PBS Eons: How We Identified One Of Earth’s Earliest Animals:
PBS Eons: How We Identified One of Earth’s Earliest Animals:
Scientists had no idea what type of organisms the life forms of the Ediacaran were—lichen, colonies of bacteria, fungi or something else. It turns out, the key to solving the puzzle of Precambrian life was a tiny bit of fossilized fat.
More Posts from Sawgrassnaturecenter and Others

One of the SNC’s permanent residents is a red rat snake we call Big Red. Red Rat Snakes are native to Florida and can be commonly found in the Everglades. All snakes have an ecological role to play in the environment, so even if you don’t like them, it is in our best interests to respect them and leave them alone.
If you want to learn more about red rat snakes and how the SNC helps them, click the link: https://sawgrassnaturecenter.org/2014/11/07/lets-learn-about-rat-snakes/
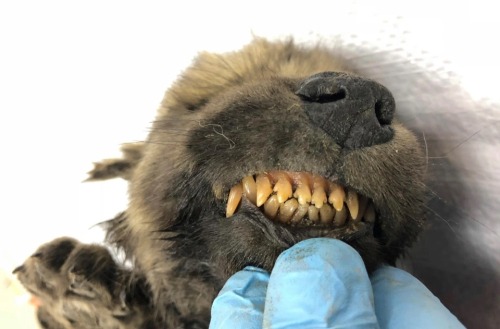

Dogor is the 18,000 year old pup that was found within the Siberian Permafrost, yet is not quite a dog nor a wolf, but a puzzling connection to both.
Dogor has been miraculously preserved within the permafrost, with its fur, teeth and even whiskers incredibly intact. Radiocarbon dating has placed the animal at 18,000 years old and researchers have suggested that the animal passed away at just 2 months old. The name Dogor means “Friend” in Yakut, a language spoken within Eastern Siberia.
Generally, genetic analysis can quite easily discern whether a discovered canine is a wolf or dog, but in this instance, the genetics suggest that it could be an ancestral link to both. Interestingly, Dogor lived at a time in canine evolutionary history when dogs and wolves began to branch off from each other.The general scientific consensus is that dogs and wolves split from a common ancestor, however, the process of how “dogs became dogs” is certainly contested, and Dogor could be a crucial piece in that puzzle.
If Dogor is determined to be a dog, it will be the oldest ever discovered. The next oldest, the Bonn-Oberkassel puppy, was discovered in Germany and was clearly determined to be a dog of around 14,000 years old, buried with a man and a woman.
The progression of climate change is melting the permafrost more rapidly, and discoveries like these are becoming more and more commonplace.
Images via Sergey Fedorov/The Siberian Times
Beautiful pictures



butterfly
Check out our resident red-shoulder hawk. A Florida native, this bird of prey has a distinct call that is uses to signal we are encroaching on his territory. Does this call sound familiar to you?
Red-Tailed Hawks can be found all over North America!
This is one of our resident parrots, Fred. Fred and his partner in crime, Alice, were surrendered upon the death of their owner to the Sawgrass Nature Center. In captivity, this particular species of parrot can live up to 80 years.







