Ocrim1967 - Senza Titolo



More Posts from Ocrim1967 and Others










What Makes Something A Planet, According To An Astrophysicist?
“A dolphin may look like a fish, but it’s really a mammal. Similarly, the composition of an object is not the only factor in classifying it: its evolutionary history is inextricably related to its properties. Scientists will likely continue to argue over how to best classify all of these worlds, but it’s not just astronomers and planetary scientists who have a stake in this. In the quest to make organizational sense of the Universe, we have to confront it with the full suite of our knowledge.
Although many will disagree, moons, asteroids, Kuiper belt and Oort cloud objects are fascinating objects just as worthy of study as modern-day planets are. They may even be better candidates for life than many of the true planets are. But each object’s properties are inextricably related to the entirety of its formation history. When we try to classify the full suite of what we’re finding, we must not be misled by appearances alone.”
You’ve heard about the IAU’s definition, where in order to be a planet, you must pull yourself into hydrostatic equilibrium, orbit the Sun and nothing else, and gravitationally clear your orbit. You’ve also heard about the controversial new definition from geophysical/planetary science arguments, that planets should be based on their ability to pull themselves into a spheroidal shape alone.
Well, what about a third way: defining planets (and a whole classification scheme) based on astrophysical concerns alone? It’s time to start thinking about it!
What is Gravitational Lensing?
A gravitational lens is a distribution of matter (such as a cluster of galaxies) between a distant light source and an observer, that is capable of bending the light from the source as the light travels towards the observer. This effect is known as gravitational lensing, and the amount of bending is one of the predictions of Albert Einstein’s general theory of relativity.

This illustration shows how gravitational lensing works. The gravity of a large galaxy cluster is so strong, it bends, brightens and distorts the light of distant galaxies behind it. The scale has been greatly exaggerated; in reality, the distant galaxy is much further away and much smaller. Credit: NASA, ESA, L. Calcada
There are three classes of gravitational lensing:
1° Strong lensing: where there are easily visible distortions such as the formation of Einstein rings, arcs, and multiple images.

Einstein ring. credit: NASA/ESA&Hubble
2° Weak lensing: where the distortions of background sources are much smaller and can only be detected by analyzing large numbers of sources in a statistical way to find coherent distortions of only a few percent. The lensing shows up statistically as a preferred stretching of the background objects perpendicular to the direction to the centre of the lens. By measuring the shapes and orientations of large numbers of distant galaxies, their orientations can be averaged to measure the shear of the lensing field in any region. This, in turn, can be used to reconstruct the mass distribution in the area: in particular, the background distribution of dark matter can be reconstructed. Since galaxies are intrinsically elliptical and the weak gravitational lensing signal is small, a very large number of galaxies must be used in these surveys.

The effects of foreground galaxy cluster mass on background galaxy shapes. The upper left panel shows (projected onto the plane of the sky) the shapes of cluster members (in yellow) and background galaxies (in white), ignoring the effects of weak lensing. The lower right panel shows this same scenario, but includes the effects of lensing. The middle panel shows a 3-d representation of the positions of cluster and source galaxies, relative to the observer. Note that the background galaxies appear stretched tangentially around the cluster.
3° Microlensing: where no distortion in shape can be seen but the amount of light received from a background object changes in time. The lensing object may be stars in the Milky Way in one typical case, with the background source being stars in a remote galaxy, or, in another case, an even more distant quasar. The effect is small, such that (in the case of strong lensing) even a galaxy with a mass more than 100 billion times that of the Sun will produce multiple images separated by only a few arcseconds. Galaxy clusters can produce separations of several arcminutes. In both cases the galaxies and sources are quite distant, many hundreds of megaparsecs away from our Galaxy.
Gravitational lenses act equally on all kinds of electromagnetic radiation, not just visible light. Weak lensing effects are being studied for the cosmic microwave background as well as galaxy surveys. Strong lenses have been observed in radio and x-ray regimes as well. If a strong lens produces multiple images, there will be a relative time delay between two paths: that is, in one image the lensed object will be observed before the other image.

