Astronaut Leland Melvin Includes His Rescued Dogs In Best NASA Portrait Ever.

Astronaut Leland Melvin includes his rescued dogs in best NASA portrait ever.
More Posts from Intergalacticnerd and Others
What’s Up for March 2016?
In March, Jupiter, it’s moons and moon shadows will all be visible in the sky. Find out when and where to look up:

Jupiter dominates the evening sky this month, rising at sunset and setting at dawn. On March 8, Jupiter reaches what is called “opposition”. Imagine that Jupiter and the sun are at opposite ends of a straight line, with the Earth in between. This brings Jupiter its closest to Earth, so it shines brighter and appears larger in telescopes.

On the nights of March 14 – 15, March 21 – 22 and March 29, two of Jupiter’s moons will cross the planet’s disk.

When the planet is at opposition and the sun shines on Jupiter’s moons, we can see the moon’s shadow crossing the planet. There are actually 11 of these double shadow transits in March!

The next six months will be awesome times for you to image Jupiter when it’s highest in the sky; near midnight now, and a little earlier each night through the late summer.
Even through the smallest telescopes or binoculars, you should be able to see the two prominent belts on each side of Jupiter’s equator made up of the four Galilean moons: Io, Europa Ganymede and Calisto. If you have a good enough view, you may even see Jupiter’s Red Spot!

Our Juno spacecraft will arrive at Jupiter on July 4th of this year and will go into orbit around the giant planet. Right now, the Juno mission science team is actively seeking amateur and professional images of the planet. These images are uploaded to a Juno website, and the public is invited to discuss points of interest in Jupiter’s atmosphere.

Locations will later be voted on and the favorites will be targets for JunoCam, the spacecraft’s imaging camera. Once JunoCam has taken the images, they’ll be posted online. Imaging participants can then process these raw mission images and re-upload them for others to view.

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com


T-2 hours - JASON-3 and Falcon 9 stand tall on the west coast. For the second time in its history, a SpaceX Falcon 9 v1.1 rocket stands at Vandenberg Air Force Base’s SLC-4E ready for launch. The 224 foot tall rocket will carry the joint NASA/NOAA JASON-3 satellite to study Earth’s oceans. Of the 20 flights of the Falcon 9 to date, all but one has occurred from Cape Canaveral’s SLC-40. The inaugural flight of Falcon 9 v1.1, Cassiope in September 2013, was also the debut of the vehicle on the west coast. The JASON-3 mission will see the final v1.1 Falcon 9 performing the vehicle’s second west coast flight. Liftoff will occur in the middle of a 30-second launch window, at 1:42 pm EST (10:42 am PST). NASA TV coverage started at 11 am EST. Watch the launch live here. p/c: SpaceX/NASA

A photo of Jupiter. Took by Voyager with VGISS on February 01, 1979 at 23:13:23. Detail page on OPUS database.






