Kevin Delaney Has Shown Us How To Make Toothpaste For Elephants!
What are some of your favorite science segments from the Tonight Show?
Hey, @luminarysiralexrluma!
We <3 science here at The Tonight Show!

Kevin Delaney has shown us how to make toothpaste for elephants!

We’ve made ping-pong balls fly.


And Kevin even hung out backstage to share 8 interesting science facts!

Jimmy and Bill Gates tried poop water.
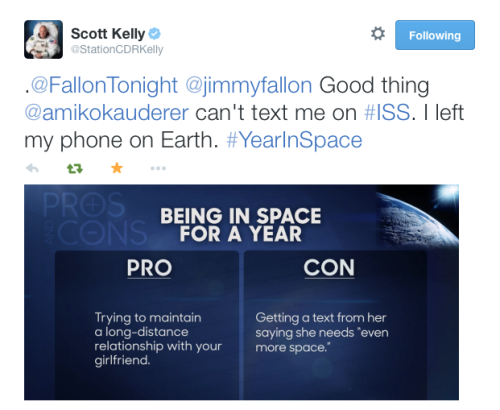
Jimmy, Julia Louis-Dreyfus, and Astronaut Scott Kelly became friends via Twitter!

Neil DeGrasse Tyson schooled us on physics!

And we tried to sell Charles Barkley on space travel!
Science rules!
Hope your week is out of this world! - Noah
More Posts from Smartler and Others

Lest we forget
funny tumblr [via imgur]
Where are her pants?









Water on Mars!

Did you hear? New findings from our Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) provide the strongest evidence yet that liquid water flows intermittently on present-day Mars.
Using an imaging spectrometer on MRO, we found hydrated minerals on slopes where mysterious streaks are seen on Mars. One thing that researchers noticed was that the darkish streaks appear to ebb and flow over time. During warm seasons, they darken and then fade in cooler seasons.

When discovered in 2010, these downhill flows known as recurring slope lineae (RSL) were thought to be related to liquid water. With the recent spectral detection of molecular water, we’re able to say it’s likely a shallow subsurface flow explains the darkening.
Mars is so cold, how could liquid water flow there? Great question! Since this liquid water is briny, the freezing point would be lower than that of pure water. Also, these saline slopes appear on Mars when temperatures are above minus 10 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 23 Celsius).
The dark, narrow streaks flowing downhill in the below image are roughly the length of a football field.

So there’s water, but how much? Currently we think this area has a very small amount of water, probably just enough to wet the top layer of the surface of Mars. The streaks are around four to five meters wide and 200 to 300 meters long.
Could humans drink this water? The salts in the water appear to be perchlorates, so you probably wouldn’t want to drink the water. It would most likely be very salty and would need to be purified before human consumption.
Perchlorate…What is that? A perchlorate is a salt that absorbs water from the air. Learn more about how it’s helping us unlock the mysteries of Mars in this video:
What’s next? We want to look for more locations where brine flows may occur. We have only covered 3% of Mars at resolutions high enough to see these features.
For more information on the Mars announcement, visit our Journey to Mars landing page. There is also a full recap of the press conference HERE, and a short recap below.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com



When can I see the supermoon eclipse tomorrow night?
On Sunday night, people in parts of western Europe, western Africa, North America and all of South America will be able to see a lunar eclipse. And this one’s extra special, because the moon will be at its perigee – the closest it gets to Earth. Not only will the moon turn red (learn why it turns red here) it will seem larger than usual.
In the first GIF I’ve listed the times the moon will enter Earth’s faint shadow (the penumbra) and then its darker, red-tinted shadow. You can figure out exact times for your location using the U.S. Naval Observatory’s handy calculator.
The second GIF shows the eclipse from another perspective - looking down on Earth’s north pole. This is to scale. It always surprises me to see how far apart the moon (the white dot) and earth (the blue circle) really are. The sun is off screen to the right, casting a long shadow. The colored lines radiating from earth show the approximate horizon lines in the four time zones. Once the lines pass, the moon is visible. Everyone in the contiguous US will be able to see the eclipse, but only people in the Easter and Central time zones will be able to see it start.
(If you want this information in song, some awesome sixth graders from Old High Middle School in Arkansas updated my eclipse song from last year. Or check out this completely original and funny song by Scarlett Simmons).
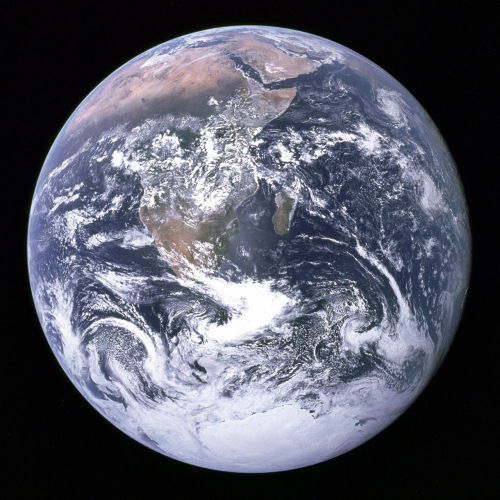
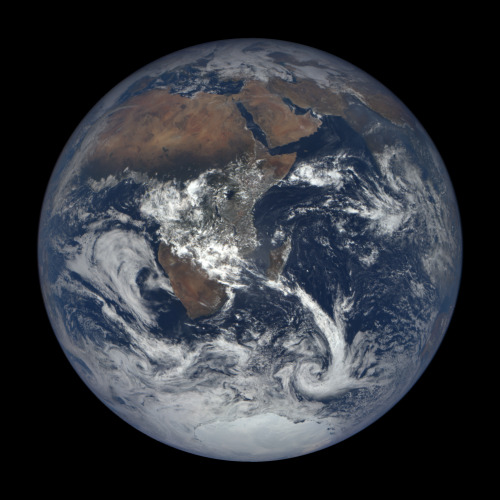






