FAMOUS AUTHORS

FAMOUS AUTHORS
Classic Bookshelf: This site has put classic novels online, from Charles Dickens to Charlotte Bronte.
The Online Books Page: The University of Pennsylvania hosts this book search and database.
Project Gutenberg: This famous site has over 27,000 free books online.
Page by Page Books: Find books by Sir Arthur Conan Doyle and H.G. Wells, as well as speeches from George W. Bush on this site.
Classic Book Library: Genres here include historical fiction, history, science fiction, mystery, romance and children’s literature, but they’re all classics.
Classic Reader: Here you can read Shakespeare, young adult fiction and more.
Read Print: From George Orwell to Alexandre Dumas to George Eliot to Charles Darwin, this online library is stocked with the best classics.
Planet eBook: Download free classic literature titles here, from Dostoevsky to D.H. Lawrence to Joseph Conrad.
The Spectator Project: Montclair State University’s project features full-text, online versions of The Spectator and The Tatler.
Bibliomania: This site has more than 2,000 classic texts, plus study guides and reference books.
Online Library of Literature: Find full and unabridged texts of classic literature, including the Bronte sisters, Mark Twain and more.
Bartleby: Bartleby has much more than just the classics, but its collection of anthologies and other important novels made it famous.
Fiction.us: Fiction.us has a huge selection of novels, including works by Lewis Carroll, Willa Cather, Sherwood Anderson, Flaubert, George Eliot, F. Scott Fitzgerald and others.
Free Classic Literature: Find British authors like Shakespeare and Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, plus other authors like Jules Verne, Mark Twain, and more.
TEXTBOOKS
Textbook Revolution: Find biology, business, engineering, mathematics and world history textbooks here.
Wikibooks: From cookbooks to the computing department, find instructional and educational materials here.
KnowThis Free Online Textbooks: Get directed to stats textbooks and more.
Online Medical Textbooks: Find books about plastic surgery, anatomy and more here.
Online Science and Math Textbooks: Access biochemistry, chemistry, aeronautics, medical manuals and other textbooks here.
MIT Open Courseware Supplemental Resources: Find free videos, textbooks and more on the subjects of mechanical engineering, mathematics, chemistry and more.
Flat World Knowledge: This innovative site has created an open college textbooks platform that will launch in January 2009.
Free Business Textbooks: Find free books to go along with accounting, economics and other business classes.
Light and Matter: Here you can access open source physics textbooks.
eMedicine: This project from WebMD is continuously updated and has articles and references on surgery, pediatrics and more.
MATH AND SCIENCE
FullBooks.com: This site has “thousands of full-text free books,” including a large amount of scientific essays and books.
Free online textbooks, lecture notes, tutorials and videos on mathematics: NYU links to several free resources for math students.
Online Mathematics Texts: Here you can find online textbooks likeElementary Linear Algebra and Complex Variables.
Science and Engineering Books for free download: These books range in topics from nanotechnology to compressible flow.
FreeScience.info: Find over 1800 math, engineering and science books here.
Free Tech Books: Computer programmers and computer science enthusiasts can find helpful books here.
CHILDREN’S BOOKS
byGosh: Find free illustrated children’s books and stories here.
Munseys: Munseys has nearly 2,000 children’s titles, plus books about religion, biographies and more.
International Children’s Digital Library: Find award-winning books and search by categories like age group, make believe books, true books or picture books.
Lookybook: Access children’s picture books here.
PHILOSOPHY AND RELIGION
Bored.com: Bored.com has music ebooks, cooking ebooks, and over 150 philosophy titles and over 1,000 religion titles.
Ideology.us: Here you’ll find works by Rene Descartes, Sigmund Freud, Karl Marx, David Hume and others.
Free Books on Yoga, Religion and Philosophy: Recent uploads to this site include Practical Lessons in Yoga and Philosophy of Dreams.
The Sociology of Religion: Read this book by Max Weber, here.
Religion eBooks: Read books about the Bible, Christian books, and more.
PLAYS
