Retro-radio-active - Retroactive Radioactive

More Posts from Retro-radio-active and Others
Pioneering with Perseverance: More Technology Firsts
From launching the largest, heaviest, most sophisticated vehicle we have ever sent to Mars, to its elegant landing at Jezero Crater – a treacherous yet promising location for finding signs of ancient life – the journey of our Perseverance rover has already been and continues to be a bold one.

But let’s not forget, building new tools and instruments or designing ways to study other worlds is not easy. Before engineers even dreamt of sending their hardware for a spin on Mars, they spent years doing all they could to validate tech on Earth – modeling in labs, flying experiments on suborbital rockets or high-altitude balloons, or testing in various facilities to simulate the harsh conditions of space.

We know that technology demonstrations – that test a new capability in space – can be risky, but trying new things is how we forge ahead, learn for future missions, and reach new heights in space.
Perseverance has already accomplished some amazing “firsts” but there are more to come. Here are four more trailblazing technologies on the Mars 2020 mission.
1. First Powered Flight on Another World
This week, the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter, a small, autonomous rotorcraft originally stowed beneath the rover, will make the first-ever attempt at powered, controlled flight of an aircraft on another planet.
In the last few weeks, Ingenuity safely deployed from Perseverance, charged up its solar panel, survived its first bone-chilling Martian night and firmly planted four legs on the ground. Once the team on Earth confirms that the rover drove about 16 feet (about 5 meters) away, and that both helicopter and rover are communicating via their onboard radios, preflight checks will begin, and Ingenuity will be on its way skyward.

Perseverance will receive and relay the final flight instructions from mission controllers at our Jet Propulsion Laboratory to Ingenuity. Ingenuity will run its rotors to 2,537 rpm and, if all final self-checks look good, lift off. After climbing at a rate of about 3 feet per second (1 meter per second), the helicopter will hover at 10 feet (3 meters) above the surface for up to 30 seconds. Then, the Mars Helicopter will descend and touch back down on the Martian surface. With a smooth landing and continued operability, up to four more flights could be attempted, each one building on the success of the last.
Ingenuity could pave the way for other advanced robotic flying vehicles. Possible uses of next-generation rotorcraft on Mars include:
A unique viewpoint not provided by current orbiters, rovers or landers
High-definition images and reconnaissance for robots or humans
Access to terrain that is difficult for rovers to reach
Could even carry light but vital payloads from one site to another
Here’s how to follow along as this flight makes history.
2. First Production of Oxygen from Martian Atmosphere
The Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment, better known as MOXIE, is preparing us for human exploration of Mars by demonstrating a way to extract oxygen directly from the Martian atmosphere. That could mean access to air for breathing, but also the ability to produce vast quantities of rocket fuel to return astronauts to Earth.

Located inside the body of Perseverance, the car battery-sized instrument works like a miniature electronic tree on the rover, inhaling carbon dioxide, separating the molecule, and exhaling carbon monoxide and oxygen.

MOXIE is the first demonstration of its kind on another planet – the first test of an in-situ resource utilization technology, meaning it generates a usable product from local materials. The farther humans go into deep space, the more important this will be, due to the limited immediate access to supplies.
MOXIE will give a go at its first operations soon, a huge first step in proving it’s feasible to make oxygen, in situ, on Mars. Future, larger versions of MOXIE (something about the size of a washing machine) could produce oxygen 200 times faster by operating continuously.
3. First Weather Reporter at Jezero Crater
The Mars Environmental Dynamics Analyzer (MEDA) system makes weather measurements including wind speed and direction, temperature and humidity, and also measures the amount and size of dust particles in the Martian atmosphere.
Using MEDA data, engineers on Earth recently pieced together the first weather report from Jezero Crater. Measurements from MEDA sensors are even helping to determine the optimal time for Ingenuity’s first flight.

The weather instrument aboard the Curiosity rover – currently located a good 2,300 miles away from Perseverance on Mars – provides similar daily weather and atmospheric data. But MEDA can record the temperature at three atmospheric heights in addition to the surface temperature. It also records the radiation budget near the surface, which will help prepare for future human exploration missions on Mars.
MEDA’s weather reports, coupled with data gathered by Curiosity and NASA’s Insight lander, will enable a deeper understanding of Martian weather patterns, events, and atmospheric turbulence that could influence planning for future endeavors like the landing or launch of the proposed Mars Sample Return mission.
4. First Radar Tool to Probe Under the Martian Surface
On Earth, scientists use radar to look for things under the ground. They use it to study Mars-like glacial regions in the Arctic and Antarctic. Ground-penetrating radar helps us locate land mines; spot underground cables, wires, and pipes; or reveal ancient human artifacts and even buried treasure! On Mars, the "buried treasure" may be ice, which helps scientists understand the possibilities for Martian life and also identifies natural resources for future human explorers.
Perseverance's Radar Imager for Mars' Subsurface Experiment (RIMFAX) uses radar waves to probe the ground and reveal the unexplored world that lies beneath the Martian surface.

