The Milky Way Over Snow-Capped Himalayas

The Milky Way over Snow-Capped Himalayas
More Posts from Starry-shores and Others


Look at the bottom gif! The long tentacles are pushed out and parallel to each other while the jelly is motionless. This behavior is predatory, which means that the Marianas Trench Jelly is set in attack mode!
Read more about the 2016 discovery of the Marianas Trench Jelly
Discovering the Universe Through the Constellation Orion
Do you ever look up at the night sky and get lost in the stars? Maybe while you’re stargazing, you spot some of your favorite constellations. But did you know there’s more to constellations than meets the eye? They’re not just a bunch of imaginary shapes made up of stars — constellations tell us stories about the universe from our perspective on Earth.

What is a constellation?
A constellation is a named pattern of stars that looks like a particular shape. Think of it like connecting the dots. If you join the dots — stars, in this case — and use your imagination, the picture would look like an object, animal, or person. For example, the ancient Greeks believed an arrangement of stars in the sky looked like a giant hunter with a sword attached to his belt, so they named it after a famous hunter in their mythology, Orion. It’s one of the most recognizable constellations in the night sky and can be seen around the world. The easiest way to find Orion is to go outside on a clear night and look for three bright stars close together in an almost-straight line. These three stars represent Orion's belt. Two brighter stars to the north mark his shoulders, and two more to the south represent his feet.

Credit: NASA/STScI
Over time, cultures around the world have had different names and numbers of constellations depending on what people thought they saw. Today, there are 88 officially recognized constellations. Though these constellations are generally based on what we can see with our unaided eyes, scientists have also invented unofficial constellations for objects that can only be seen in gamma rays, the highest-energy form of light.
Perspective is everything
The stars in constellations may look close to each other from our point of view here on Earth, but in space they might be really far apart. For example, Alnitak, the star at the left side of Orion's belt, is about 800 light-years away. Alnilam, the star in the middle of the belt, is about 1,300 light-years away. And Mintaka, the star at the right side of the belt, is about 900 light-years away. Yet they all appear from Earth to have the same brightness. Space is three-dimensional, so if you were looking at the stars that make up the constellation Orion from another part of our galaxy, you might see an entirely different pattern!

The superstars of Orion
Now that we know a little bit more about constellations, let’s talk about the supercool cosmic objects that form them – stars! Though over a dozen stars make up Orion, two take center stage. The red supergiant Betelgeuse (Orion's right shoulder) and blue supergiant Rigel (Orion's left foot) stand out as the brightest members in the constellation.

Credit: Derrick Lim
Betelgeuse is a young star by stellar standards, about 10 million years old, compared to our nearly 5 billion-year-old Sun. The star is so huge that if it replaced the Sun at the center of our solar system, it would extend past the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter! But due to its giant mass, it leads a fast and furious life.

Betelgeuse is destined to end in a supernova blast. Scientists discovered a mysterious dimming of Betelgeuse in late 2019 caused by a traumatic outburst that some believed was a precursor to this cosmic event. Though we don’t know if this incident is directly related to an imminent supernova, there’s a tiny chance it might happen in your lifetime. But don't worry, Betelgeuse is about 550 light-years away, so this event wouldn't be dangerous to us – but it would be a spectacular sight.
Rigel is also a young star, estimated to be 8 million years old. Like Betelgeuse, Rigel is much larger and heavier than our Sun. Its surface is thousands of degrees hotter than Betelgeuse, though, making it shine blue-white rather than red. These colors are even noticeable from Earth. Although Rigel is farther from Earth than Betelgeuse (about 860 light-years away), it is intrinsically brighter than its companion, making it the brightest star in Orion and one of the brightest stars in the night sky.

Credit: Rogelio Bernal Andreo
Buckle up for Orion’s belt
Some dots that make up constellations are actually more than one star, but from a great distance they look like a single object. Remember Mintaka, the star at the far right side of Orion's belt? It is not just a single star, but actually five stars in a complex star system.

Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/GSFC/M. Corcoran et al.; Optical: Eckhard Slawik
Sword or a stellar nursery?
Below the three bright stars of Orion’s belt lies his sword, where you can find the famous Orion Nebula. The nebula is only 1,300 light-years away, making it the closest large star-forming region to Earth. Because of its brightness and prominent location just below Orion’s belt, you can actually spot the Orion Nebula from Earth! But with a pair of binoculars, you can get a much more detailed view of the stellar nursery. It’s best visible in January and looks like a fuzzy “star” in the middle of Orion’s sword.

