to rapidly cool down or heat up, which is important for flight.

-
 vanesa reblogged this · 11 years ago
vanesa reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 errante-aderyn liked this · 11 years ago
errante-aderyn liked this · 11 years ago -
 alwaysroonilwazlib reblogged this · 11 years ago
alwaysroonilwazlib reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 firebolt93 reblogged this · 11 years ago
firebolt93 reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 linseymiller reblogged this · 11 years ago
linseymiller reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 juan-hamish-watson reblogged this · 11 years ago
juan-hamish-watson reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 onefishtwofishredfishbluefishxd reblogged this · 11 years ago
onefishtwofishredfishbluefishxd reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 thatsmradhoctoyou reblogged this · 11 years ago
thatsmradhoctoyou reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 ali-mhally reblogged this · 11 years ago
ali-mhally reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 s0ph1sticated reblogged this · 11 years ago
s0ph1sticated reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 lightsbridgearts liked this · 11 years ago
lightsbridgearts liked this · 11 years ago -
 mcdecesare liked this · 11 years ago
mcdecesare liked this · 11 years ago -
 husdant reblogged this · 11 years ago
husdant reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 memoria-veleidosa reblogged this · 11 years ago
memoria-veleidosa reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 imastarboy liked this · 11 years ago
imastarboy liked this · 11 years ago -
 pelusaur reblogged this · 11 years ago
pelusaur reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 nupurdftba liked this · 11 years ago
nupurdftba liked this · 11 years ago -
 briannashay liked this · 11 years ago
briannashay liked this · 11 years ago -
 jvdbooks liked this · 11 years ago
jvdbooks liked this · 11 years ago -
 smallntender-blog reblogged this · 11 years ago
smallntender-blog reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 terrorbyrd-old-blog reblogged this · 11 years ago
terrorbyrd-old-blog reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 star--babe liked this · 11 years ago
star--babe liked this · 11 years ago -
 manicfringe reblogged this · 11 years ago
manicfringe reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 meta-cetera liked this · 11 years ago
meta-cetera liked this · 11 years ago -
 cades-jake liked this · 11 years ago
cades-jake liked this · 11 years ago -
 neaptidejewelry liked this · 11 years ago
neaptidejewelry liked this · 11 years ago -
 chairroll reblogged this · 11 years ago
chairroll reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 stuff-worth-visiting reblogged this · 11 years ago
stuff-worth-visiting reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 mikan-the-cat reblogged this · 11 years ago
mikan-the-cat reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 ignacio310 reblogged this · 11 years ago
ignacio310 reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 sojamo-blog liked this · 11 years ago
sojamo-blog liked this · 11 years ago -
 dumbkidgrownup liked this · 11 years ago
dumbkidgrownup liked this · 11 years ago -
 yellow-buds-of-may liked this · 11 years ago
yellow-buds-of-may liked this · 11 years ago -
 orientaldelicacy-blog liked this · 11 years ago
orientaldelicacy-blog liked this · 11 years ago -
 yetticascissorhands reblogged this · 11 years ago
yetticascissorhands reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 its-kind-of-uh-big-deal liked this · 11 years ago
its-kind-of-uh-big-deal liked this · 11 years ago -
 martin-chan reblogged this · 11 years ago
martin-chan reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 bitesizedbiology-blog liked this · 11 years ago
bitesizedbiology-blog liked this · 11 years ago -
 alicecdco liked this · 11 years ago
alicecdco liked this · 11 years ago
An assortment of scientific things from the wonderful world of biology
77 posts