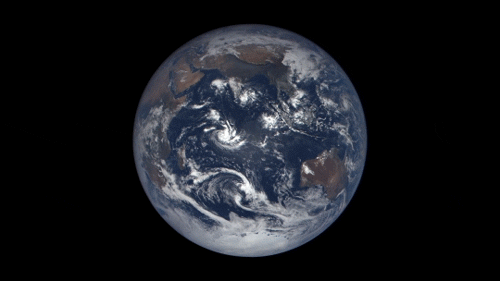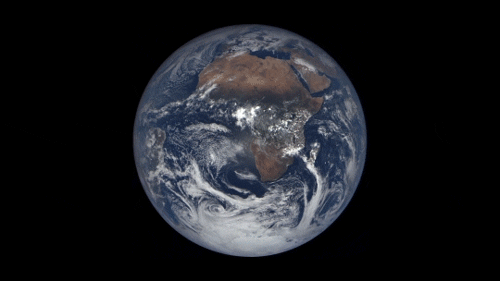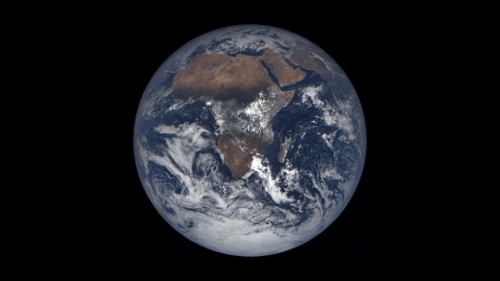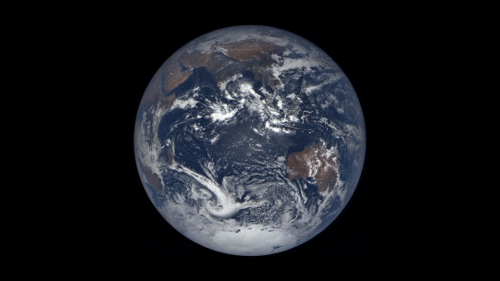
43 years ago, on December 7, 1972, the crew of Apollo 17 snapped a shot of the nearly fully illuminated Earth on their way to the moon. It became an iconic image representing Earth’s frailty and the global activist movements of the 70s.
Since then, no human has been far enough away from Earth to capture the entire globe. But thanks to a satellite called the Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR) we can now see up to date new blue marble-esque images almost every day.
The satellite monitors solar wind and solar magnetic storms to help scientists better forecast severe space weather events that can actually knock out power here on earth. It sits some 900,000 miles away from earth at Lagrangian Point 1, a place in space the pull of the earth and the sun balance each other out and a satellite can maintain a stable position.
On board, NASA’s Earth Polychromatic Imaging Camera (EPIC) is perpetually staring back at Earth, capturing images of our planet and beaming them home. You can see them at this website.