hubble’s panorama of the carina nebula, some 7500 light years away from earth, and about fifty light years in length here. stars old and new illuminate clouds of cosmic dust and gas, like the clumping hydrogen from which they were born.
the top star seen at the bisection of the first two panels, part of the eta carinae binary star system (most stars are in binary systems), is estimated to be more than a hundred times the mass of the sun - large enough to go supernoava in about a million years.
it also produces four million times as much light as the sun, and was once the second brightest star in the night sky. but surrounding dust and gas has dimmed our view of the star, though it’s still visible in the night sky to all but those in the most light polluted cities.
the fifth panel shows ‘the mystic mountain,’ where nascent stars in the dust cloud are spewing hot ionized gas and dust at 850,000 miles an hour. eventually, the ultraviolet radiation from these stars will blow away the dust, leaving visible the stars, like the cluster seen at the top of the panel, which were formed only half a million years ago.
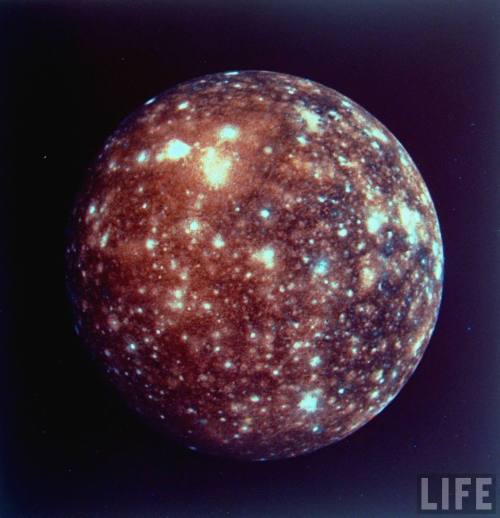
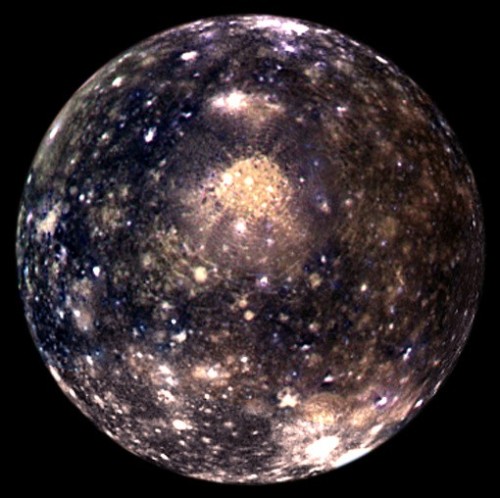
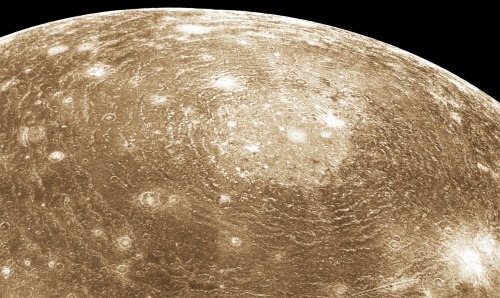
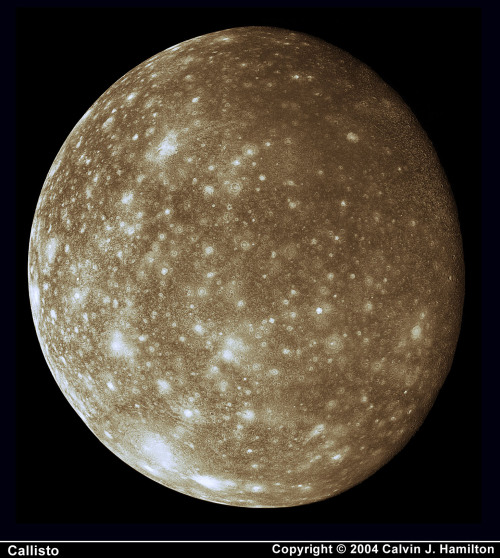
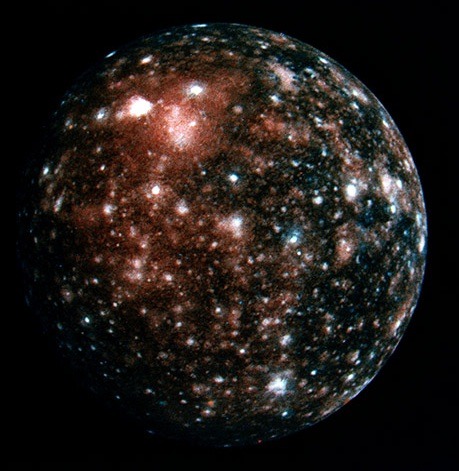




Jupiter’s moon, Callisto.

Grasping the stars 💫⭐










A recap of January in pictures! Winters the best time for astrophotography which is why I’ve had plenty of opportunities to get outside and capture the cosmos!

