There Are Many Different Ways To Make Nanomaterials But Weaving, The Oldest And Most Enduring Method
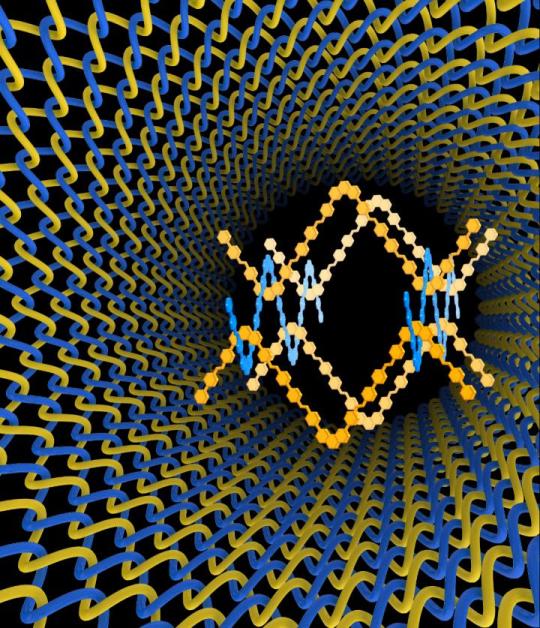
There are many different ways to make nanomaterials but weaving, the oldest and most enduring method of making fabrics, has not been one of them – until now. An international collaboration led by scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and the University of California (UC) Berkeley, has woven the first three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks (COFs) from helical organic threads. The woven COFs display significant advantages in structural flexibility, resiliency and reversibility over previous COFs – materials that are highly prized for their potential to capture and store carbon dioxide then convert it into valuable chemical products.
“We have taken the art of weaving into the atomic and molecular level, giving us a powerful new way of manipulating matter with incredible precision in order to achieve unique and valuable mechanical properties,” says Omar Yaghi, a chemist who holds joint appointments with Berkeley Lab’s Materials Sciences Division and UC Berkeley’s Chemistry Department, and is the co-director of the Kavli Energy NanoScience Institute (Kavli-ENSI).
“Weaving in chemistry has been long sought after and is unknown in biology,” Yaghi says. “However, we have found a way of weaving organic threads that enables us to design and make complex two- and three-dimensional organic extended structures.”
Continue Reading.
More Posts from Smartler and Others
(Credits go to TaySwiftVidz)
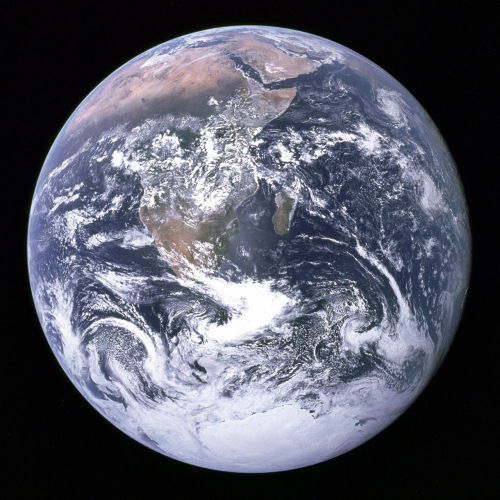
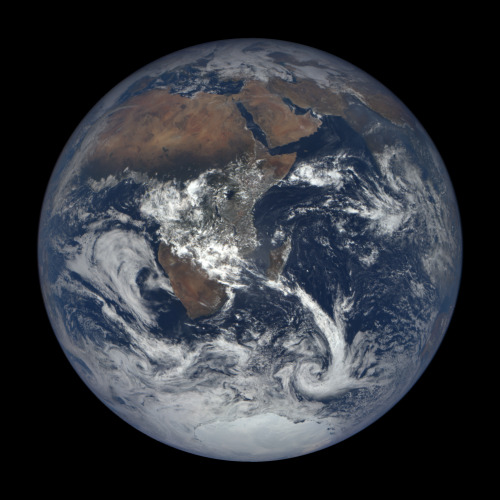







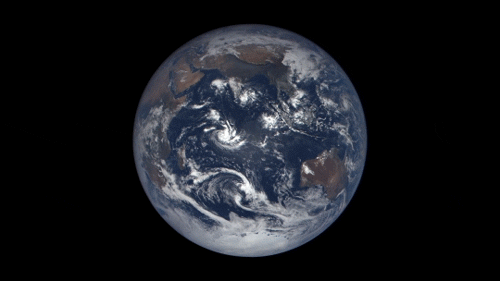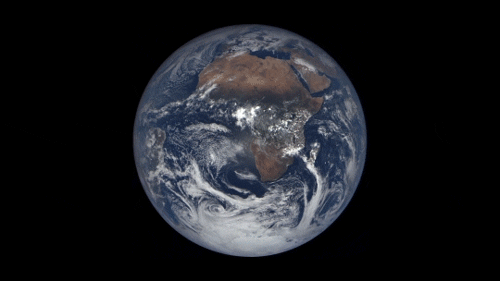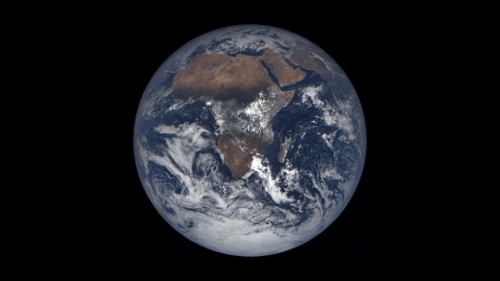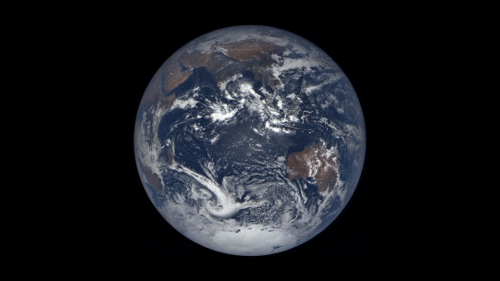
43 years ago, on December 7, 1972, the crew of Apollo 17 snapped a shot of the nearly fully illuminated Earth on their way to the moon. It became an iconic image representing Earth’s frailty and the global activist movements of the 70s.
Since then, no human has been far enough away from Earth to capture the entire globe. But thanks to a satellite called the Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR) we can now see up to date new blue marble-esque images almost every day.
The satellite monitors solar wind and solar magnetic storms to help scientists better forecast severe space weather events that can actually knock out power here on earth. It sits some 900,000 miles away from earth at Lagrangian Point 1, a place in space the pull of the earth and the sun balance each other out and a satellite can maintain a stable position.
On board, NASA’s Earth Polychromatic Imaging Camera (EPIC) is perpetually staring back at Earth, capturing images of our planet and beaming them home. You can see them at this website.
New video on the Hubble Sequence! Had a lot of fun making this one, enjoy!

