Submitted By @asapscience
Submitted by @asapscience
Science is so amazing, but it’s being de-funded around the world. We hope to make a difference with this video:
Your sharing is greatly appreciated.
More Posts from Smartler and Others









I love Science bracelet
DNA Ring
I love Science Necklace
Science Pencil Case
Science Shot Glasses
DNA Necklace
Science Poster
Science Necklace
Here is where you can find more amazing products from etsy.

For more amazing images and posts about how Astronomy is Awesome, check us out!
http://astronomyisawesome.com/
As always, please feel free to ask questions and we love it when you reblog!
#astronomy #space #nasa #hubble space telescope #nebula #nebulae #galaxy
“This Love” - Taylor Swift (Piano & String Version) by Sam Yung.
credit to the owners

Chemical flames.
Sea otters—gardeners of the eel grass

Photo: Ron Eby
In the 1970s, researchers discovered that kelp forests are healthier and home to many more species with otters than without them. By keeping kelp-devouring sea urchins in check, otters promote kelp growth, which in turn supports a diverse community of algae, fish, invertebrates, and marine mammals.
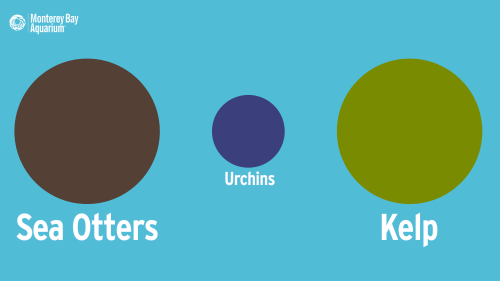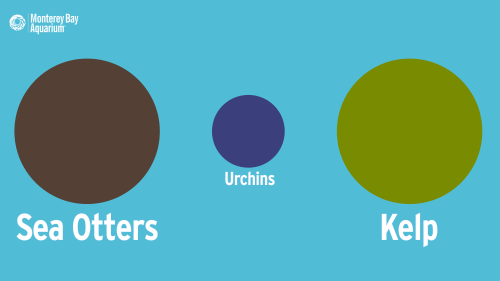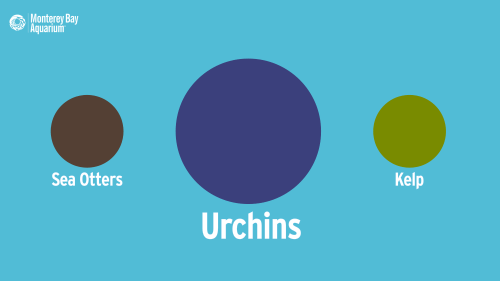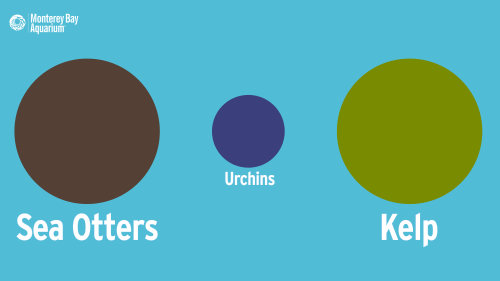
If otter abundance is up, so is the kelp’s; if urchin abundance is up, the otter and kelp abundance will be down. This domino effect is called a three-step trophic cascade.
But wait, there’s more!

Photo: Ron Eby
Researchers from UC Santa Cruz monitoring sea otters living in Elkhorn Slough, an estuary in Monterey Bay, noticed something incredible: after otters moved into the area, the eel grass beds became healthier. They took a closer look and discovered that otters are also a keystone species in the eel grass community!


We’ve been studying sea otters for over 30 years, and they continue to impress us every day.
Simple actions—like protecting sea otters—can have drastic, surprising, and positive impacts throughout the environment. To find out how you—yep, you, right there—can help us continue our research, take a look at our Sea Otter Program page.
Here’s to the next 30 years of sea otter research!