Ultraviolet Coverage of the Hubble Ultra Deep Field
js
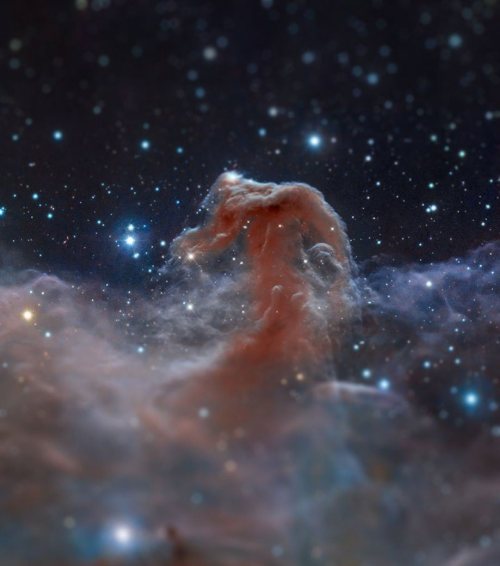
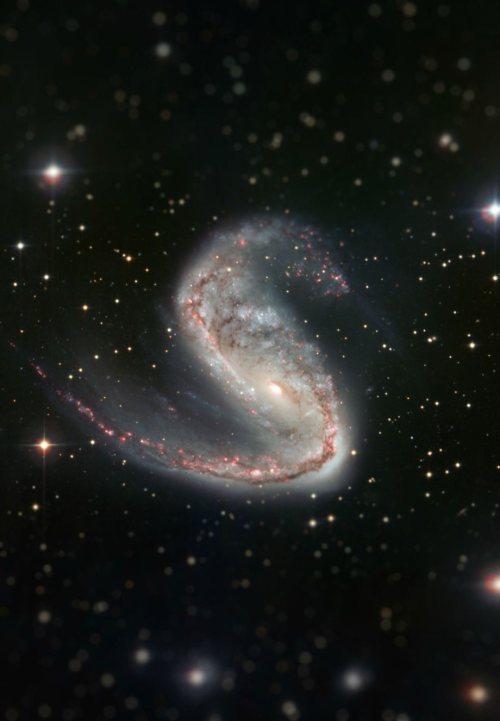
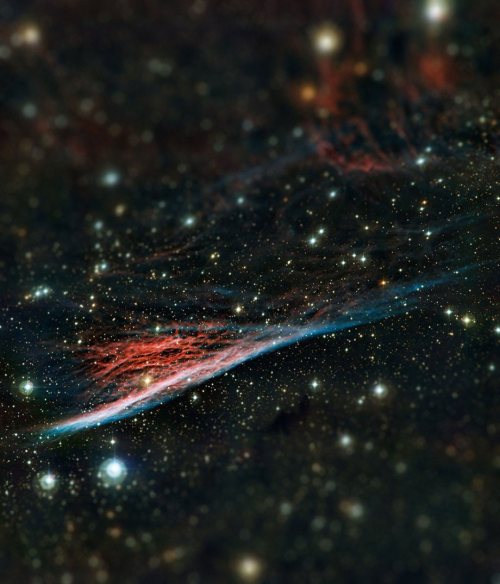
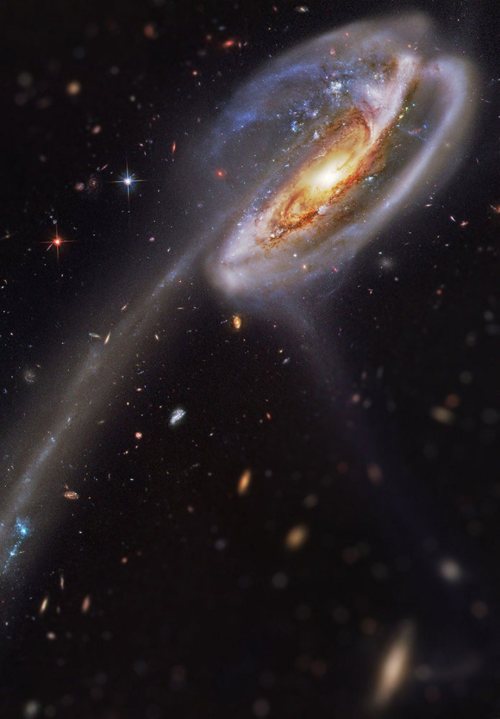










Tilt Shift filters applied to Hubble Space Telescope photos.
Tilt Shift filters make the foreground and background of images more blurred, changing the depth of field of these images.
(x)
[Click for more interesting science facts and gifs]

