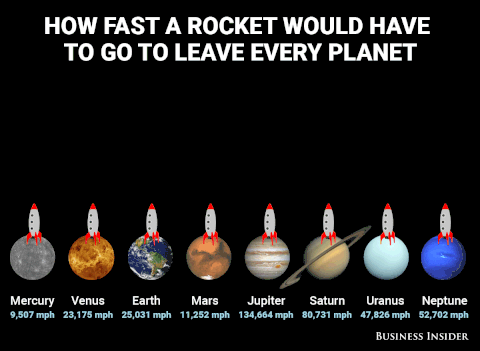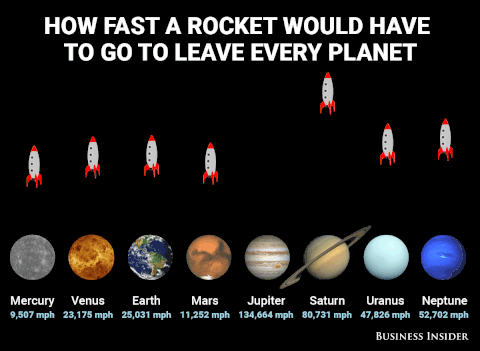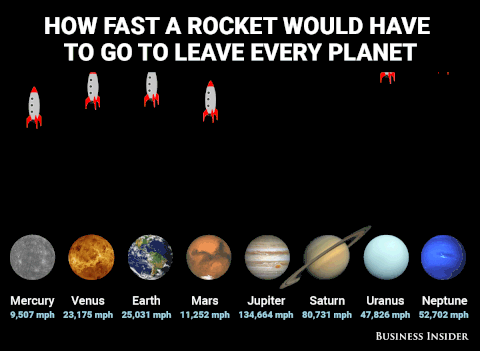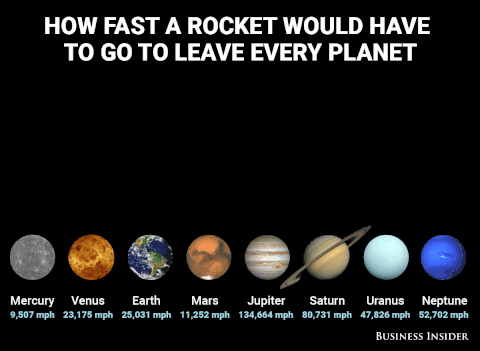
Plutoisnotaplanet - Gnat In Space

More Posts from Plutoisnotaplanet and Others

“Pluto, the newest planet,” & “Neptune, next to farthest planet.” Buck Rogers’ Space World. ca. 1940. Rumsey. Chart detail.
10 Times More Galaxies!
The universe suddenly looks a lot more crowded…
We already estimated that there were about 100 billion galaxies in the observable universe, but new research shows that this estimate is at least 10 times too low!

First, what is the observable universe? Well, it is the most distant part of the universe we can see from Earth because, in theory, the light from these objects have had time to reach Earth.

In a new study using surveys taken by the Hubble Space Telescope and other observatories, astronomers came to the surprising conclusion that there are at least 10 times more galaxies in the observable universe than previously thought. This places the universe’s estimated population at, minimally, 2 trillion galaxies!

The results have clear implications for galaxy formation, and also helps shed light on an ancient astronomical paradox – why is the sky dark at night?
Most of these newly discovered galaxies were relatively small and faint, with masses similar to those of the satellite galaxies surrounding the Milky Way.

Using deep-space images from the Hubble Space Telescope and other observatories, astronomers converted the images into 3-D, in order to make accurate measurements of the number of galaxies at different epochs in the universe’s history.
In addition, they used new mathematical models, which allowed them to infer the existence of galaxies that the current generation of telescopes cannot observe. This led to the surprising conclusion that in order for the numbers of galaxies we now see and their masses to add up, there must be a further 90% of galaxies in the observable universe that are too faint and too far away to be seen with present-day telescopes.

The myriad small faint galaxies from the early universe merged over time into the larger galaxies we can now observe.
That means that over 90% of the galaxies in the universe have yet to be studied! In the near future, the James Webb Space Telescope will be able to study these ultra-faint galaxies and give us more information about their existence.

