Dear @thought-cafe Team, We Need More Crash Course Astronomy Episodes! Can You Please Do A Season 2?
Dear @thought-cafe team, we need more Crash Course Astronomy episodes! Can you please do a Season 2? Dr. Phil Plait is awesome, and we miss him!

If you’re excited about the juno news today, sink your teeth into a Crash Course episode that’s all about Jupiter! 🔭 https://youtu.be/Xwn8fQSW7-8
More Posts from Starry-shores and Others

Daphnis and the Rings of Saturn : What’s happening to the rings of Saturn? A little moon making big waves. The moon is 8-kilometer Daphnis and it is making waves in the Keeler Gap of Saturn’s rings using just its gravity – as it bobs up and down, in and out. The featured image is a colored and more detailed version of a previously released images taken in 2017 by the robotic Cassini spacecraft during one of its Grand Finale orbits. Daphnis can be seen on the far right, sporting ridges likely accumulated from ring particles. Daphnis was discovered in Cassini images in 2005 and raised mounds of ring particles so high in 2009 – during Saturn’s equinox when the ring plane pointed directly at the Sun – that they cast notable shadows. via NASA
I found a really cool Youtube channel called History of the Earth that covers topics in the incredibly distant past. I'm talking billions of years ago. And learning how the Earth itself formed and where water came from and about the very first single-celled organisms is just like... woah. WOAH.
It's wild that billions of years ago there were just some bacteria hanging out in the ocean and now we have all this. It's really humbling and puts into perspective how precious our planet is. How precious life is.
The Kepler space telescope has shown us our galaxy is teeming with planets — and other surprises

The Kepler space telescope has taught us there are so many planets out there, they outnumber even the stars. Here is a sample of these wondrous, weird and unexpected worlds (and other spectacular objects in space) that Kepler has spotted with its “eye” opened to the heavens.
Kepler has found that double sunsets really do exist.

Yes, Star Wars fans, the double sunset on Tatooine could really exist. Kepler discovered the first known planet around a double-star system, though Kepler-16b is probably a gas giant without a solid surface.
Kepler has gotten us closer to finding planets like Earth.

Nope. Kepler hasn’t found Earth 2.0, and that wasn’t the job it set out to do. But in its survey of hundreds of thousands of stars, Kepler found planets near in size to Earth orbiting at a distance where liquid water could pool on the surface. One of them, Kepler-62f, is about 40 percent bigger than Earth and is likely rocky. Is there life on any of them? We still have a lot more to learn.
This sizzling world is so hot iron would melt!

One of Kepler’s early discoveries was the small, scorched world of Kepler-10b. With a year that lasts less than an Earth day and density high enough to imply it’s probably made of iron and rock, this “lava world” gave us the first solid evidence of a rocky planet outside our solar system.
If it’s not an alien megastructure, what is this oddly fluctuating star?

When Kepler detected the oddly fluctuating light from “Tabby’s Star,” the internet lit up with speculation of an alien megastructure. Astronomers have concluded it’s probably an orbiting dust cloud.
Kepler caught this dead star cannibalizing its planet.

What happens when a solar system dies? Kepler discovered a white dwarf, the compact corpse of a star in the process of vaporizing a planet.
These Kepler planets are more than twice the age of our Sun!

The five small planets in Kepler-444 were born 11 billion years ago when our galaxy was in its youth. Imagine what these ancient planets look like after all that time?
Kepler found a supernova exploding at breakneck speed.

This premier planet hunter has also been watching stars explode. Kepler recorded a sped-up version of a supernova called a “fast-evolving luminescent transit” that reached its peak brightness at breakneck speed. It was caused by a star spewing out a dense shell of gas that lit up when hit with the shockwave from the blast.
* All images are artist illustrations.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
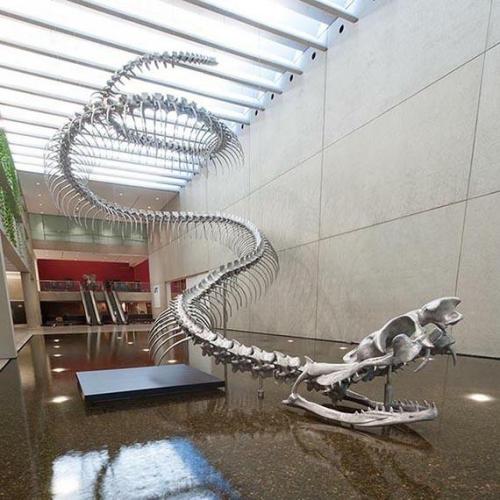