Hi! My name is Abby De la Rocha and I am the Volunteer Coordinator at the Sawgrass Nature Center and Wildlife Hospital in Coral Springs, Florida. I was born in Puerto Rico and lived there until my family moved to Botswana when I was 8 years old. I returned to Puerto Rico when I was 16 and finished high school in Ponce. I then moved to New Orleans where I studied at Loyola University. I have been in Florida since 2006.
In this post, I’m going to tell you about Hispanic Heritage month as well as some interesting facts about Puerto Rico’s agriculture and its most precious ecosystem El Yunque.
What is Hispanic Heritage Month?
Each year, we observe National Hispanic Heritage Month from September 15 to October 15 by celebrating the histories, cultures, and contributions of American citizens whose ancestors came from Spain, Mexico, the Caribbean, and Central and South America.
This year’s Hispanic Heritage Month theme- Hispanics: Be Proud of Your Past, Embrace the Future – invites us to embrace our backgrounds, to be proud of who we are and where we came from.
Embracing the Future
The future of agriculture in Puerto Rico
Currently, Puerto Rico imports 85% of its food. This is a huge vulnerability for an island with a population of 3.1 million. For several years, my family has been involved in the agroecological movement which seeks to increase the self-sufficiency of Puerto Rico through their agricultural project Finca El Reverdecer. This movement has been largely spearheaded by young people who are eager to make a difference. I believe that by looking at our past we can create a better future.
The present agricultural reality of Puerto Rico can be traced back to Puerto Rico’s history as a Spanish colony and later as a Commonwealth of the United States. The establishment of the monoculture of sugarcane meant that many Puerto Ricans worked on sugarcane plantations. My grandfather worked cutting cane during his youth. Later, he would go on to own land that he cultivated for his own consumption. At the age of 93 he continues to enjoy getting his hands dirty on my parents’ farm.
Eventually, the sugarcane industry on the island collapsed. Its demise was due to various factors including hurricanes that decimated the island as well as policies imposed by the Federal Government. In particular, a land tax imposed in 1901 known as the Hollander Bill. As a result of this bill, many local farmers were forced to sell their land. This eventually led to mass migration from the island to the mainland. It also led to a decrease in farming in general as people did not have land to farm. Subsequently, attitudes towards farming became unfavorable, especially among young people. This is changing. Today, many small farms produce high-quality products that are sought out by individuals and restaurants alike. While still a work in progress, the path to agricultural self-sufficiency is being forged.
Celebrating the only U.S. National Forest located on an island
The El Yunque National Forest is the only tropical rainforest in the national forest system. At nearly 29,000 acres, it is one of the smallest in size, yet one of the most biologically diverse.
The United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service. (2020) describes El Yunque, “Caressed by gentle easterly winds the forest has an average temperature of 73° F, and seasonal changes are almost imperceptible. It is the ideal climate for exuberant tropical vegetation. The rain forest is noted for its biodiversity; it is “home” to thousands of native plants including 150 fern species, 240 tree species (88 of these are endemic or rare and 23 are exclusively found in this forest). The El Yunque National Forest has no large wildlife species, but hundreds of smaller animals abound in this gentle forest, many of which exist nowhere else on the planet.”
To embrace the future, we must plan and prepare for it. Looking forwards requires us to look back at our history so that we can make sense of our present. Puerto Rico’s future is being planned by those who work the land in order to provide food for its people as well as those who work to preserve the natural wonder that is El Yunque National Forest.
If you’d like to learn more about some of the agricultural projects on the island check out the links below:
Proyecto Agroecologico el Josco Bravo
Organización Boricuá de Agricultura Ecológica de Puerto Rico
El Departamento de la Comida
Finca El Reverdecer
References:
Charles, D. (2017, May 13) How Puerto Rico Lost Its Home-Grown Food, But Might Find It Again. NPR. Retrieved from https://www.npr.org/sections/thesalt/2017/05/13/527934047/how-puerto-rico-lost-its-home-grown-food-but-might-find-it-again
U.S. Census Bureau (2019). Quick Facts Puerto Rico. Retrieved from https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/PR.
The United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service. (2020) About the Forest. Retrieved from https://www.fs.usda.gov/main/elyunque/about-forest
Dick, D. L. (2015) U.S. Tax Imperialism in Puerto Rico. American University Law Review. Retrieved from http://www.aulawreview.org/us-tax-imperialism-in-puerto-rico/#_ftn220
https://sawgrassnaturecenter.org/2020/09/29/hispanic-heritage-month/
This Wildlife Wednesday we are featuring our resident Red Rat Snake. This guy in particular has a permanent stay at the Nature Center due to a degenerative nerve disease that causes him to twitch.
Rat Snakes are non-venomous, constrictor snakes. They also happen to be very skilled climbers, to the point where they have been known to scale brick walls! This helps them catch prey like lizards, small mammals, and hatchlings.
Rat Snakes are popular in the pet trade and have been bred in many different colors and patterns.