ReadBookOnline.net: Here you can read plays by Chekhov, Thomas Hardy, Ben Jonson, Shakespeare, Edgar Allan Poe and others.
Plays: Read Pygmalion, Uncle Vanya or The Playboy of the Western World here.
The Complete Works of William Shakespeare: MIT has made available all of Shakespeare’s comedies, tragedies, and histories.
Plays Online: This site catalogs “all the plays [they] know about that are available in full text versions online for free.”
ProPlay: This site has children’s plays, comedies, dramas and musicals.
MODERN FICTION, FANTASY AND ROMANCE
Public Bookshelf: Find romance novels, mysteries and more.
The Internet Book Database of Fiction: This forum features fantasy and graphic novels, anime, J.K. Rowling and more.
Free Online Novels: Here you can find Christian novels, fantasy and graphic novels, adventure books, horror books and more.
Foxglove: This British site has free novels, satire and short stories.
Baen Free Library: Find books by Scott Gier, Keith Laumer and others.
The Road to Romance: This website has books by Patricia Cornwell and other romance novelists.
Get Free Ebooks: This site’s largest collection includes fiction books.
John T. Cullen: Read short stories from John T. Cullen here.
SF and Fantasy Books Online: Books here include Arabian Nights,Aesop’s Fables and more.
Free Novels Online and Free Online Cyber-Books: This list contains mostly fantasy books.
FOREIGN LANGUAGE
Project Laurens Jz Coster: Find Dutch literature here.
ATHENA Textes Francais: Search by author’s name, French books, or books written by other authors but translated into French.
Liber Liber: Download Italian books here. Browse by author, title, or subject.
Biblioteca romaneasca: Find Romanian books on this site.
Bibliolteca Virtual Miguel de Cervantes: Look up authors to find a catalog of their available works on this Spanish site.
KEIMENA: This page is entirely in Greek, but if you’re looking for modern Greek literature, this is the place to access books online.
Proyecto Cervantes: Texas A&M’s Proyecto Cervantes has cataloged Cervantes’ work online.
Corpus Scriptorum Latinorum: Access many Latin texts here.
Project Runeberg: Find Scandinavian literature online here.
Italian Women Writers: This site provides information about Italian women authors and features full-text titles too.
Biblioteca Valenciana: Register to use this database of Catalan and Valencian books.
Ketab Farsi: Access literature and publications in Farsi from this site.
Afghanistan Digital Library: Powered by NYU, the Afghanistan Digital Library has works published between 1870 and 1930.
CELT: CELT stands for “the Corpus of Electronic Texts” features important historical literature and documents.
Projekt Gutenberg-DE: This easy-to-use database of German language texts lets you search by genres and author.
HISTORY AND CULTURE
LibriVox: LibriVox has a good selection of historical fiction.
The Perseus Project: Tufts’ Perseus Digital Library features titles from Ancient Rome and Greece, published in English and original languages.
Access Genealogy: Find literature about Native American history, the Scotch-Irish immigration in the 19th and 20th centuries, and more.
Free History Books: This collection features U.S. history books, including works by Paul Jennings, Sarah Morgan Dawson, Josiah Quincy and others.
Most Popular History Books: Free titles include Seven Days and Seven Nights by Alexander Szegedy and Autobiography of a Female Slave by Martha G. Browne.
RARE BOOKS
Questia: Questia has 5,000 books available for free, including rare books and classics.
ARTS AND ENTERTAINMENT
Books-On-Line: This large collection includes movie scripts, newer works, cookbooks and more.
Chest of Books: This site has a wide range of free books, including gardening and cooking books, home improvement books, craft and hobby books, art books and more.
Free e-Books: Find titles related to beauty and fashion, games, health, drama and more.
2020ok: Categories here include art, graphic design, performing arts, ethnic and national, careers, business and a lot more.
Free Art Books: Find artist books and art books in PDF format here.
Free Web design books: OnlineComputerBooks.com directs you to free web design books.
Free Music Books: Find sheet music, lyrics and books about music here.
Free Fashion Books: Costume and fashion books are linked to the Google Books page.
MYSTERY
MysteryNet: Read free short mystery stories on this site.