From water on Mars to Pluto’s heart, 2015 was a huge year of discovery for NASA. These don’t even mention, the “close encounters” we had with celestial objects this year.
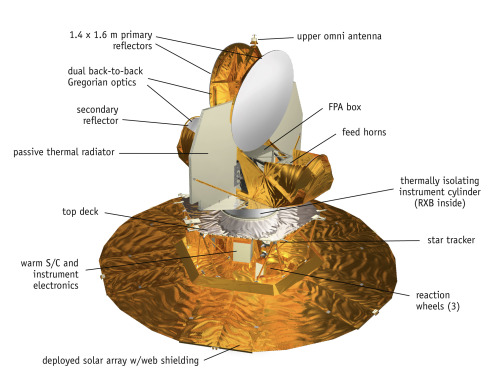
The WMAP only had a 9 year mission. It was deactivated October 28, 2010 after 9 years, 1 month and 19 days in space collecting data to help Scientists make some of the most awesome discoveries in the last several decades of mankind.
http://astronomyisawesome.com/universe/the-age-of-the-universe/

Check out our infographic on Venus here: http://astronomyisawesome.com/infographics/10-facts-about-venus/
Shine bright like a blood strain
Net-The-Average-Boy (via not-the-average-boy)
Net the average boy?
-
 thenorthernlytes liked this · 8 years ago
thenorthernlytes liked this · 8 years ago -
 martilizzy liked this · 8 years ago
martilizzy liked this · 8 years ago -
 goldeneagletree-old reblogged this · 8 years ago
goldeneagletree-old reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 rinablet liked this · 9 years ago
rinablet liked this · 9 years ago -
 strawberriesinheavysyrup liked this · 9 years ago
strawberriesinheavysyrup liked this · 9 years ago -
 nippytubes liked this · 9 years ago
nippytubes liked this · 9 years ago -
 huesofjadeharley reblogged this · 9 years ago
huesofjadeharley reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 almondandpistachio95 reblogged this · 9 years ago
almondandpistachio95 reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 chefreeni reblogged this · 9 years ago
chefreeni reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 spiderdave-blog1 reblogged this · 9 years ago
spiderdave-blog1 reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 dontfeedthescientists reblogged this · 9 years ago
dontfeedthescientists reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 almondandpistachio95 reblogged this · 9 years ago
almondandpistachio95 reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 keepupwithmyrandomness reblogged this · 9 years ago
keepupwithmyrandomness reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 suicidalneurotica liked this · 9 years ago
suicidalneurotica liked this · 9 years ago -
 tackyunicornprincess reblogged this · 9 years ago
tackyunicornprincess reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 tackyunicornprincess liked this · 9 years ago
tackyunicornprincess liked this · 9 years ago -
 sylviabastroschen-blog liked this · 9 years ago
sylviabastroschen-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 crazyecho liked this · 9 years ago
crazyecho liked this · 9 years ago -
 listen-look-feel reblogged this · 9 years ago
listen-look-feel reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 asmeikal liked this · 9 years ago
asmeikal liked this · 9 years ago -
 johnjohnz liked this · 9 years ago
johnjohnz liked this · 9 years ago -
 your-majestbug liked this · 9 years ago
your-majestbug liked this · 9 years ago -
 sexual-pan69 reblogged this · 9 years ago
sexual-pan69 reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 sexual-pan69 liked this · 9 years ago
sexual-pan69 liked this · 9 years ago -
 saskia-the-fucking-dragon-slayer liked this · 9 years ago
saskia-the-fucking-dragon-slayer liked this · 9 years ago -
 memorylog-reari reblogged this · 9 years ago
memorylog-reari reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 crotchbiscuits liked this · 9 years ago
crotchbiscuits liked this · 9 years ago -
 lillarissa-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago
lillarissa-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 sweetinnocentphotographer liked this · 9 years ago
sweetinnocentphotographer liked this · 9 years ago -
 alfonzwerth liked this · 9 years ago
alfonzwerth liked this · 9 years ago -
 plutoflash2 liked this · 9 years ago
plutoflash2 liked this · 9 years ago -
 tatateeth reblogged this · 9 years ago
tatateeth reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 tatateeth liked this · 9 years ago
tatateeth liked this · 9 years ago -
 landoftheexies-blog liked this · 9 years ago
landoftheexies-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 rationaleidolon reblogged this · 9 years ago
rationaleidolon reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 galenharris liked this · 9 years ago
galenharris liked this · 9 years ago -
 profoundmisfitdichotomy liked this · 9 years ago
profoundmisfitdichotomy liked this · 9 years ago -
 angelina-amethyst liked this · 9 years ago
angelina-amethyst liked this · 9 years ago -
 adventure-through-my-lens liked this · 9 years ago
adventure-through-my-lens liked this · 9 years ago -
 leornado-doujinshi-blog liked this · 9 years ago
leornado-doujinshi-blog liked this · 9 years ago