As an exoplanet passes in front of a more distant star, its gravity causes the trajectory of the starlight to bend, and in some cases results in a brief brightening of the background star as seen by a telescope. The artistic concept illustrates this effect. This phenomenon of gravitational microlensing enables scientists to search for exoplanets that are too distant and dark to detect any other way.Credits: NASA Ames/JPL-Caltech/T. Pyle
Explanation in terms of space–time curvature

Simulated gravitational lensing by black hole by: Earther
In general relativity, light follows the curvature of spacetime, hence when light passes around a massive object, it is bent. This means that the light from an object on the other side will be bent towards an observer’s eye, just like an ordinary lens. In General Relativity the speed of light depends on the gravitational potential (aka the metric) and this bending can be viewed as a consequence of the light traveling along a gradient in light speed. Light rays are the boundary between the future, the spacelike, and the past regions. The gravitational attraction can be viewed as the motion of undisturbed objects in a background curved geometry or alternatively as the response of objects to a force in a flat geometry.

A galaxy perfectly aligned with a supernova (supernova PS1-10afx) acts as a cosmic magnifying glass, making it appear 100 billion times more dazzling than our Sun. Image credit: Anupreeta More/Kavli IPMU.
To learn more, click here.
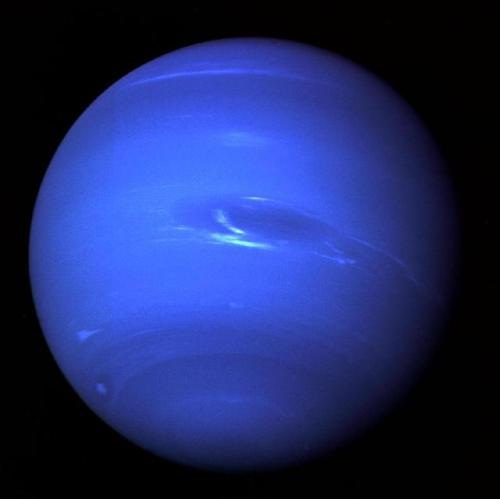
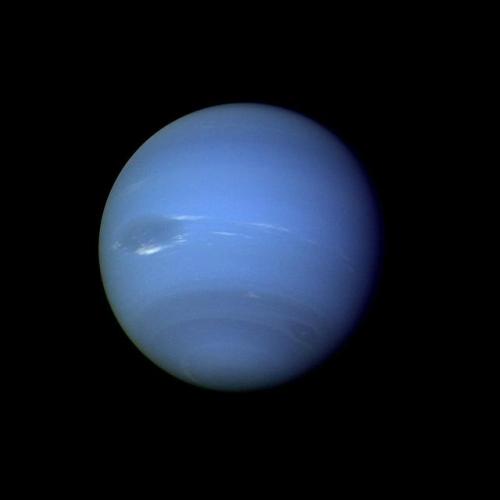
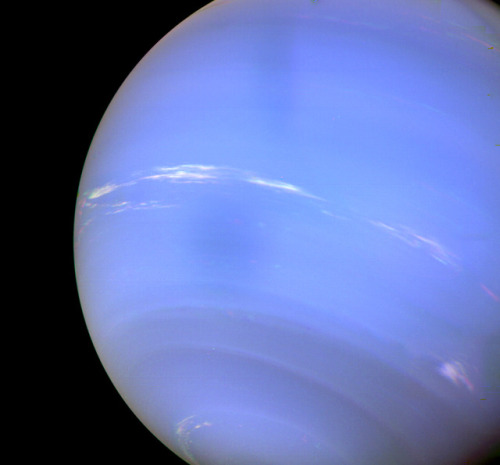
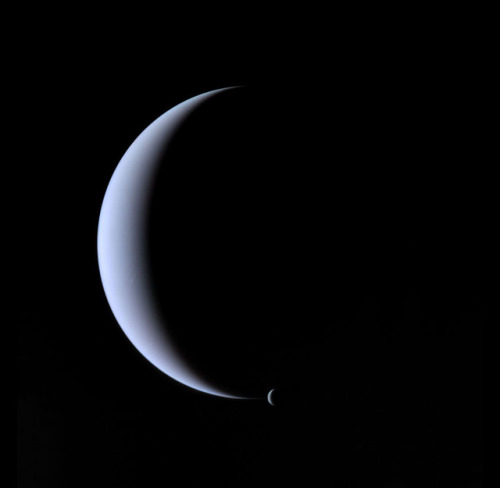