A Eurasian Collared Dove built a nest in our yard

There isn’t a slow season for Nature Centers and Wildlife Hospitals. There is only busy and busier season. Raccoons, squirrels, and opossums are some of the native wildlife in Florida that are most affected by growth in human population and urban expansion. Every time a new building goes up, their homes are disrupted. Every time a new highway is opened, they are the ones that sustain the most injuries. In a normal day, we see a lot of injuries. During baby season, we get many more abandoned babies.
Injured, sick, or abandoned raccoons legally require the care of a wildlife professional. So if you see one, it is not in their best interest to be raised in your home. The best option is to bring them to a local Wildlife Hospital and Nature Center.
If you want to learn more about how the SNC takes care of the native wildlife that gets brought to us, or donate to help us keep up with costs of animal care, check out our website here: https://sawgrassnaturecenter.org/

Hummingbirds Use Sense of Smell to Make Foraging Decisions: Study
http://www.sci-news.com/biology/hummingbird-olfaction-10037.html
-
 insert-meaningful-username liked this · 3 years ago
insert-meaningful-username liked this · 3 years ago -
 piscisludicrous liked this · 3 years ago
piscisludicrous liked this · 3 years ago -
 mysticalblizzardcolor liked this · 3 years ago
mysticalblizzardcolor liked this · 3 years ago -
 cherrywinethechicken liked this · 4 years ago
cherrywinethechicken liked this · 4 years ago -
 creakling reblogged this · 4 years ago
creakling reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 nicetigress7653 liked this · 4 years ago
nicetigress7653 liked this · 4 years ago -
 goulishcoffin liked this · 4 years ago
goulishcoffin liked this · 4 years ago -
 nicetigeress7653-blog liked this · 4 years ago
nicetigeress7653-blog liked this · 4 years ago -
 out-one liked this · 4 years ago
out-one liked this · 4 years ago -
 seasicksandile reblogged this · 4 years ago
seasicksandile reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 that-weird-artist-kid liked this · 4 years ago
that-weird-artist-kid liked this · 4 years ago -
 3r4d liked this · 4 years ago
3r4d liked this · 4 years ago -
 shadycomputerflower liked this · 4 years ago
shadycomputerflower liked this · 4 years ago -
 demiurge-de-fleurs reblogged this · 4 years ago
demiurge-de-fleurs reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 bookwyrmth1rt33n liked this · 4 years ago
bookwyrmth1rt33n liked this · 4 years ago -
 dog-equals-sphear reblogged this · 4 years ago
dog-equals-sphear reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 bentsc-blog liked this · 4 years ago
bentsc-blog liked this · 4 years ago -
 nakakabagot liked this · 4 years ago
nakakabagot liked this · 4 years ago -
 iamidentical liked this · 4 years ago
iamidentical liked this · 4 years ago -
 ripstikgirl1 liked this · 4 years ago
ripstikgirl1 liked this · 4 years ago -
 defalternative reblogged this · 4 years ago
defalternative reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 sciencetylia reblogged this · 4 years ago
sciencetylia reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 otusshrine liked this · 4 years ago
otusshrine liked this · 4 years ago -
 arbane235 reblogged this · 4 years ago
arbane235 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 kadaverschreiber liked this · 4 years ago
kadaverschreiber liked this · 4 years ago -
 happy-joy-joy reblogged this · 4 years ago
happy-joy-joy reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 thomasbrisenio reblogged this · 4 years ago
thomasbrisenio reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 sakuraisthill reblogged this · 4 years ago
sakuraisthill reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 sakuraisthill liked this · 4 years ago
sakuraisthill liked this · 4 years ago -
 balasora reblogged this · 4 years ago
balasora reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 theviceprovost liked this · 4 years ago
theviceprovost liked this · 4 years ago -
 endquire liked this · 4 years ago
endquire liked this · 4 years ago -
 yabadabadoodre liked this · 4 years ago
yabadabadoodre liked this · 4 years ago -
 intelligentliving reblogged this · 4 years ago
intelligentliving reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 cottonneko liked this · 4 years ago
cottonneko liked this · 4 years ago -
 picricacidsoul liked this · 4 years ago
picricacidsoul liked this · 4 years ago -
 urbancelt reblogged this · 4 years ago
urbancelt reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 urbancelt liked this · 4 years ago
urbancelt liked this · 4 years ago -
 rainbow9167 reblogged this · 4 years ago
rainbow9167 reblogged this · 4 years ago

The Sawgrass Nature Center (SNC) is a nonprofit located in South Florida. Our mission is to educate the public about native wildlife and environmental stewardship. We also rescue, rehabilitate, and release injured, orphaned, or sick wildlife. Animals that cannot be released due to permanent injuries or disabilities are given a forever home on site with animal keepers that know how to properly care for them. We are able to operate due to donations from generous patrons. If you are interested in helping us further our mission, check us out at: https://sawgrassnaturecenter.org/
202 posts