TopMystery.com: Read books by Edgar Allan Poe, Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, GK Chesterton and other mystery writers here.
Mystery Books: Read books by Sue Grafton and others.
POETRY
The Literature Network: This site features forums, a copy of The King James Bible, and over 3,000 short stories and poems.
Poetry: This list includes “The Raven,” “O Captain! My Captain!” and “The Ballad of Bonnie and Clyde.”
Poem Hunter: Find free poems, lyrics and quotations on this site.
Famous Poetry Online: Read limericks, love poetry, and poems by Robert Browning, Emily Dickinson, John Donne, Lord Byron and others.
Google Poetry: Google Books has a large selection of poetry, fromThe Canterbury Tales to Beowulf to Walt Whitman.
QuotesandPoem.com: Read poems by Maya Angelou, William Blake, Sylvia Plath and more.
CompleteClassics.com: Rudyard Kipling, Allen Ginsberg and Alfred Lord Tennyson are all featured here.
PinkPoem.com: On this site, you can download free poetry ebooks.
MISC
Banned Books: Here you can follow links of banned books to their full text online.
World eBook Library: This monstrous collection includes classics, encyclopedias, children’s books and a lot more.
DailyLit: DailyLit has everything from Moby Dick to the recent phenomenon, Skinny Bitch.
A Celebration of Women Writers: The University of Pennsylvania’s page for women writers includes Newbery winners.
Free Online Novels: These novels are fully online and range from romance to religious fiction to historical fiction.
ManyBooks.net: Download mysteries and other books for your iPhone or eBook reader here.
Authorama: Books here are pulled from Google Books and more. You’ll find history books, novels and more.
Prize-winning books online: Use this directory to connect to full-text copies of Newbery winners, Nobel Prize winners and Pulitzer winners.
More Posts from Philosophical-amoeba and Others
In general I am a casual observer and usually do not make comments, especially since I am here to learn and have no background in linguistics. But in this case I feel strongly compelled to put my 2 cents' worth of thoughts in.
Although I cannot say that I am anything like fluent, I do have a reasonable amount of Mandarin Chinese and Japanese, and I have to say the first thing I thought when I saw this article was "ah". Because although I can see how katakana is derived from Chinese, using the rather restricted stroke combinations that is the basis of all Chinese characters, the same cannot be said for hiragana, because at the very least, squiggles do not exist in Chinese, at least by the time it was exported to Japan. What you might think are squiggles in Chinese are in fact just our possibly lazy, or perhaps more elegant way of writing, the way cursive would look compared to printed letters. Hirangana bears only a superficial resemblance to Chinese and always feels like it must have another source of inspiration.
Also keep in mind that Chinese was basically an imported language into Japan, and an attempt to shoehorn Japanese sounds into Chinese characters (which I think I can safely say did not sound the same) must have been unwieldy at best. In fact, today, Japanese pronouciations of kanji differ so much from the Chinese, and often their usage too, that I would use my knowledge of the characters only as a rough starting point as to what they might mean in Japanese.
Also, I looked up Kūkai, and, to cut a long story short, he was a Japanese Buddhist monk who went to China to study the sutras, and, to quote from the Wikipedia page directly:
Kūkai arrived back in Japan in 806 as the eighth Patriarch of Esoteric Buddhism, having learnt Sanskrit and its Siddhaṃ script, studied Indian Buddhism, as well as having studied the arts of Chinese calligraphy and poetry, all with recognized masters. He also arrived with a large number of texts, many of which were new to Japan and were esoteric in character, as well as several texts on the Sanskrit language and the Siddhaṃ script.
And a quick look at the Siddham script shows that it has its roots in the Aramaic alphabet.
This is the man to whom the invention of the kana system is attributed to, and if that is the case, I see a possible connection that is as not as far-fetched as it seems.
The History of Hiragana
In Japanese language, we have three types of letters, Kanji, Hiragana, Katakana.
Hiragana’s root is from old Ivrit and Palmyra letters.