It’s the first ground-penetrating radar on the surface of Mars. RIMFAX will provide a highly detailed view of subsurface structures down to at least 30 feet (10 meters). With those measurements, the instrument will reveal hidden layers of geology and help find clues to past environments on Mars, especially those with conditions necessary for supporting life.
Stay tuned in to the latest Perseverance updates on the mission website and follow NASA Technology on Twitter and Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com






worm pins :^)
The Exploration Behind the Inspiration at NASA
Are we alone? How did we get here? Where are we headed?
At NASA, our mission is to explore. We visit destinations in our solar system and study worlds beyond to better understand these big questions.
We also dream. We dream of traveling to distant worlds, and what that might be like. In the video above you can see fanciful, imagined adventures to real places we’ve studied at NASA.
How We Did It
Check out how we created these otherworldly scenes in the video below. A NASA videographer used green screens to add motion and real people to bring life to our series of solar system and exoplanet travel posters.
Let’s dive into one example from the video. The shot of kayaking on Titan showcases the real rivers and lakes of liquid methane and ethane that slosh and flow on Saturn's largest moon. Titan's mysterious surface was revealed by our Cassini spacecraft, which also deployed the European Space Agency’s Huygens probe to the surface. The atmosphere on Titan is so thick, and the gravity so light, that with each strike of a paddle, you might be lofted above the swift current as you ride the tides through a narrow strait called the Throat of Kraken. NASA scientist Mike Malaska studies Titan and collaborated on the poster featured in the video. His research informed the artwork, and so did a hobby: kayaking. Those ultra-cold chemical seas might be even more of a challenge than shown here. Your boat might crack, or even dissolve, Malaska said.

We’ll learn more about Titan when our Dragonfly mission of dual quadcoptors — rotorcraft with eight blades each — visits the icy moon in 2034.
Science Never Stops
Our understanding of other worlds is always evolving, and sometimes we learn new details after we illustrate our science. In one of our travel posters, we show a traveler standing on the surface of exoplanet Kepler-16b with two shadows formed by the planet’s two suns. The planet does indeed orbit two stars, but with later size and mass refinements, we now think it would be hard to stand there and enjoy a binary sunset. There isn't a solid surface to stand on a gas planet, and that's what Kepler-16b now appears to be!
In addition to sharing how sublime science can be, these scenes are a reminder that there are lots of careers in the space program, not just scientist, engineer, or astronaut. A creative team at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California produced the travel posters, originally to help share the work of NASA's Exoplanet Exploration Program. They are the result of lots of brainstorming and discussion with real NASA scientists, engineers, and expert communicators. The video versions of these spacey travel scenes were produced by visualization experts at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
All of this work is meant to inspire, and to explore the edge of possibility. It’s also an invitation. With science, we’re stepping into the future. Join us?

Paul Johnson Aliens Magazine Cover Art (Dark Horse, 1993) https://ift.tt/2TLrMm2 November 02, 2020 at 10:43PM +visit our fellow Goethepunk art page

“Never Kill Santa Claus”









✨I love Outer Space ✨ gifs made by me :)

¡Seres de primera categoría!
Antes que las elimine del celular, les comparto mi penúltimo proyecto de arma #scifi y/o #raygun
Este divertido hobby que he estado trabajando y que además está ligado a mi trabajo literario en los diferentes géneros #punk como en la saga #Maliseche de ciencia ficción #Raypunk
Si gustan saber más de cómo realizar este proceso, les cuento que en mi instagram (www.instagram.com/jesus.todemun) podrán encontrar una mini serie del proceso realizado en otro de mis proyectos
Espero les guste ¡Nos vemos en futuros proyectos!
https://www.instagram.com/p/CTVG5oxp__A/?utm_medium=tumblr
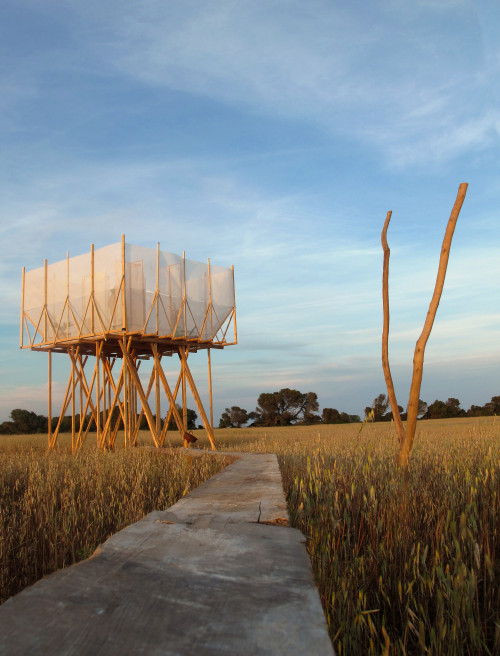