More to discover in constellations
In addition to newborn stars, Orion also has some other awesome cosmic objects hanging around. Scientists have discovered exoplanets, or planets outside of our solar system, orbiting stars there. One of those planets is a giant gas world three times more massive than Jupiter. It’s estimated that on average there is at least one planet for every star in our galaxy. Just think of all the worlds you may be seeing when you look up at the night sky!
It’s also possible that the Orion Nebula might be home to a black hole, making it the closest known black hole to Earth. Though we may never detect it, because no light can escape black holes, making them invisible. However, space telescopes with special instruments can help find black holes. They can observe the behavior of material and stars that are very close to black holes, helping scientists find clues that can lead them closer to discovering some of these most bizarre and fascinating objects in the cosmos.

Next time you go stargazing, remember that there’s more to the constellations than meets the eye. Let them guide you to some of the most incredible and mysterious objects of the cosmos — young stars, brilliant nebulae, new worlds, star systems, and even galaxies!

To keep up with the most recent stellar news, follow NASA Universe on Twitter and Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!

Comet meets cluster by europeanspaceagency
What are brown dwarfs?
In order to understand what is a brown dwarf, we need to understand the difference between a star and a planet. It is not easy to tell a star from a planet when you look up at the night sky with your eyes. However, the two kinds of objects look very different to an astronomer using a telescope or spectroscope. Planets shine by reflected light; stars shine by producing their own light. So what makes some objects shine by themselves and other objects only reflect the light of some other body? That is the important difference to understand – and it will allow us to understand brown dwarfs as well.

As a star forms from a cloud of contracting gas, the temperature in its center becomes so large that hydrogen begins to fuse into helium – releasing an enormous amount of energy which causes the star to begin shining under its own power. A planet forms from small particles of dust left over from the formation of a star. These particles collide and stick together. There is never enough temperature to cause particles to fuse and release energy. In other words, a planet is not hot enough or heavy enough to produce its own light.

Brown dwarfs are objects which have a size between that of a giant planet like Jupiter and that of a small star. In fact, most astronomers would classify any object with between 13 times the mass of Jupiter and 75 times the mass of Jupiter to be a brown dwarf. Given that range of masses, the object would not have been able to sustain the fusion of hydrogen like a regular star; thus, many scientists have dubbed brown dwarfs as “failed stars”.

A Trio of Brown Dwarfs
This artist’s conception illustrates what brown dwarfs of different types might look like to a hypothetical interstellar traveler who has flown a spaceship to each one. Brown dwarfs are like stars, but they aren’t massive enough to fuse atoms steadily and shine with starlight – as our sun does so well.

On the left is an L dwarf, in the middle is a T dwarf, and on the right is a Y dwarf. The objects are progressively cooler in atmospheric temperatures as you move from left to right. Y dwarfs are the newest and coldest class of brown dwarfs and were discovered by NASA’s Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE. WISE was able to detect these Y dwarfs for the first time because it surveyed the entire sky deeply at the infrared wavelengths at which these bodies emit most of their light. The L dwarf is seen as a dim red orb to the eye. The T dwarf is even fainter and appears with a darker reddish, or magenta, hue. The Y dwarf is dimmer still. Because astronomers have not yet detected Y dwarfs at the visible wavelengths we see with our eyes, the choice of a purple hue is done mainly for artistic reasons. The Y dwarf is also illustrated as reflecting a faint amount of visible starlight from interstellar space.
In this rendering, the traveler’s spaceship is the same distance from each object. This illustrates an unusual property of brown dwarfs – that they all have the same dimensions, roughly the size of the planet Jupiter, regardless of their mass. This mass disparity can be as large as fifteen times or more when comparing an L to a Y dwarf, despite the fact that both objects have the same radius. The three brown dwarfs also have very different atmospheric temperatures. A typical L dwarf has a temperature of 2,600 degrees Fahrenheit (1,400 degrees Celsius). A typical T dwarf has a temperature of 1,700 degrees Fahrenheit (900 degrees Celsius). The coldest Y dwarf so far identified by WISE has a temperature of less than about 80 degrees Fahrenheit (25 degrees Celsius).
Sources: starchild.gsfc.nasa.gov & nasa.gov
image credit: NASA / JPL-Caltech
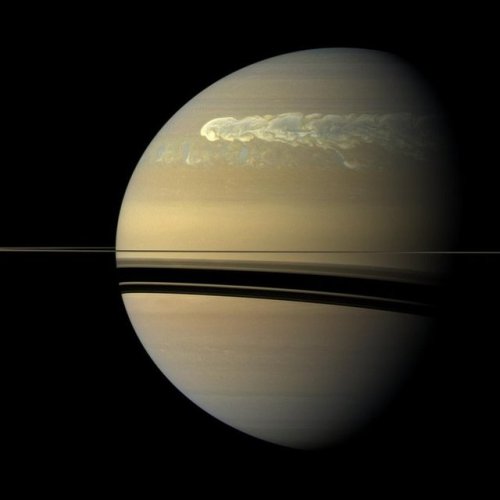