The first column: Phoenician alphabet The second column: Ostracon The third column: Old Aramaic The forth column: Imperial Aramaic The fifth column: Dead Sea scrolls The sixth column: Palmyrene script The seventh column: Palmyra

The first column: Hiragana The second column: Consonants The third column: Vowels The forth column: combined with the consonant and the vowel The fifth column: Sousho-tai (a hand writing style) The sixth column: Kanji
Do you any tips about using ms paint?
I think I have few tips
#1Use 500x500 px or bigger canvas size. Any smaller size will make a brush look messy and shit.Here look:


Can you see the difference?? Lineart in 600x600 px is so much smoother
#2

#3

#4 RIGHT MOUSE BUTTON YOU NEED IT

#5

*:・゚✧it’s like manga : *✧・゚
that’s all tbh
i hope this was somewhat helpful



Throughout the Watergate scandal, Richard Nixon and his supporters accused the press of being biased against his administration. In response to the criticism, Time, which had done significant investigative work on Watergate, took a moment for self-reflection with a July 8, 1974, cover story examining the press’ role in the event. Weighing the notion that the press had become too involved for its own good, the magazine still concluded that further investigation was necessary:
“If the press were to stop digging, analyzing and attempting to keep the record straight, the investigative momentum could easily falter once more. The press can help assure that the constitutional process continues to function. After all that has happened, the country is entitled to a definitive verdict.”
Nevertheless, accusations persisted that Time and other publications were merely pursuing a liberal agenda. In February 1976 Reed Irvine and his conservative organization Accuracy in Media bought a full-page ad in the Washington Post to print a story alleging that Democratic National Committee officials knew about plans to break into the Watergate offices beforehand. The ad implied that the DNC was something other than an innocent victim and that the press had refused to make this assertion for partisan reasons. In this memo from Time’s Washington Bureau correspondent Hays Gorey to his editors, Gorey outlines the investigation done into the potential story and defends the consensus among his colleagues that it did not merit publication. He writes:
“I’m sure Reed Irvine can wow audiences by telling this story and claiming it is news being covered up. But where are his facts? Hundreds of Watergate stories went unwritten and unpublished because there were no facts to support them. This is one.“
Time July 8, 1974 cover reprint. Time Inc. Records. Editor-in-Chief: Hedley Donovan Files: Subject Files: 1959-1979: Time: Bias. New-York Historical Society.
Hays Gorey to Hedley Donovan, Henry Grunwald, and D. Duncan. February 27, 1976. Time Inc. Records. Editor-in-Chief: Hedley Donovan Files: Subject Files: 1959-1979: [Time: Bias: Kennedy and Nixon]. New-York Historical Society.
Processing of the Time Inc. Archive is made possible through the generous support of the Henry Luce Foundation

1971 Japanese re-release poster for THE GRADUATE (Mike Nichols, USA, 1967)
Designer: unknown
Poster source: Heritage Auctions
Celebrating the films of storyboard artist Harold Michelson and researcher Lillian Michelson–the subjects of the upcoming HAROLD AND LILLIAN - A HOLLYWOOD LOVE STORY. This weekend, TCM will mark the 50th anniversary of The Graduate—a film that Harold storyboarded and contributed an iconic shot to—by screening a 4K restoration of the film in 700 theaters nationwide on April 23 and 26. Read more at the Harold and Lillian blog and find out where to see The Graduate here.
HAROLD AND LILLIAN opens next Friday at the Quad Cinema in New York.
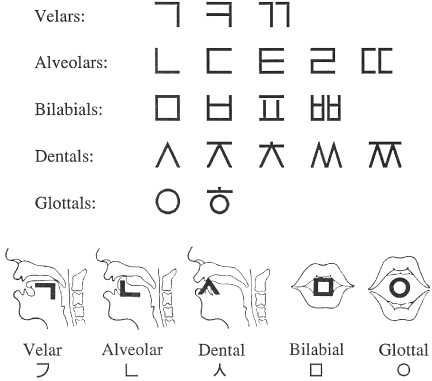