Spanish Retreat by Gartnerfuglen + Mariana de Delas
Visual Writing Prompt #87

-
 homesick92 liked this · 7 months ago
homesick92 liked this · 7 months ago -
 thewigmaster liked this · 8 months ago
thewigmaster liked this · 8 months ago -
 mothyca reblogged this · 8 months ago
mothyca reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 annaxvanity reblogged this · 8 months ago
annaxvanity reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 kottenkandykittens reblogged this · 8 months ago
kottenkandykittens reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 papichulo712 reblogged this · 8 months ago
papichulo712 reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 under-the-knife reblogged this · 8 months ago
under-the-knife reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 love-me-like-a-reptile liked this · 8 months ago
love-me-like-a-reptile liked this · 8 months ago -
 hesitantmemories reblogged this · 8 months ago
hesitantmemories reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 thedrugdude liked this · 8 months ago
thedrugdude liked this · 8 months ago -
 calaverasinvisibles liked this · 8 months ago
calaverasinvisibles liked this · 8 months ago -
 el-amor-es-un-capitulo-aparte liked this · 8 months ago
el-amor-es-un-capitulo-aparte liked this · 8 months ago -
 aluc-art liked this · 8 months ago
aluc-art liked this · 8 months ago -
 a-hospital--for-souls reblogged this · 8 months ago
a-hospital--for-souls reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 mddy316 reblogged this · 8 months ago
mddy316 reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 disappleasure reblogged this · 8 months ago
disappleasure reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 annaxvanity liked this · 8 months ago
annaxvanity liked this · 8 months ago -
 king-tyrone36 reblogged this · 8 months ago
king-tyrone36 reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 thesavageking4ever reblogged this · 8 months ago
thesavageking4ever reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 thesavageking4ever liked this · 8 months ago
thesavageking4ever liked this · 8 months ago -
 thegreenfuz liked this · 8 months ago
thegreenfuz liked this · 8 months ago -
 arimonsterwolf reblogged this · 8 months ago
arimonsterwolf reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 arimonsterwolf liked this · 8 months ago
arimonsterwolf liked this · 8 months ago -
 a-high-femme liked this · 8 months ago
a-high-femme liked this · 8 months ago -
 a-little-lynx reblogged this · 8 months ago
a-little-lynx reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 thelittlest-lynx liked this · 8 months ago
thelittlest-lynx liked this · 8 months ago -
 amalitaimagines reblogged this · 8 months ago
amalitaimagines reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 kattywompuss reblogged this · 8 months ago
kattywompuss reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 kattywompuss liked this · 8 months ago
kattywompuss liked this · 8 months ago -
 teacuprevelry liked this · 8 months ago
teacuprevelry liked this · 8 months ago -
 kintsugi-tigerstripes liked this · 8 months ago
kintsugi-tigerstripes liked this · 8 months ago -
 kintsugi-tigerstripes reblogged this · 8 months ago
kintsugi-tigerstripes reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 rileycruel liked this · 8 months ago
rileycruel liked this · 8 months ago -
 rileycruel reblogged this · 8 months ago
rileycruel reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 marcyonacross reblogged this · 8 months ago
marcyonacross reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 charlieburns reblogged this · 8 months ago
charlieburns reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 milascenta liked this · 8 months ago
milascenta liked this · 8 months ago -
 clsscl-msc liked this · 8 months ago
clsscl-msc liked this · 8 months ago -
 hagravenholm liked this · 8 months ago
hagravenholm liked this · 8 months ago -
 sigatos reblogged this · 8 months ago
sigatos reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 sigatos liked this · 8 months ago
sigatos liked this · 8 months ago -
 lordgroose reblogged this · 8 months ago
lordgroose reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 lordgroose liked this · 8 months ago
lordgroose liked this · 8 months ago -
 the-black-knight666 liked this · 8 months ago
the-black-knight666 liked this · 8 months ago
