Tokyo Stock Exchange, Circa 1910, On The Right.

Tokyo Stock Exchange, circa 1910, on the right.
More Posts from Philosophical-amoeba and Others
Jumps, Explained
So, going by the tags on my recent jump gifsets, the difference between jumps is apparently still a source of great bewilderment for some people. Now I could link you to some excellent posts on the topic, but since I am, as usual, an extra lil piece of dirt with too much work to do and a lifetime’s worth of procrastination, I’ve decided to put together my own layman’s guide to identifying figure skating jumps (stressed on the layman part).
First, here be a flowchart, since everybody loves flowcharts, right?

If the flowchart works as intended and you can now tell the jumps apart, great! If you need a bit more explanation and illustration, read on.
Keep reading
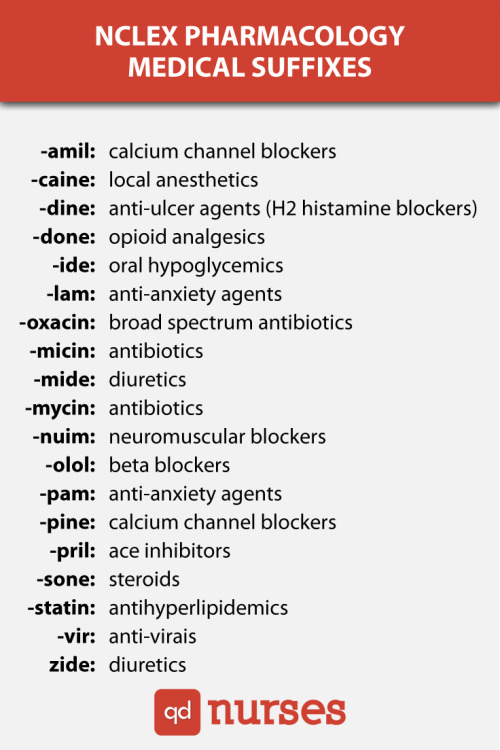
NCLEX Pharmacology Medical Suffixes
-amil = calcium channel blockers
-caine = local anesthetics
-dine = anti-ulcer agents (H2 histamine blockers)
-done = opioid analgesics
-ide = oral hypoglycemics
-lam = anti-anxiety agents
-oxacin = broad spectrum antibiotics
-micin = antibiotics
-mide = diuretics
-mycin = antibiotics
-nuim = neuromuscular blockers
-olol = beta blockers
-pam = anti-anxiety agents
-pine = calcium channel blockers
-pril = ace inhibitors
-sone = steroids
-statin =antihyperlipidemics
-vir = anti-virais
-zide = diuretics
Oval Eggs
The word egg was a borrowing from Old Norse egg, replacing the native word ey (plural eyren) from Old English ǣġ, plural ǣġru. Like “children” and “kine” (obsolete plural of cow), the plural ending -en was added redundantly to the plural form in Middle English. As with most borrowings from Old Norse, this showed up first in northern dialects of English, and gradually moved southwards, so that for a while, ey and egg were used in different parts of England.
In 1490, when William Caxton printed the first English-language books, he wrote a prologue to his publication of Eneydos (Aeneid in contemporary English) in which he discussed the problems of choosing a dialect to publish in, due to the wide variety of English dialects that existed at the time. This word was a specific example he gave. He told a story about some merchants from London travelling down the Thames and stopping in a village in Kent
And one of theym… cam in to an hows and axed for mete and specyally he axyd after eggys, and the goode wyf answerde that she could speke no Frenshe. And the marchaunt was angry, for he also coude speke no Frenshe, but wolde have hadde egges; and she understode hym not. And thenne at laste a-nother sayd that he wolde have eyren. Then the good wyf sayd that she understod hym wel. Loo, what sholde a man in thyse dayes now wryte, egges, or eyren? Certaynly it is hard to playse every man, by-cause of dyversite and chaunge of langage.
The merchant in this story was only familiar with the word egg, while the woman only knew ey, and the confusion was only resolved by someone who knew both words. Indeed, the woman in the story was so confused by this unfamiliar word egg that she assumed it must be a French word! The word “meat” (or “mete” as Caxton spelled it) was a generic word for “food” at the time.
The word ey may also survive in the term Cockney, thought to derive from the Middle English cocken ey (”cock’s egg”), a term given to a small misshapen egg, and applied by rural people to townspeople
Both egg and ey derived from the same Proto-Germanic root, *ajją, which apparently had a variant *ajjaz in West Germanic. This Proto-Germanic form in turn derived from Proto-Indo-European *h2ōwyóm. In Latin, this root became ōvum, from which the adjective ōvalis meaning “egg-shaped”, was derived. Ōvum itself was borrowed into English in the biological sense of the larger gamete in animals, while ōvalis is the source of oval.
The PIE root is generally though to derive from the root *h2éwis, “bird”, which is the source of Latin avis “bird”, source of English terms such as aviation. This word may also be related to *h2ówis “sheep”, which survived in English as ewe. One theory is that they were both derived from a root meaning something like “to dress”, “to clothe”, with bird meaning “one who is clothed [in feathers]” and sheep meaning “one who clothes [by producing wool]”.