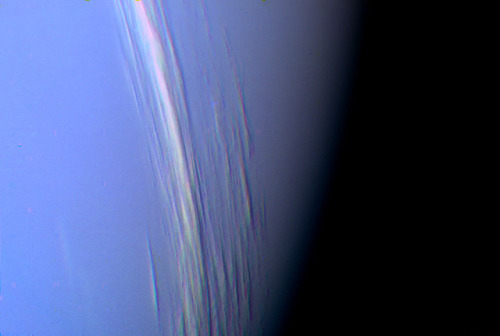





Neptune ♆
On this day in 1846 was discovered the planet Neptune.
The ice giant Neptune was the first planet located through mathematical predictions rather than through regular observations of the sky. (Galileo had recorded it as a fixed star during observations with his small telescope in 1612 and 1613.) When Uranus didn’t travel exactly as astronomers expected it to, a French mathematician, Urbain Joseph Le Verrier, proposed the position and mass of another as yet unknown planet that could cause the observed changes to Uranus’ orbit. After being ignored by French astronomers, Le Verrier sent his predictions to Johann Gottfried Galle at the Berlin Observatory, who found Neptune on his first night of searching in 1846. Seventeen days later, its largest moon, Triton, was also discovered.
Neptune is invisible to the naked eye because of its extreme distance from Earth. Interestingly, the highly eccentric orbit of the dwarf planet Pluto brings Pluto inside Neptune’s orbit for a 20-year period out of every 248 Earth years. Pluto can never crash into Neptune, though, because for every three laps Neptune takes around the Sun, Pluto makes two. This repeating pattern prevents close approaches of the two bodies.
Nearly 4.5 billion kilometers (2.8 billion miles) from the Sun, Neptune orbits the Sun once every 165 years.
Uranus’ blue-green color is also the result of atmospheric methane, but Neptune is a more vivid, brighter blue, so there must be an unknown component that causes the more intense color.
Despite its great distance and low energy input from the Sun, Neptune’s winds can be three times stronger than Jupiter’s and nine times stronger than Earth’s.
Winds on Neptune travel faster than the speed of sound.
In 1989, Voyager 2 tracked a large, oval-shaped, dark storm in Neptune’s southern hemisphere. This “Great Dark Spot” was large enough to contain the entire Earth.
Neptune has five known rings. Voyager 2’s observations confirmed that these unusual rings are not uniform but have four thick regions (clumps of dust) called arcs. The rings are thought to be relatively young and short-lived.
Neptune has 14 known moons, six of which were discovered by Voyager 2.
Triton, Neptune’s largest moon, orbits the planet in the opposite direction compared with the rest of the moons, suggesting that it may have been captured by Neptune in the distant past.
To know more about the planet Neptune click here and here.
Images credit: NASA/JPL- Caltech (some images processed by Kevin M. Gill)
NASA Science Show & Tell
This week, we’re at one of the biggest science conferences in the country, where our scientists are presenting new results from our missions and projects. It’s called the American Geophysical Union’s Fall Meeting.
Here are a few of the things we shared this week…

The Sun
A few months into its seven-year mission, Parker Solar Probe has already flown far closer to the Sun than any spacecraft has ever gone. The data from this visit to the Sun has just started to come back to Earth, and scientists are hard at work on their analysis.