Shuttle Plume Shadow Points to the Moon
In early 2001 during a launch of Atlantis, the Sun, Earth, Moon, and rocket were all properly aligned for this photogenic coincidence. First, for the space shuttle’s plume to cast a long shadow, the time of day must be either near sunrise or sunset. Only then will the shadow be its longest and extend all the way to the horizon. Finally, during a Full Moon, the Sun and Moon are on opposite sides of the sky. Just after sunset, for example, the Sun is slightly below the horizon, and, in the other direction, the Moon is slightly above the horizon. Therefore, as Atlantis blasted off, just after sunset, its shadow projected away from the Sun toward the opposite horizon, where the Full Moon just happened to be.
Image Credit: Pat McCracken, NASA
(via NASA)
-
 pipale reblogged this · 1 month ago
pipale reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 saandruh liked this · 2 months ago
saandruh liked this · 2 months ago -
 baphometsbike liked this · 2 months ago
baphometsbike liked this · 2 months ago -
 blueeyesbalam2 liked this · 2 months ago
blueeyesbalam2 liked this · 2 months ago -
 thegurlfromipanemaa reblogged this · 2 months ago
thegurlfromipanemaa reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 holydimension reblogged this · 2 months ago
holydimension reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 obeycriminal liked this · 2 months ago
obeycriminal liked this · 2 months ago -
 3-frogs-in-a-suit liked this · 2 months ago
3-frogs-in-a-suit liked this · 2 months ago -
 ansor-brim liked this · 2 months ago
ansor-brim liked this · 2 months ago -
 karlapetrova13 liked this · 2 months ago
karlapetrova13 liked this · 2 months ago -
 skullsinheaven reblogged this · 2 months ago
skullsinheaven reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 lumi-nous liked this · 2 months ago
lumi-nous liked this · 2 months ago -
 clownesvanzandt liked this · 2 months ago
clownesvanzandt liked this · 2 months ago -
 shar3dmom3nts liked this · 2 months ago
shar3dmom3nts liked this · 2 months ago -
 nationalcatclub reblogged this · 2 months ago
nationalcatclub reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 nationalcatclub liked this · 2 months ago
nationalcatclub liked this · 2 months ago -
 jbrfreitas liked this · 2 months ago
jbrfreitas liked this · 2 months ago -
 kayeatsrainbows16 reblogged this · 2 months ago
kayeatsrainbows16 reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 thebonesofhoudini reblogged this · 2 months ago
thebonesofhoudini reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 thebonesofhoudini liked this · 2 months ago
thebonesofhoudini liked this · 2 months ago -
 95306 liked this · 2 months ago
95306 liked this · 2 months ago -
 artlessbabe liked this · 2 months ago
artlessbabe liked this · 2 months ago -
 catlizard liked this · 2 months ago
catlizard liked this · 2 months ago -
 y0ufancymemad liked this · 2 months ago
y0ufancymemad liked this · 2 months ago -
 kickasstorrents liked this · 2 months ago
kickasstorrents liked this · 2 months ago -
 gropesbabe liked this · 2 months ago
gropesbabe liked this · 2 months ago -
 oflline reblogged this · 2 months ago
oflline reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 oflline liked this · 2 months ago
oflline liked this · 2 months ago -
 beyond-the-beast liked this · 2 months ago
beyond-the-beast liked this · 2 months ago -
 layuredteeth liked this · 2 months ago
layuredteeth liked this · 2 months ago -
 iownherbodysheownsmysoul liked this · 2 months ago
iownherbodysheownsmysoul liked this · 2 months ago -
 tfisathoughtfulnickelbakeryfire liked this · 2 months ago
tfisathoughtfulnickelbakeryfire liked this · 2 months ago -
 cumsockpoprocks liked this · 2 months ago
cumsockpoprocks liked this · 2 months ago -
 tragic-red-orchids reblogged this · 2 months ago
tragic-red-orchids reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 tragic-red-orchids liked this · 2 months ago
tragic-red-orchids liked this · 2 months ago -
 fixshion reblogged this · 2 months ago
fixshion reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 fixshion liked this · 2 months ago
fixshion liked this · 2 months ago -
 nephertiri liked this · 2 months ago
nephertiri liked this · 2 months ago -
 daddyfuckedme reblogged this · 2 months ago
daddyfuckedme reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 thehiddenyogi reblogged this · 2 months ago
thehiddenyogi reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 the-reckless-ronin liked this · 2 months ago
the-reckless-ronin liked this · 2 months ago -
 the-reckless-ronin reblogged this · 2 months ago
the-reckless-ronin reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 thikthighsenpai reblogged this · 2 months ago
thikthighsenpai reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 3298sblog liked this · 2 months ago
3298sblog liked this · 2 months ago -
 kawaiidesu reblogged this · 2 months ago
kawaiidesu reblogged this · 2 months ago
"Astronomy compels the soul to look upwards and leads us from this world to another." - Plato
147 posts