The last, but not least of starry scholastic month!
This week’s entry: Black Holes
http://www.space.com/15421-black-holes-facts-formation-discovery-sdcmp.html
http://www.space.com/19339-black-holes-facts-explained-infographic.html

Lest we forget
funny tumblr [via imgur]


reindeer are the only mammals whose eyes are known to change colour, going from a gold in the summer, when the sun is a constant presence in the arctic, to a less reflective blue in the near perpetually dark winter months.
in dark conditions, muscles in your irises contract to dilate your pupils and allow more light into your eyes. when it’s bright again, the irises widen and the pupils shrink. the same thing happens in reindeer, but the arctic winter forces their pupils dilate for months at a time.
this constant effort to stay dilated ends up blocking the small vessels that drain fluid out of the eyes, which causes pressure to build up. this in turn compresses the collagen fibers that make up tapetum - a mirrored layer that sits behind the retina (seen in the second photo).
when compressed, these fibers in the eye reflect blue wavelengths of lights instead of the yellow which accompanies a typical spacing of the fibers, as in summer. (photos x, x)
-
 inamabile reblogged this · 5 years ago
inamabile reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 perfural reblogged this · 7 years ago
perfural reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 venusian-8 reblogged this · 9 years ago
venusian-8 reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 india93 reblogged this · 9 years ago
india93 reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 perfural liked this · 9 years ago
perfural liked this · 9 years ago -
 skinzu reblogged this · 9 years ago
skinzu reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 thestarsniper liked this · 9 years ago
thestarsniper liked this · 9 years ago -
 thestarsniper reblogged this · 9 years ago
thestarsniper reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 chris-basquiat reblogged this · 9 years ago
chris-basquiat reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 com-passio liked this · 9 years ago
com-passio liked this · 9 years ago -
 maturerusername reblogged this · 9 years ago
maturerusername reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 kaxtniss liked this · 9 years ago
kaxtniss liked this · 9 years ago -
 thecosmicquest liked this · 9 years ago
thecosmicquest liked this · 9 years ago -
 wormwizerd liked this · 9 years ago
wormwizerd liked this · 9 years ago -
 saltshaker1234 reblogged this · 9 years ago
saltshaker1234 reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 theycallmebobcat liked this · 9 years ago
theycallmebobcat liked this · 9 years ago -
 wojnicz reblogged this · 9 years ago
wojnicz reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 kitsunwho reblogged this · 9 years ago
kitsunwho reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 kitsunwho liked this · 9 years ago
kitsunwho liked this · 9 years ago -
 aesthleteuniverse reblogged this · 9 years ago
aesthleteuniverse reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 aesthleteuniverse liked this · 9 years ago
aesthleteuniverse liked this · 9 years ago -
 barbarabyers liked this · 9 years ago
barbarabyers liked this · 9 years ago -
 sabreman82 liked this · 9 years ago
sabreman82 liked this · 9 years ago -
 bassplayinbabe reblogged this · 9 years ago
bassplayinbabe reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 silence-sea-and-sky liked this · 9 years ago
silence-sea-and-sky liked this · 9 years ago -
 leek77 liked this · 9 years ago
leek77 liked this · 9 years ago -
 dreaming-or-sinking liked this · 9 years ago
dreaming-or-sinking liked this · 9 years ago -
 toomentallyhilarious reblogged this · 9 years ago
toomentallyhilarious reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 onceuponadnastrand reblogged this · 9 years ago
onceuponadnastrand reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 nicolehazel2 reblogged this · 9 years ago
nicolehazel2 reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 nicolehazel2 liked this · 9 years ago
nicolehazel2 liked this · 9 years ago -
 todd-the-foxx reblogged this · 9 years ago
todd-the-foxx reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 todd-the-foxx liked this · 9 years ago
todd-the-foxx liked this · 9 years ago -
 big-x liked this · 9 years ago
big-x liked this · 9 years ago -
 big-x reblogged this · 9 years ago
big-x reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 littlemeanings liked this · 9 years ago
littlemeanings liked this · 9 years ago -
 bubblewrench liked this · 9 years ago
bubblewrench liked this · 9 years ago