My life in a picture



For a moment, that black and white photo should seem like a full color image. (You have to keep both the image and your head very still).
This illusion was used in the new BBC Four series Colour: The Spectrum of Science.
It demonstrates a phenomenon called “cone fatigue.” When we stare at the purple hillside in picture above, photoreceptors in our eyes called cones are stimulated. They send a signal to our brains that says “You’re looking at something purple.” But the sensing ability of those cones decreases the longer we stare at the image - those receptors are, in a way, temporarily used up.
Then when we look at the black and white image, those same cones can’t detect any purple light. Instead they sense the color that remains: green.
Tonight: A Supermoon Lunar Eclipse
(via APOD; Video Credit: NASA’s GSFC, David Ladd (USRA) & Krystofer Kim (USRA) )
Tonight a bright full Moon will fade to red. Tonight’s moon will be particularly bright because it is reaching its fully lit phase when it is relatively close to the Earth in its elliptical orbit. In fact, by some measures of size and brightness, tonight’s full Moon is designated a supermoon, although perhaps the “super” is overstated because it will be only a few percent larger and brighter than the average full Moon. However, our Moon will fade to a dim red because it will also undergo a total lunar eclipse – an episode when the Moon becomes completely engulfed in Earth’s shadow. The faint red color results from blue sunlight being more strongly scattered away by the Earth’s atmosphere. Tonight’s moon can also be called a Harvest Moon as it is the full Moon that occurs closest to the September equinox, a time signaling crop harvest in Earth’s northern hemisphere. Total eclipses of supermoons are relatively rare – the last supermoon lunar eclipse was in 1982, and the next will be in 2033. Tonight’s supermoon total eclipse will last over an hour and be best visible from eastern North America after sunset, South America in the middle of the night, and Western Europe before sunrise.










Here are ten thoughts that will change the way you think about existence.
8 of the world’s most bizarre flowers:
1.) Swaddled Babies

2.) Flying Duck Orchid

3.) Hooker’s Lips Orchid

4.) Ballerina Orchid

5.) Monkey Orchid

6.) Naked Man Orchid

7.) Laughing Bumblebee Orchid

8.) White Egret Orchid


(photo by Fallska)
-
 imiq liked this · 8 years ago
imiq liked this · 8 years ago -
 demonputty reblogged this · 8 years ago
demonputty reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 joaoscatarino reblogged this · 9 years ago
joaoscatarino reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 tumorravenus3 reblogged this · 9 years ago
tumorravenus3 reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 tumorravenus3 liked this · 9 years ago
tumorravenus3 liked this · 9 years ago -
 vapingonland liked this · 9 years ago
vapingonland liked this · 9 years ago -
 nessinby liked this · 9 years ago
nessinby liked this · 9 years ago -
 deltaperseii liked this · 9 years ago
deltaperseii liked this · 9 years ago -
 tratane reblogged this · 9 years ago
tratane reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 tratane liked this · 9 years ago
tratane liked this · 9 years ago -
 goddessofblood liked this · 9 years ago
goddessofblood liked this · 9 years ago -
 willem2de liked this · 9 years ago
willem2de liked this · 9 years ago -
 demisexuali-titty liked this · 9 years ago
demisexuali-titty liked this · 9 years ago -
 magneticmagpie reblogged this · 9 years ago
magneticmagpie reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 livingloopholes liked this · 9 years ago
livingloopholes liked this · 9 years ago -
 spiderdave-blog1 reblogged this · 9 years ago
spiderdave-blog1 reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 aslimewithagun reblogged this · 9 years ago
aslimewithagun reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 1kristabean1-blog liked this · 9 years ago
1kristabean1-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 westcoastwildflower reblogged this · 9 years ago
westcoastwildflower reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 tempustrove-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago
tempustrove-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 skadoo3 reblogged this · 9 years ago
skadoo3 reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 the-electric-boogaloo reblogged this · 9 years ago
the-electric-boogaloo reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 hgg77 liked this · 9 years ago
hgg77 liked this · 9 years ago -
 skadoo3 liked this · 9 years ago
skadoo3 liked this · 9 years ago -
 sciencetylia reblogged this · 9 years ago
sciencetylia reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 warriorofsass reblogged this · 9 years ago
warriorofsass reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 incorporateoleate-blog liked this · 9 years ago
incorporateoleate-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 upcomingart-gallery liked this · 9 years ago
upcomingart-gallery liked this · 9 years ago -
 tetrahydrofuran liked this · 9 years ago
tetrahydrofuran liked this · 9 years ago -
 axell101 reblogged this · 9 years ago
axell101 reblogged this · 9 years ago