Parker Solar Probe sent us this new view of the Sun’s outer atmosphere, the corona. The image was taken by the mission’s WISPR instrument on Nov. 8, 2018, and shows a coronal streamer seen over the east limb of the Sun. Coronal streamers are structures of solar material within the Sun’s atmosphere, the corona, that usually overlie regions of increased solar activity. The fine structure of the streamer is very clear, with at least two rays visible. Parker Solar Probe was about 16.9 million miles from the Sun’s surface when this image was taken. The bright object near the center of the image is Mercury, and the dark spots are a result of background correction.
Hurricane Maria
Using a satellite view of human lights, our scientists watched the lights go out in Puerto Rico after Hurricane Maria. They could see the slow return of electricity to the island, and track how rural and mountainous regions took longer to regain power.

In the spring, a team of scientists flew a plane over Puerto Rico’s forests, using a laser instrument to measure how trees were damaged and how the overall structure of the forests had changed.

Earth’s Ice
Our scientists who study Antarctica saw some surprising changes to East Antarctica. Until now, most of the continent’s melting has been on the peninsula and West Antarctica, but our scientists have seen glaciers in East Antarctica lose lots of ice in the last few years.


Our ICESat-2 team showed some of their brand new data. From the changing height of Antarctic ice to lagoons off the coast of Mexico, the little satellite has spent its first few months measuring our planet in 3D. The laser pulses even see individual ocean waves, in this graph.

Scientists are using our satellite data to track Adélie penguin populations, by using an unusual proxy – pictures of their poop! Penguins are too small to be seen by satellites, but they can see large amounts of their poop (which is pink!) and use that as a proxy for penguin populations.

Asteroid Bennu
Our OSIRIS-REx mission recently arrived at its destination, asteroid Bennu. On approach, data from the spacecraft’s spectrometers revealed chemical signatures of water trapped in clay minerals. While Bennu itself is too small to have ever hosted liquid water, the finding indicates that liquid water was present at some time on Bennu’s parent body, a much larger asteroid.
We also released a new, detailed shape model of Bennu, which is very similar to our ground-based observations of Bennu’s shape. This is a boon to ground-based radar astronomy since this is our first validation of the accuracy of the method for an asteroid! One change from the original shape model is the size of the large boulder near Bennu’s south pole, nicknamed “Benben.” The boulder is much bigger than we thought and overall, the quantity of boulders on the surface is higher than expected. Now the team will make further observations at closer ranges to more accurately assess where a sample can be taken on Bennu to later be returned to Earth.

Jupiter
The Juno mission celebrated it’s 16th science pass of #Jupiter, marking the halfway point in data collection of the prime mission. Over the second half of the prime mission — science flybys 17 through 32 — the spacecraft will split the difference, flying exactly halfway between each previous orbit. This will provide coverage of the planet every 11.25 degrees of longitude, providing a more detailed picture of what makes the whole of Jupiter tick.

Mars
The Mars 2020 team had a workshop to discuss the newly announced landing site for our next rover on the Red Planet. The landing site…Jezero Crater! The goal of Mars 2020 is to learn whether life ever existed on Mars. It’s too cold and dry for life to exist on the Martian surface today. But after Jezero Crater formed billions of years ago, water filled it to form a deep lake about the same size as Lake Tahoe. Eventually, as Mars’ climate changed, Lake Jezero dried up. And surface water disappeared from the planet.
Interstellar Space
Humanity now has two interstellar ambassadors. On Nov. 5, 2018, our Voyager 2 spacecraft left the heliosphere — the bubble of the Sun’s magnetic influence formed by the solar wind. It’s only the second-ever human-made object to enter interstellar space, following its twin, Voyager 1, that left the heliosphere in 2012.

Scientists are especially excited to keep receiving data from Voyager 2, because — unlike Voyager 1 — its plasma science instrument is still working. That means we’ll learn brand-new information about what fills the space between the stars.
Learn more about NASA Science at science.nasa.gov.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com


Gif by Satiricon
Hilarious Animal Snapchats That Are Impossible Not To Laugh At






















Chandra Spots Extremely Long Cosmic Jet in Early Universe
http://www.sci-news.com/astronomy/chandra-extremely-long-cosmic-jet-early-universe-09436.html
How Do You Like Your Turkey? Home-Cooked or Rocket-Launched?