A basic schematic of why the Korean alphabet is so cool, from Wright House:
Unlike almost every other alphabet in the world, the Korean alphabet did not evolve. It was invented in 1443 (promulgated in 1446) by a team of linguists and intellectuals commissioned by King Sejong the Great.
In the diagram [above], the Korean consonants are arranged into five main linguistic groups (one per row), depending on where in the mouth contact is made. Notice that there is a graphic element common to all the consonants in a particular row. The first consonant in each row is the most basic and is graphically the simplest; this representative consonant for each group is the building block for the other characters in that group. Certain of these modifications are systematic, and yield similarly modified characters in several groups, such as adding a horizontal line to a simple consonant (a “stop” consonant–such as t/d or p/b–rather than a nasal consonant) to form the aspirated consonants (those made with extra air) and doubling simple consonants to form “tense” consonants (no real equivalent in English).
Notice that the five representative consonants (the ones in the first column in the upper part of the diagram) are also depicted in the drawings that make up the lower part of the diagram showing the relevant part of the mouth involved. Ingeniously, each of these representative consonants is a kind of simplified schematic diagram showing the position of the mouth in forming those consonants.
More details, including subsequent historical changes to Hangul, in the Wikipedia article.
I am not a native Japanese speaker but the first word that comes to mind is 懐かしい (natsukashii), which is that warm fuzzy feeling you have when you think upon a fond memory or experience. Or that feeling you are having when you say, "sure brings back memories." Depending on context it gets translated to nostalgic, or longing, or dear, but by themselves they all feel somewhat inadequate.
For Chinese mandarin, I can think of 骗我的感情 (pian wo de gan qing) (there should be tone markers, but I don't know how to put them in, sorry!), which is literally "trick/bluff my feelings", which I am now finding quite to explain! Hmm... it's that disappointment you feel when someone sets your expectations up for something and then fails to deliver. I suppose like feeling cheated.
Hope that helps and good luck!
bobbies
YOU SPEAK A LANGUAGE AND I NEED YOUR HELP PLEASE I BEG YOU
hi. sorry about that catchy title, but you have something i need. you speak a language, maybe even multiple languages. you use emotions words everyday. i’m sure you know that languages have their own emotion words that are very hard to translate to other languages, for example, the word ‘anxiety’ doesn’t really exist in Polish, it is always a challenge to translate it in such way to convey its true meaning. Polish people don’t really feel anxiety, because they don’t have the word for it. i need your help with something: tell me an emotion word that is unique to your language or hard to translate. i’ll ask you a few questions and maybe i’ll write an essay about it using the natural semantic metalanguage (NSM). it’s a linguistic theory, whatever. please help a linguist out. i need an A. i promise i won’t get an F on your precious word.
i am interested in emotion words from every language except for Polish and English.
you can reply under this post, you can message me privately, i can give you my e-mail, whatever works for you. it would really help me if you reblogged this post, but no pressure
help education.. pretty please?

(Image caption: If this picture makes you feel uncomfortable, you feel empathic pain. This sensation activates the same brain regions as real pain. © Kai Weinsziehr for MPG)
The anatomy of pain
Grimacing, we flinch when we see someone accidentally hit their thumb with a hammer. But is it really pain we feel? Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences in Leipzig and other institutions have now proposed a new theory that describes pain as a multi-layered gradual event which consists of specific pain components, such as a burning sensation in the hand, and more general components, such as negative emotions. A comparison of the brain activation patterns during both experiences could clarify which components the empathic response shares with real pain.
Imagine you’re driving a nail into a wall with a hammer and accidentally bang your finger. You would probably injure finger tissue, feel physical distress, focus all your attention on your injured finger and take care not to repeat the misfortune. All this describes physical and psychological manifestations of “pain” – specifically, so-called nociceptive pain experienced by your body, which is caused by the stimulation of pain receptors.
Now imagine that you see a friend injure him or herself in the same way. You would again literally wince and feel pain, empathetic pain in this case. Although you yourself have not sustained any injury, to some extent you would experience the same symptoms: You would feel anxiety; you may recoil to put distance between yourself and the source of the pain; and you would store information about the context of the experience in order to avoid pain in the future.
Activity in the brain
Previous studies have shown that the same brain structures – namely the anterior insula and the cingulate cortex – are activated, irrespective of whether the pain is personally experienced or empathetic. However, despite this congruence in the underlying activated areas of the brain, the extent to which the two forms of pain really are similar remains a matter of considerable controversy.
To help shed light on the matter, neuroscientists, including Tania Singer, Director at the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences in Leipzig, have now proposed a new theory: “We need to get away from this either-or question, whether the pain is genuine or not.”
Instead, it should be seen as a complex interaction of multiple elements, which together form the complex experience we call “pain”. The elements include sensory processes, which determine, for example, where the pain stimulus was triggered: in the hand or in the foot? In addition, emotional processes, such as the negative feeling experienced during pain, also come into play. “The decisive point is that the individual processes can also play a role in other experiences, albeit in a different activation pattern,” Singer explains – for example, if someone tickles your hand or foot, or you see images of people suffering on television. Other processes, such as the stimulation of pain receptors, are probably highly specific to pain. The neuroscientists therefore propose comparing the elements of direct and empathetic pain: Which elements are shared and which, by contrast, are specific and unique to the each form of pain?
Areas process general components
A study that was published almost simultaneously by scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences and the University of Geneva has provided strong proof of this theory: They were able to demonstrate for the first time that during painful experiences the anterior insula region and the cingulate cortex process both general components, which also occur during other negative experiences such as disgust or indignation, and specific pain information – whether the pain is direct or empathic.
The general components signal that an experience is in fact unpleasant and not joyful. The specific information, in turn, tells us that pain – not disgust or indignation – is involved, and whether the pain is being experienced by you or someone else. “Both the nonspecific and the specific information are processed in parallel in the brain structures responsible for pain. But the activation patterns are different,” says Anita Tusche, also a neuroscientist at the Max Planck Institute in Leipzig and one of the authors of the study.
Thanks to the fact that our brain deals with these components in parallel, we can process various unpleasant experiences in a time-saving and energy-saving manner. At the same time, however, we are able register detailed information quickly, so that we know exactly what kind of unpleasant event has occurred – and whether it affects us directly or vicariously. “The fact that our brain processes pain and other unpleasant events simultaneously for the most part, no matter if they are experienced by us or someone else, is very important for social interactions,” Tusche says, “because it helps to us understand what others are experiencing.”