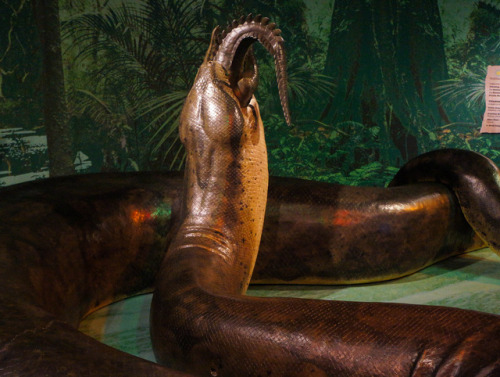



Titanoboa
Titanoboa is an extinct genus of snakes that is known to have lived in present-day La Guajira in northern Colombia. The giant snake lived during the Middle to Late Paleocene epoch, a 10-million-year period immediately following the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event.
The only known species is Titanoboa cerrejonensis, the largest snake ever discovered. By comparing the sizes and shapes of its fossilized vertebrae to those of extant snakes, researchers estimated that the largest individuals of T. cerrejonensis found had a total length around 42 feet and weighed about 2,500 pounds.
While initially thought to have been an apex predator of the Paleocene ecosystem in which it lived, evidence has pointed to the genus being predominantly piscivorous. Titanoboa’s massive size would have made it difficult to move on land, so the giant snake would probably have spent most of its life in the water, hunting for fish and other aquatic prey.

Leedsichthys is a giant member of the Pachycormidae, an extinct group of Mesozoic bony fish, that lived in the oceans of the Middle Jurassic period. The first remains of Leedsichthys were identified in the nineteenth century. Leedsichthys fossils have been found in England, France, Germany and Chile. Along with its close pachycormid relatives Bonnerichthys and Rhinconichthys, Leedsichthys is part of a lineage of large-sized filter-feeders who swam the Mesozoic seas for over 100 million years, from the middle Jurassic until the end of the Cretaceous period. Pachycormids might represent an early branch of Teleostei, the group most modern bony fishes belong to; in that case Leedsichthys is the largest known teleost fish.
Leedsichthys fossils have been difficult to interpret, because the skeletons were not completely made of bone. Large parts consisted of cartilage that did not fossilise. On several occasions the enigmatic large partial remains have been mistaken for stegosaurian dinosaur bones. As the vertebrae are among the parts that have not been preserved, it is hard to determine the total body length. Estimates have varied wildly. At the beginning of the twentieth century a length of nine metres was seen as plausible, but by its end Leedsichthys was sometimes claimed to have been over thirty metres long. Recent research has lowered this to about sixteen meters for the largest individuals. Skull bones have been found indicating that Leedsichthys had a large head with bosses on the skull roof. Fossilised bony finrays show large elongated pectoral fins and a tall vertical tail fin. The gill arches were lined by gill rakers, equipped by a unique system of delicate bone plates, that filtered plankton from the sea water, the main food source.
I really wish people would jump on the marine exploration bandwagon as much as space exploration.
Eclipsing Suns
I can’t remember which novel JR said influenced the world of S6, but I was recently reminded of Asimov’s Nightfall and wonder whether its eclipse narrative might have some bearing on the plot …
[Spoilers for Nightfall ahead – highly recommend you read the story (it’s short!)]
For anyone not familiar, Nightfall is set on a planet with six suns - enough suns that the planet never experiences darkness. Every 2000 years or so, the suns and the planet’s moon align just so, and an eclipse occurs. And every 2000 years, something cataclysmic occurs that ends civilization. The only records of the event are embedded in the mythology of an ancient cult’s scripture.
During one of these cycles, a team of astronomers and psychologists collaborate with the cult, and together determine that they are weeks away from the next eclipse. The scientists lock their loved ones away in a bunker and prepare equipment to document the eclipse, which they do not believe they will survive. (Having never experienced nighttime, they have a pathological fear of the dark. Even more concerning, however, is the threat of the Stars mentioned in ancient scripture, for these have the power to burn cities and drive men to madness.)
And when the eclipse occurs and people see the night sky for the first time in two thousand years, they are struck with terror and knowledge of their insignificance, and all the world over, people set their cities on fire to blot out the stars’ truth and the horror of the long night.
… What little we do know about S6 reminds me of this. Like Clarke and co., these scientists attempt to learn what happened to a lost civilization (Eligius III) while hampered by a cult-like organization (Second Dawn? Wonkru? Whoever now inhabits the planet?) that has attached mythological meaning to the natural phenomenon of the eclipse. JR has said that something crucial happens when the suns eclipse, and though suns eclipsing themselves does not create total darkness, as here, we can guess that there will be psychological ramifications attached to it.
So I just discovered that the famous depth chart of Lake Baikal, you know, this one

Is
Uh
Not the whole picture

So this is going to haunt me forever

Tarantula Nebula by NASA Hubble

Lunar Sand taken from the rim of the Shorty Crater by the Apollo 17 Astronauts. This “Orange Soil” is a result of volcanic activity on The Moon 3.8 billion years ago. It is so spherical and smooth due to the lack of gravity - pulling the molten substance in towards itself at the time of eruption and thus creating these round particles. ⠀
⠀Via Gary Greenberg, Carol Kiely, and Kate Clover
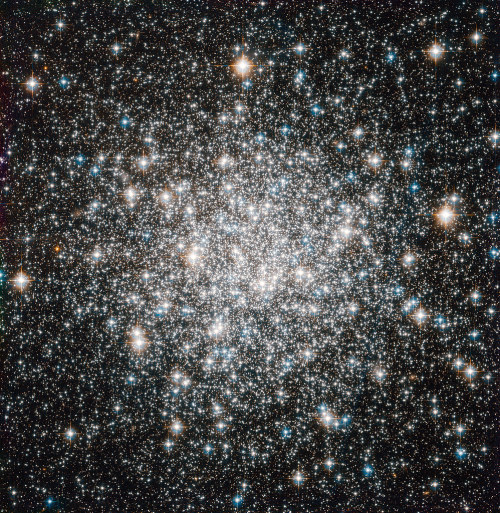