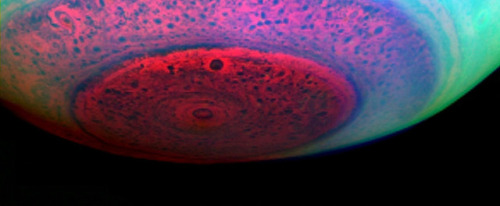
Saturn’s atmosphere exhibits a banded pattern similar to Jupiter’s, but Saturn’s bands are much fainter and are much wider near the equator. The nomenclature used to describe these bands is the same as on Jupiter. Saturn’s finer cloud patterns were not observed until the flybys of the Voyager spacecraft during the 1980s. Since then, Earth-based telescopy has improved to the point where regular observations can be made. The composition of the clouds varies with depth and increasing pressure.
The winds on Saturn are the second fastest among the Solar System’s planets, after Neptune’s. Voyager data indicate peak easterly winds of 500 m/s (1,800 km/h).
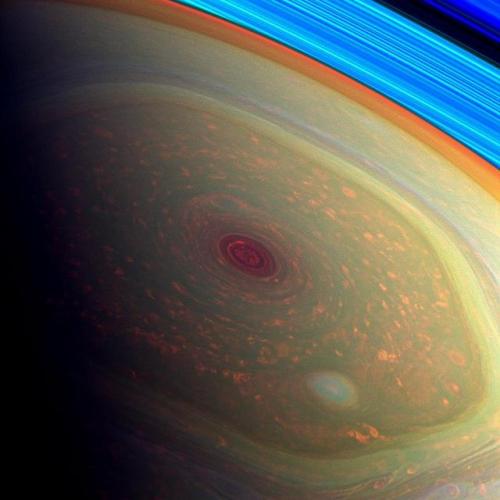
Thermography has shown that Saturn’s south pole has a warm polar vortex, the only known example of such a phenomenon in the Solar System. Whereas temperatures on Saturn are normally −185 °C, temperatures on the vortex often reach as high as −122 °C, suspected to be the warmest spot on Saturn.
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Space Science Institute and Kevin M. Gill