Laplace transform table. Source. (I’m obsessed. <3 And figured y’all would like this one, too!)
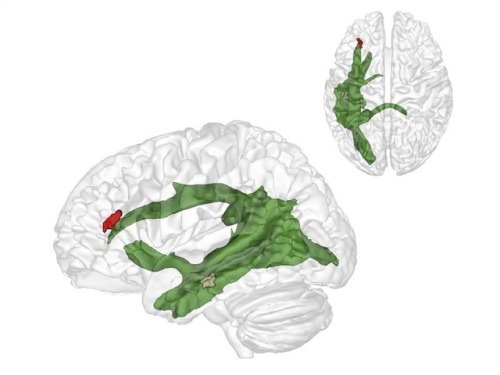
(Image caption: The maturation of fibres of a brain structure called the arcuate fascicle (green) between the ages of three and four years establishes a connection between two critical brain regions: a region (brown) at the back of the temporal lobe that supports adults thinking about others and their thoughts, and a region (red) in the frontal lobe that is involved in keeping things at different levels of abstraction and, therefore, helps us to understand what the real world is and what the thoughts of others are. Credit: © MPI CBS)
The importance of relating to others: why we only learn to understand other people after the age of four
When we are around four years old we suddenly start to understand that other people think and that their view of the world is often different from our own. Researchers in Leiden and Leipzig have explored how that works. Publication in Nature Communications on 21 March.
At around the age of four we suddenly do what three-year-olds are unable to do: put ourselves in someone else’s shoes. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences (MPI CBS) in Leipzig and at Leiden University have shown how this enormous developmental step occurs: a critical fibre connection in the brain matures. Senior researcher and Leiden developmental psychologist Nikolaus Steinbeis, co-author of the article, took part in the research. Lead author, PhD candidate Charlotte Grosse-Wiesmann, worked under his supervision.
Little Maxi
If you tell a 3-year-old child the following story of little Maxi, they will most probably not understand: Maxi puts his chocolate on the kitchen table, then goes to play outside. While he is gone, his mother puts the chocolate in the cupboard. Where will Maxi look for his chocolate when he comes back? A 3-year-old child will not understand why Maxi would be surprised not to find the chocolate on the table where he left it. It is only by the age of 4 years that a child will correctly predict that Maxi will look for his chocolate where he left it and not in the cupboard where it is now.
Theory of Mind
The researchers observed something similar when they showed a 3-year-old child a chocolate box that contained pencils instead of chocolates. When the child was asked what another child would expect to be in the box, they answered “pencils”, although the other child would not know this. Only a year later, around the age of four years, however, will they understand that the other child had hoped for chocolates. Thus, there is a crucial developmental breakthrough between three and four years: this is when we start to attribute thoughts and beliefs to others and to understand that their beliefs can be different from ours. Before that age, thoughts don’t seem to exist independently of what we see and know about the world. That is, this is when we develop a Theory of Mind.
Independent development
The researchers have now discovered what is behind this breakthrough. The maturation of fibres of a brain structure called the arcuate fascicle between the ages of three and four years establishes a connection between two critical brain regions: a region at the back of the temporal lobe that supports adult thinking about others and their thoughts, and a region in the frontal lobe that is involved in keeping things at different levels of abstraction and, therefore, helps us to understand what the real world is and what the thoughts of others are. Only when these two brain regions are connected through the arcuate fascicle can children start to understand what other people think. This is what allows us to predict where Maxi will look for his chocolate. Interestingly, this new connection in the brain supports this ability independently of other cognitive abilities, such as intelligence, language ability or impulse control.
-
 thisiseye reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
thisiseye reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 coolpillowindeed reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
coolpillowindeed reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 mirrorsandmasonjars reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
mirrorsandmasonjars reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 lovedripdrop reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
lovedripdrop reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 bigbromelvin reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
bigbromelvin reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 raddestinycollector liked this · 3 weeks ago
raddestinycollector liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 alwayselusivelove liked this · 3 weeks ago
alwayselusivelove liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 derniererondeavantlanuit-blog liked this · 3 weeks ago