It’s Thanksgiving, which means that you’re probably thinking about food right now. And here at NASA, we have to think about food very seriously when we explore space!
Astronauts Need to Eat, Too!
Like for you on Earth, nutrition plays a key role in maintaining the health and optimal performance of the astronauts. The Space Food Systems team is required to meet the nutritional needs of each crew member while adhering to the requirements of limited storage space, limited preparation options, and the difficulties of eating without gravity.
Good food is necessary being comfortable on a mission a long way from home — especially for crewmembers who are on board for many months at a time. It’s important that the astronauts like the food they’re eating everyday, even given the preparation constraints!
Astronaut Food Has Not Always Been Appetizing

The early space programs were groundbreaking in a lot of ways — but not when it came to food. Like today, crumbs had to be prevented from scattering in microgravity and interfering with the instruments. Mercury astronauts had to endure bite-sized cubes, freeze-dried powders, and semi-liquids stuffed into aluminum tubes. The freeze-dried food were hard to rehydrate, squeezing the tubes was understandable unappetizing, and the food was generally considered to be, like spaceflight, a test of endurance.
However, over the years, packaging improved, which in turn enhanced food quality and choices. The Apollo astronauts were the first to have hot water, which made rehydrating foods easier and improved the food’s taste. And even the Space Shuttle astronauts had opportunities to design their own menus and choose foods commercially available on grocery store shelves.
The Wonders of Modern Space Food

Nowadays, astronauts on the International Space Station have the opportunity to sample a variety of foods and beverages prepared by the Space Food Systems team and decide which ones they prefer. They can add water to rehydratable products or eat products that are ready to eat off the shelf.
All the cooking and preparation has been done for them ahead of time because 1) they don’t have room for a kitchen to cook on the space station 2) they don’t have time to cook! The crewmembers are extremely occupied with station maintenance as well as scientific research on board, so meal times have to be streamlined as much as possible.
Instead of going grocery shopping, bulk overwrap bags (BOBs!) are packed into cargo transfer bags for delivery to the space station. Meal based packaging allows the astronauts to have entrees, side dishes, snacks, and desserts to choose from.
Taste in Space

The perception of taste changes in space. In microgravity, astronauts experience a fluid shift in their bodies, so the sensation is similar to eating with a headcold. The taste is muted so crewmembers prefer spicy foods or food with condiments to enhance the flavor.
We Can’t Buy Groceries, But We Can Grow Food!
Growing plants aboard the space station provides a unique opportunity to study how plants adapt to microgravity. Plants may serve as a food source for long term missions, so it’s critical to understand how spaceflight affects plant growth. Plus, having fresh food available in space can have a positive impact on astronauts’ moods!
Since 2002, the Lada greenhouse has been used to perform almost continuous plant growth experiments on the station. We have grown a vast variety of plants, including thale cress, swiss chard, cabbage, lettuce, and mizuna.

And in 2015, Expedition 44 members became the first American astronauts to eat plants grown in space when they munched on their harvest of Red Romaine.
Earthlings Can Eat Space Food, Too
To give you a clear idea of how diverse the selection is for astronauts on board the space station, two earthlings gave the astronaut menu a try for a full week. Besides mentioning once that hot sauce was needed, they fared pretty well! (The shrimp cocktail was a favorite.)
Space Technology for Food on Earth
Not only has our space food improved, but so has our ability measure food production on Earth. Weather that is too dry, too wet, too hot, or too cool can strongly affect a farmer’s ability to grow crops. We collaborated with the United States Agency for International Development to create a system for crop yield prediction based on satellite data: the GEOGLAM Crop Monitor for Early Warning.