The song “It’s a long way to Tipperary” was enormously popular in New Zealand as a sound recording sung by Stanley Kirkby, with shops advertising new arrivals of stock from overseas in early 1915. At the same time, a film of the same title was also being shown in cinemas, and sheet music for an orchestral arrangement was available at the “Golden Horn” music store in Vivian Street Wellington. Copies of this Maori postcard with its “Tipirere “ translation were handed out to members of the 2nd Maori Contingent of the New Zealand Expeditionary Force after they marched through the streets of Wellington on Saturday 16 September 1915 (See Evening Post, 20 September 1915, page 8).
[Postcard]. Tipirere. N.Z.M.E.C. Hokowhitu-a-Tu. [ca 1915].
Eph-B-POSTCARD-Vol-12-003-btm



David Bowie (1947-2016) at Kyoto - Japan - 1980
Photos by Sukita Masayoshi 鋤田 正義

1971 Japanese re-release poster for THE GRADUATE (Mike Nichols, USA, 1967)
Designer: unknown
Poster source: Heritage Auctions
Celebrating the films of storyboard artist Harold Michelson and researcher Lillian Michelson–the subjects of the upcoming HAROLD AND LILLIAN - A HOLLYWOOD LOVE STORY. This weekend, TCM will mark the 50th anniversary of The Graduate—a film that Harold storyboarded and contributed an iconic shot to—by screening a 4K restoration of the film in 700 theaters nationwide on April 23 and 26. Read more at the Harold and Lillian blog and find out where to see The Graduate here.
HAROLD AND LILLIAN opens next Friday at the Quad Cinema in New York.
-
 i-love-books-because-reasons liked this · 1 year ago
i-love-books-because-reasons liked this · 1 year ago -
 the-wild-heroes-of-berlin reblogged this · 6 years ago
the-wild-heroes-of-berlin reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 better-than-buzzfeed-98 reblogged this · 6 years ago
better-than-buzzfeed-98 reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 bocaina2012-blog liked this · 8 years ago
bocaina2012-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 ageesen-blog liked this · 8 years ago
ageesen-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 bouquetofflours reblogged this · 8 years ago
bouquetofflours reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 onlysilentawe liked this · 8 years ago
onlysilentawe liked this · 8 years ago -
 redsector-a reblogged this · 8 years ago
redsector-a reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 mason-tattoo liked this · 8 years ago
mason-tattoo liked this · 8 years ago -
 deathvsthemaiden reblogged this · 8 years ago
deathvsthemaiden reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 theprimeofmissvemm liked this · 8 years ago
theprimeofmissvemm liked this · 8 years ago -
 cause-sleep-is-not-my-frien-blog liked this · 8 years ago
cause-sleep-is-not-my-frien-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 pint-sized-crab liked this · 8 years ago
pint-sized-crab liked this · 8 years ago -
 scoticus reblogged this · 8 years ago
scoticus reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 compulsive-storytelling reblogged this · 8 years ago
compulsive-storytelling reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 yin-writing reblogged this · 8 years ago
yin-writing reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 historylessontime liked this · 8 years ago
historylessontime liked this · 8 years ago -
 cheshirecatnyc liked this · 8 years ago
cheshirecatnyc liked this · 8 years ago -
 faqier123-blog liked this · 8 years ago
faqier123-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 schadenfreudessa reblogged this · 8 years ago
schadenfreudessa reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 linsygasmr liked this · 8 years ago
linsygasmr liked this · 8 years ago -
 linsygasmr reblogged this · 8 years ago
linsygasmr reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 sjwmothman reblogged this · 8 years ago
sjwmothman reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 sjwmothman liked this · 8 years ago
sjwmothman liked this · 8 years ago -
 edwardashley reblogged this · 8 years ago
edwardashley reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 elvenqueenrachel reblogged this · 8 years ago
elvenqueenrachel reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 elvenqueenrachel liked this · 8 years ago
elvenqueenrachel liked this · 8 years ago -
 acollier5919-blog liked this · 8 years ago
acollier5919-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 aleclikescake liked this · 8 years ago
aleclikescake liked this · 8 years ago -
 dcircle21 liked this · 8 years ago
dcircle21 liked this · 8 years ago -
 ms-mandy-m liked this · 8 years ago
ms-mandy-m liked this · 8 years ago -
 battyragdoll liked this · 8 years ago
battyragdoll liked this · 8 years ago -
 mosleymoe liked this · 8 years ago
mosleymoe liked this · 8 years ago -
 sassyenthusiasthistorylover333 liked this · 8 years ago
sassyenthusiasthistorylover333 liked this · 8 years ago -
 steamship-historical-society liked this · 8 years ago
steamship-historical-society liked this · 8 years ago -
 jimilized reblogged this · 8 years ago
jimilized reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 mscumberbatchedhiddlestoned liked this · 8 years ago
mscumberbatchedhiddlestoned liked this · 8 years ago -
 brycemlewis reblogged this · 8 years ago
brycemlewis reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 rain-view liked this · 8 years ago
rain-view liked this · 8 years ago -
 saxophone100 reblogged this · 8 years ago
saxophone100 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 ladymantillon liked this · 8 years ago
ladymantillon liked this · 8 years ago -
 ammg-old reblogged this · 8 years ago
ammg-old reblogged this · 8 years ago
A reblog of nerdy and quirky stuff that pique my interest.
291 posts