So back to the question…Why is the sky dark at night if the universe contains an infinity of stars? Researchers came to the conclusion that indeed there actually is such an abundance of galaxies that, in principle, every patch in the sky contains part of a galaxy.
However, starlight from the galaxies is invisible to the human eye and most modern telescopes due to other known factors that reduce visible and ultraviolet light in the universe. Those factors are the reddening of light due to the expansion of space, the universe’s dynamic nature, and the absorption of light by intergalactic dust and gas. All combined, this keeps the night sky dark to our vision.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
important message
scienceeeeeeeeeeeeeee
is there a smell comparable to space ? i assume we dont know because we would die if we tried to smell it but thats so cool
yeah if humans tried to smell space just like that, we’d die, no doubt about it
but the smell of space lingers on spacewalk suits, and docking hatches when astronauts open them!
apparently, space itself smells like burning hot metal, or a hot barbeque grill with a slight hint of spent gasoline. The moon, apparently, smells like a gun after its been shot!
The coolest thing about it all is that the smell is actually what are left of dying stars- it’s literally the smell of stardust, and the particles smell like that because they’re so rich in hydrocarbons- something so very essential to life, and speculated by a lot of astronomers and astrobiologists and such to be the very thing life on earth started from!
another neat fact is that no two solar systems smell the same- ours smells like that because our solar system in particular is extremely rich in carbon, and other solar systems and places in the universe will have extremely different smells depending on what elements are most abundant in their system!
Pluto x Eris
i guess you could say their relationship is...strictly plutonic
A sand pendulum that creates a beautiful pattern only by its movement.
But why does the ellipse change shape?
The pattern gets smaller because energy is not conserved (and in fact decreases) in the system. The mass in the pendulum gets smaller and the center of mass lowers as a function of time. Easy as that, an amazing pattern arises through the laws of physics.
-
 grapefruit101honeymilk-blog liked this · 1 month ago
grapefruit101honeymilk-blog liked this · 1 month ago -
 najatraicoeira liked this · 11 months ago
najatraicoeira liked this · 11 months ago -
 fivewanderingfingers liked this · 1 year ago
fivewanderingfingers liked this · 1 year ago -
 wild-tea-rose liked this · 1 year ago
wild-tea-rose liked this · 1 year ago -
 lulimoon reblogged this · 1 year ago
lulimoon reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 the-mike-est-of-michaels reblogged this · 1 year ago
the-mike-est-of-michaels reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 the-mike-est-of-michaels liked this · 1 year ago
the-mike-est-of-michaels liked this · 1 year ago -
 nonsenseplayercharacter reblogged this · 1 year ago
nonsenseplayercharacter reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 nonsenseplayercharacter liked this · 1 year ago
nonsenseplayercharacter liked this · 1 year ago -
 latinafangirl206 reblogged this · 1 year ago
latinafangirl206 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 summer-l0ver reblogged this · 1 year ago
summer-l0ver reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 generication reblogged this · 1 year ago
generication reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 generication liked this · 1 year ago
generication liked this · 1 year ago -
 mokacheer reblogged this · 1 year ago
mokacheer reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 mokacheer liked this · 1 year ago
mokacheer liked this · 1 year ago -
 koi---kun reblogged this · 1 year ago
koi---kun reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 omusa-inola reblogged this · 1 year ago
omusa-inola reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 cursed--alien reblogged this · 1 year ago
cursed--alien reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 carppaws liked this · 1 year ago
carppaws liked this · 1 year ago -
 10dunksfansinatrenchcoat liked this · 1 year ago
10dunksfansinatrenchcoat liked this · 1 year ago -
 riot2011frontlines liked this · 1 year ago
riot2011frontlines liked this · 1 year ago -
 iwillhaveamoonbase liked this · 1 year ago
iwillhaveamoonbase liked this · 1 year ago -
 sluuttyplant liked this · 1 year ago
sluuttyplant liked this · 1 year ago -
 justremainingmyself liked this · 2 years ago
justremainingmyself liked this · 2 years ago -
 book-pause liked this · 2 years ago
book-pause liked this · 2 years ago -
 juliuli reblogged this · 2 years ago
juliuli reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 juliuli liked this · 2 years ago
juliuli liked this · 2 years ago -
 geddyqueer liked this · 2 years ago
geddyqueer liked this · 2 years ago -
 zeplife liked this · 2 years ago
zeplife liked this · 2 years ago -
 keepcalmandcarryfire reblogged this · 2 years ago
keepcalmandcarryfire reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 keepcalmandcarryfire liked this · 2 years ago
keepcalmandcarryfire liked this · 2 years ago -
 summerofsmiles reblogged this · 2 years ago
summerofsmiles reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 christchristoph-ohmy liked this · 2 years ago
christchristoph-ohmy liked this · 2 years ago -
 pyorin reblogged this · 2 years ago
pyorin reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 quantroup reblogged this · 2 years ago
quantroup reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 quantroup liked this · 2 years ago
quantroup liked this · 2 years ago -
 littlepeachwithahalo liked this · 2 years ago
littlepeachwithahalo liked this · 2 years ago -
 justanotherrinserepeat liked this · 2 years ago
justanotherrinserepeat liked this · 2 years ago
welcome to my space space (see what i did there) (space means two different things)
232 posts