This map measures the health, or “greenness” of vegetation based on how much red or near-infrared light the leaves reflect. Healthy vegetation reflects more infrared light and less visible light than stressed vegetation. As you can see from the map, a severe drought spread across southern Mexico to Panama in June to August of this year.
The Crop Monitor compiles different types of crop condition indicators — such as temperature, precipitation, and soil moisture — and shares them with 14 national and international partners to inform relief efforts.
Thanksgiving in Space
Space food has certainly come a long way from semi-liquids squeezed into aluminum tubes! This year, Expedition 57 crewmembers Commander Alexander Gerst and Flight Engineer Serena M. Auñón-Chancellor are looking forward to enjoying a Thanksgiving meal that probably sounds pretty familiar to you: turkey, stuffing, candied yams, and even spicy pound cakes!
Hungry for More?
If you can’t get enough of space food, tune into this episode of “Houston, We Have a Podcast” and explore the delicious science of astronaut mealtime with Takiyah Sirmons.
And whether you’re eating like a king or an astronaut, we wish everybody a happy and safe Thanksgiving!
When the Moon's Shadow Falls on Earth
On July 2, 2019, a total solar eclipse will pass over parts of Argentina and Chile.

Solar eclipses happen when the Moon passes directly between the Sun and Earth, casting its shadow onto Earth’s surface. Because the Moon’s orbit isn’t perfectly in line with the Sun and Earth, its shadow usually passes above or below Earth. But when it lines up just right, we get a solar eclipse!

People in the inner part of the Moon’s shadow — the umbra — have the chance to witness a total solar eclipse, while those in the outer part of the shadow — the penumbra — experience a partial solar eclipse.

The path of the total solar eclipse stretches across parts of Chile and Argentina. People outside this path may see a partial eclipse or no eclipse at all.
During a total solar eclipse, the Moon blocks out the Sun’s bright face, revealing its comparatively faint outer atmosphere, the corona. The corona is a dynamic region that is thought to hold the answers to questions about the fundamental physics of the Sun — like why the corona is so much hotter than the Sun’s surface and how the Sun’s constant outflow of material, the solar wind, is accelerated to such high speeds.

Image Credit: Miloslav Druckmüller, Peter Aniol, Shadia Habbal
Our Parker Solar Probe and the upcoming Solar Orbiter mission from the European Space Agency are exploring these questions by flying through the corona itself and taking unprecedented measurements of the conditions there. Plus, our newly-chosen PUNCH mission will create tiny, artificial eclipses in front of its cameras — using an instrument called a coronagraph — to study structures in the Sun’s corona and examine how it generates the solar wind.
Watching the eclipse
It’s never safe to look directly at the uneclipsed or partially eclipsed Sun – so you’ll need special solar viewing glasses or an indirect viewing method, like pinhole projection, to watch the eclipse.

For people in the path of totality, there will be a few brief moments when it is safe to look directly at the eclipse. Only once the Moon has completely covered the Sun and there is no sunlight shining is it safe to look at the eclipse. Make sure you put your eclipse glasses back on or return to indirect viewing before the first flash of sunlight appears around the Moon’s edge.
No matter where you are, you can watch the eclipse online! The Exploratorium will be streaming live views of the eclipse with commentary in both English and Spanish starting at 4 p.m. EDT / 1 p.m. PDT on July 2. Watch with us at nasa.gov/live!
Para más información e actualizaciones en español acerca del eclipse, sigue a @NASA_es en Twitter o vea esta hoja de hechos.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.