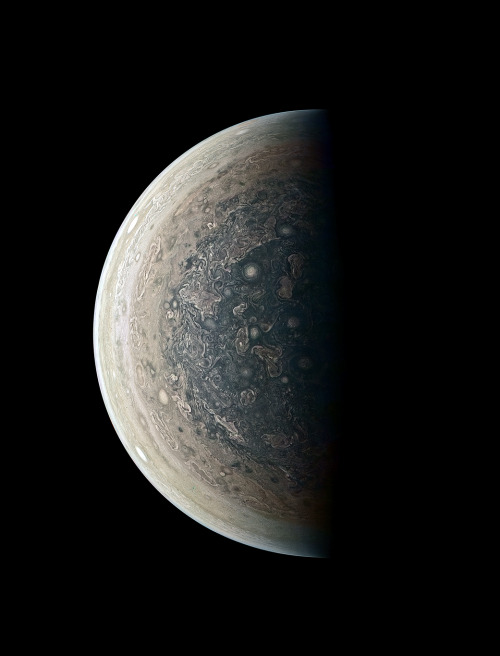
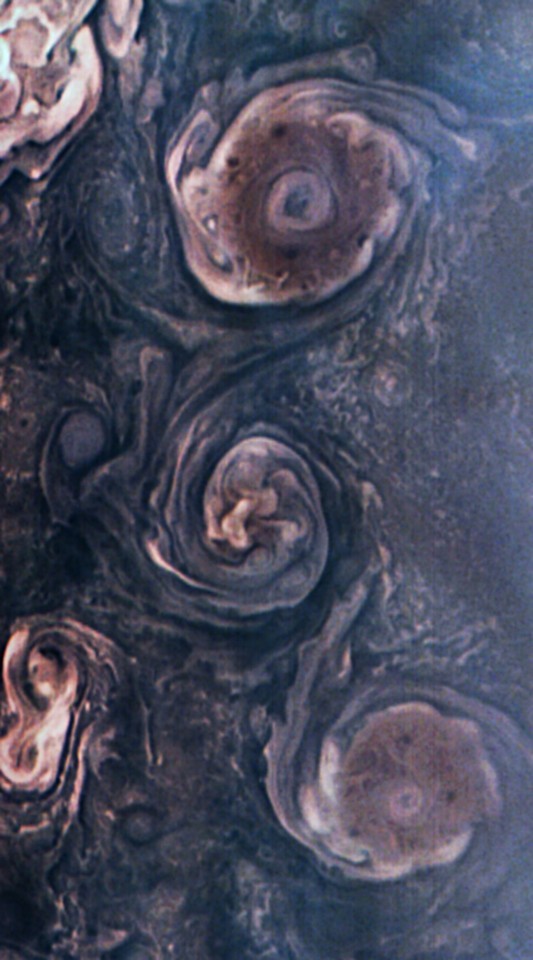
In Roman mythology, the god Jupiter drew a veil of clouds around himself to hide his mischief. It was only Jupiter’s wife, the goddess Juno, who could peer through the clouds and reveal Jupiter’s true nature. Our @NASAJuno spacecraft is looking beneath the clouds of the massive gas giant, not seeking signs of misbehavior, but helping us to understand the planet’s structure and history… Now, @NASAJuno just published its first findings on the amount of water in the gas giant’s atmosphere. The Juno results estimate that at the equator, water makes up about 0.25% of the molecules in Jupiter’s atmosphere — almost three times that of the Sun. An accurate total estimate of this water is critical to solving the mystery of how our solar system formed.
The JunoCam imager aboard Juno captured this image of Jupiter’s southern equatorial region on Sept. 1, 2017. The bottom image is oriented so Jupiter’s poles (not visible) run left-to-right of frame.
Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS/Kevin M. Gill
-
 ferrrrrxd liked this · 4 years ago
ferrrrrxd liked this · 4 years ago -
 melisa-may-taylor72 reblogged this · 4 years ago
melisa-may-taylor72 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 melisa-may-taylor72 liked this · 4 years ago
melisa-may-taylor72 liked this · 4 years ago -
 jackolynsparrow liked this · 4 years ago
jackolynsparrow liked this · 4 years ago -
 l-over-bo-y liked this · 4 years ago
l-over-bo-y liked this · 4 years ago -
 trinikins liked this · 4 years ago
trinikins liked this · 4 years ago -
 slaphappywench reblogged this · 5 years ago
slaphappywench reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 vintagebrandyrose reblogged this · 5 years ago
vintagebrandyrose reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 nlockett liked this · 5 years ago
nlockett liked this · 5 years ago -
 ever-student liked this · 5 years ago
ever-student liked this · 5 years ago -
 mickmacker23 reblogged this · 5 years ago
mickmacker23 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 gymrat21 liked this · 5 years ago
gymrat21 liked this · 5 years ago -
 ayydaisy-blog liked this · 5 years ago
ayydaisy-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 666sv-blog liked this · 5 years ago
666sv-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 cloudy457 reblogged this · 5 years ago
cloudy457 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 akita-kira liked this · 5 years ago
akita-kira liked this · 5 years ago -
 elorna liked this · 5 years ago
elorna liked this · 5 years ago -
 firebirdtransam68 liked this · 5 years ago
firebirdtransam68 liked this · 5 years ago -
 ambersagt reblogged this · 5 years ago
ambersagt reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 zippy6958 liked this · 5 years ago
zippy6958 liked this · 5 years ago -
 sexgodsonnett-blog liked this · 5 years ago
sexgodsonnett-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 mothershipiv liked this · 5 years ago
mothershipiv liked this · 5 years ago -
 man-handler liked this · 5 years ago
man-handler liked this · 5 years ago -
 ivkraft liked this · 5 years ago
ivkraft liked this · 5 years ago -
 strikelikeahawk liked this · 5 years ago
strikelikeahawk liked this · 5 years ago -
 ruthsic reblogged this · 5 years ago
ruthsic reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 totoedu liked this · 5 years ago
totoedu liked this · 5 years ago -
 gilglirthemaia liked this · 5 years ago
gilglirthemaia liked this · 5 years ago -
 magistermantis reblogged this · 5 years ago
magistermantis reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 magistermantis liked this · 5 years ago
magistermantis liked this · 5 years ago -
 soyala04 reblogged this · 5 years ago
soyala04 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 the-enemys-gate-is-down liked this · 5 years ago
the-enemys-gate-is-down liked this · 5 years ago -
 remichuuu liked this · 5 years ago
remichuuu liked this · 5 years ago -
 astrolui liked this · 5 years ago
astrolui liked this · 5 years ago -
 mariorafael liked this · 5 years ago
mariorafael liked this · 5 years ago -
 sevenxe7 liked this · 5 years ago
sevenxe7 liked this · 5 years ago

Amateur astronomer, owns a telescope. This is a side blog to satiate my science-y cravings! I haven't yet mustered the courage to put up my personal astro-stuff here. Main blog : @an-abyss-called-life
212 posts