derniererondeavantlanuit-blog liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 demonablack83 reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
demonablack83 reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 demonablack83 liked this · 3 weeks ago
demonablack83 liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 floating-hasselblad liked this · 3 weeks ago
floating-hasselblad liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 alexandercakedust liked this · 3 weeks ago
alexandercakedust liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 icannotbejondenden47 liked this · 3 weeks ago
icannotbejondenden47 liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 direwolfgamer liked this · 3 weeks ago
direwolfgamer liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 shinidoesthings liked this · 3 weeks ago
shinidoesthings liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 knifeyrat liked this · 3 weeks ago
knifeyrat liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 mari-writes liked this · 3 weeks ago
mari-writes liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 spammingsouls reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
spammingsouls reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 eldritchsquared liked this · 3 weeks ago
eldritchsquared liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 grillcheeser liked this · 3 weeks ago
grillcheeser liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 bigtiddygothhusband reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
bigtiddygothhusband reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 nbmakoto liked this · 3 weeks ago
nbmakoto liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 skuttlebuddy reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
skuttlebuddy reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 skuttlebuddy liked this · 3 weeks ago
skuttlebuddy liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 unikirin reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
unikirin reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 pikaemmy13 liked this · 3 weeks ago
pikaemmy13 liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 sunfishfusions liked this · 3 weeks ago
sunfishfusions liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 chocopulse reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
chocopulse reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 ronan-pynch-221b reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
ronan-pynch-221b reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 feweggo liked this · 3 weeks ago
feweggo liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 supernaturaltitty reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
supernaturaltitty reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 supernaturaltitty liked this · 3 weeks ago
supernaturaltitty liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 regret-with-a-u liked this · 3 weeks ago
regret-with-a-u liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 zcassiandra liked this · 3 weeks ago
zcassiandra liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 brushzillas liked this · 3 weeks ago
brushzillas liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 sempiternalmellifluousti reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
sempiternalmellifluousti reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 tobemadeofglass reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
tobemadeofglass reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 nimbuscloudydazed liked this · 3 weeks ago
nimbuscloudydazed liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 jaco2208 liked this · 3 weeks ago
jaco2208 liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 lyrija liked this · 3 weeks ago
lyrija liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 metamorphicnessy reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
metamorphicnessy reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 squashiemoto reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
squashiemoto reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 squashiemoto liked this · 3 weeks ago
squashiemoto liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 thrasys reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
thrasys reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 frankenpagie liked this · 3 weeks ago
frankenpagie liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 imbalanceofhumors liked this · 3 weeks ago
imbalanceofhumors liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 themissrabbit reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
themissrabbit reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 flwhy liked this · 3 weeks ago
flwhy liked this · 3 weeks ago
A reblog of nerdy and quirky stuff that pique my interest.
291 posts