Ten Solstice Facts That Everyone Should Know
“9.) The solstices are neither the hottest nor coldest days of the year. This one is actually very specific to Earth: the hottest times of the year typically correspond to approximately 6 weeks after the summer solstice, and approximately 6 weeks after the winter solstice. Other planets don’t have this same phenomenon for one very important reason: they don’t have the majority of their surfaces covered in liquid water.
The oceans themselves, being composed of large quantities of water and containing approximately 1,000 times the mass of Earth’s atmospheres, contain a tremendous amount of heat, and are slow to change their temperatures. We might receive more (or less) energy from the Sun on the summer (or winter) solstices, but the oceans require time to heat up or cool down. Global average temperature extremes, therefore, usually occur in early August and February, rather than at the June and December solstices.”
The solstice, Latin for the Sun standing still in the sky, occurs whenever the Earth’s axial tilt reaches a maximum relative to the Earth’s orbital plane around the Sun. With a tilt of 23.5 degrees, but a tilt that’s independent of our elliptical orbit around the Sun, many surprising and counterintuitive facts arise.
Want to know as many of them as possible? Come get this remarkable and fascinating list of educational facts on this year’s solstice: June 21, 2019!
-
 galactictides52 liked this · 11 months ago
galactictides52 liked this · 11 months ago -
 ringa-starr reblogged this · 11 months ago
ringa-starr reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 mscdom liked this · 11 months ago
mscdom liked this · 11 months ago -
 armariellcuazon reblogged this · 11 months ago
armariellcuazon reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 live-loved reblogged this · 11 months ago
live-loved reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 belleinblush liked this · 11 months ago
belleinblush liked this · 11 months ago -
 psalm-twenty-three reblogged this · 11 months ago
psalm-twenty-three reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 anchoredin-him liked this · 11 months ago
anchoredin-him liked this · 11 months ago -
 geauxgetta reblogged this · 11 months ago
geauxgetta reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 l0vehaswon reblogged this · 11 months ago
l0vehaswon reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 legitimately liked this · 11 months ago
legitimately liked this · 11 months ago -
 tedxman reblogged this · 11 months ago
tedxman reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 tedxman liked this · 11 months ago
tedxman liked this · 11 months ago -
 graceandcaffeine reblogged this · 11 months ago
graceandcaffeine reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 shammah8 liked this · 11 months ago
shammah8 liked this · 11 months ago -
 sugaryluna-x liked this · 11 months ago
sugaryluna-x liked this · 11 months ago -
 massivefestivalfarmnerd-blog reblogged this · 11 months ago
massivefestivalfarmnerd-blog reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 massivefestivalfarmnerd-blog liked this · 11 months ago
massivefestivalfarmnerd-blog liked this · 11 months ago -
 revista reblogged this · 11 months ago
revista reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 inmymomera liked this · 11 months ago
inmymomera liked this · 11 months ago -
 osugahunnyicedtea liked this · 11 months ago
osugahunnyicedtea liked this · 11 months ago -
 icannotbejondenden47 reblogged this · 11 months ago
icannotbejondenden47 reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 icannotbejondenden47 liked this · 11 months ago
icannotbejondenden47 liked this · 11 months ago -
 coffeecupofsky reblogged this · 11 months ago
coffeecupofsky reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 coffeecupofsky liked this · 11 months ago
coffeecupofsky liked this · 11 months ago -
 fightinglikeaman reblogged this · 11 months ago
fightinglikeaman reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 onebackspace liked this · 1 year ago
onebackspace liked this · 1 year ago -
 tipsy-state-one liked this · 1 year ago
tipsy-state-one liked this · 1 year ago -
 starrlove28 reblogged this · 1 year ago
starrlove28 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 starrlove28 liked this · 1 year ago
starrlove28 liked this · 1 year ago -
 fightinglikeaman reblogged this · 1 year ago
fightinglikeaman reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 goosey-things liked this · 1 year ago
goosey-things liked this · 1 year ago -
 deliciousgalaxydream reblogged this · 1 year ago
deliciousgalaxydream reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 karmen-fourie liked this · 1 year ago
karmen-fourie liked this · 1 year ago -
 anamericanman97 liked this · 1 year ago
anamericanman97 liked this · 1 year ago -
 fightinglikeaman reblogged this · 1 year ago
fightinglikeaman reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 blazed-memories reblogged this · 3 years ago
blazed-memories reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 merpichi reblogged this · 3 years ago
merpichi reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 racheyrachey liked this · 4 years ago
racheyrachey liked this · 4 years ago -
 rongrace liked this · 4 years ago
rongrace liked this · 4 years ago -
 gelseyt liked this · 4 years ago
gelseyt liked this · 4 years ago -
 daisyhtoo reblogged this · 4 years ago
daisyhtoo reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 daisyhtoo liked this · 4 years ago
daisyhtoo liked this · 4 years ago