A ten billion-year stellar dance by europeanspaceagency
-
 starry-shores reblogged this · 3 years ago
starry-shores reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 an-abyss-called-life liked this · 3 years ago
an-abyss-called-life liked this · 3 years ago -
 novellearningblog liked this · 6 years ago
novellearningblog liked this · 6 years ago -
 penis-serious reblogged this · 6 years ago
penis-serious reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 icegeek liked this · 6 years ago
icegeek liked this · 6 years ago -
 detroitlib liked this · 6 years ago
detroitlib liked this · 6 years ago -
 mobilepubliclibraryteens reblogged this · 6 years ago
mobilepubliclibraryteens reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 mobilepubliclibraryteens liked this · 6 years ago
mobilepubliclibraryteens liked this · 6 years ago -
 pagan-n-proud reblogged this · 7 years ago
pagan-n-proud reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 yoel12canseco liked this · 8 years ago
yoel12canseco liked this · 8 years ago -
 kmdn12-blog liked this · 8 years ago
kmdn12-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 nobeerreviews liked this · 8 years ago
nobeerreviews liked this · 8 years ago -
 ximajs reblogged this · 8 years ago
ximajs reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 a-arik liked this · 8 years ago
a-arik liked this · 8 years ago -
 called-by-name liked this · 8 years ago
called-by-name liked this · 8 years ago -
 murmurpupupu liked this · 8 years ago
murmurpupupu liked this · 8 years ago -
 namelessfreak99 liked this · 8 years ago
namelessfreak99 liked this · 8 years ago -
 webtechczar liked this · 8 years ago
webtechczar liked this · 8 years ago -
 lemmingsworld liked this · 8 years ago
lemmingsworld liked this · 8 years ago -
 theneighbourhoodstar-blog liked this · 8 years ago
theneighbourhoodstar-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 findingsomewhere liked this · 8 years ago
findingsomewhere liked this · 8 years ago -
 missbcm reblogged this · 8 years ago
missbcm reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 allofusdust liked this · 8 years ago
allofusdust liked this · 8 years ago -
 komadina61 liked this · 8 years ago
komadina61 liked this · 8 years ago -
 astronomyinspires reblogged this · 8 years ago
astronomyinspires reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 stargazer-scientist liked this · 8 years ago
stargazer-scientist liked this · 8 years ago -
 cyclonetequila liked this · 8 years ago
cyclonetequila liked this · 8 years ago -
 mooaaz-blog liked this · 8 years ago
mooaaz-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 flyingsquidzeez liked this · 8 years ago
flyingsquidzeez liked this · 8 years ago -
 modernrenaissancewoman-blog1 reblogged this · 8 years ago
modernrenaissancewoman-blog1 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 modernrenaissancewoman-blog1 liked this · 8 years ago
modernrenaissancewoman-blog1 liked this · 8 years ago -
 nyominebula liked this · 8 years ago
nyominebula liked this · 8 years ago -
 trans-bunny-nerd liked this · 8 years ago
trans-bunny-nerd liked this · 8 years ago -
 little-dashie liked this · 8 years ago
little-dashie liked this · 8 years ago -
 nixnax liked this · 8 years ago
nixnax liked this · 8 years ago -
 kooldewd123 liked this · 8 years ago
kooldewd123 liked this · 8 years ago -
 drew887 liked this · 8 years ago
drew887 liked this · 8 years ago -
 trillsabells liked this · 8 years ago
trillsabells liked this · 8 years ago -
 spacegirl1339 liked this · 8 years ago
spacegirl1339 liked this · 8 years ago -
 shana87 reblogged this · 8 years ago
shana87 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 dial221forthedoctor liked this · 8 years ago
dial221forthedoctor liked this · 8 years ago -
 oakforthevines liked this · 8 years ago
oakforthevines liked this · 8 years ago -
 prionailurus liked this · 8 years ago
prionailurus liked this · 8 years ago -
 livesonpluto liked this · 8 years ago
livesonpluto liked this · 8 years ago -
 lexsalad liked this · 8 years ago
lexsalad liked this · 8 years ago -
 justlivedieandenjoytheride reblogged this · 8 years ago
justlivedieandenjoytheride reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 opheliagreen liked this · 8 years ago
opheliagreen liked this · 8 years ago

Amateur astronomer, owns a telescope. This is a side blog to satiate my science-y cravings! I haven't yet mustered the courage to put up my personal astro-stuff here. Main blog : @an-abyss-called-life
212 posts