Gravitational Waves Exist: The Inside Story Of How Scientists Finally Found Them

Gravitational Waves Exist: The Inside Story of How Scientists Finally Found Them
How a group of scientists proved Einstein right—and expanded our view of the universe.
More Posts from Intergalacticnerd and Others








Images of Hubble Ultra Deep Field (the farthest we’ve ever seen into the universe) and it’s close-ups. Astronomers, in 1996, attempted something extraordinary. They pointed the Hubble Space Telescope into a part of the sky that seemed utterly empty, a patch devoid of any planets, stars and galaxies. This area was close to the Big Dipper, a very familiar constellation. The patch of sky was no bigger than a grain of sand held out at arms length. There was a real risk that the images returned would be as black as the space at which it was being pointed. Nevertheless, they opened the telescope and slowly, over the course of 10 full days, photons that had been travelling for over 13 billion years finally ended their journey on the detector of humanity’s most powerful telescope. When the telescope was finally closed, the light from over 3,000 galaxies had covered the detector, producing one of the most profound and humbling images in all of human history - every single spot, smear, and dot was an entire galaxy, each one containing hundreds of billions of stars.
Later, in 2004, they did it again, this time pointing the telescope toward an area near the constellation Orion. They opened the shutter for over 11 days and 400 complete orbits around the Earth. Detectors with increased sensitivity and filters that allowed more light through than ever before allowed over 10,000 galaxies to appear in what became known as the Ultra Deep Field, an image that represented the farthest we’ve ever seen into the universe.The photons from these galaxies left when the universe was only 500 million years old, and 13 billion years later, they end their long journey as a small blip on a telescope’s CCD.
There are over 100 billion galaxies in the universe. Simply saying that number doesn’t really mean much to us because it doesn’t provide any context. Our brains have no way to accurately put that in any meaningful perspective. When we look at this image, however, and think about the context of how it was made, and really understand what it means, we instantly gain the perspective and cannot help but be forever changed by it. We pointed the most powerful telescope ever built by human beings at absolutely nothing, for no other reason than because we were curious, and discovered that we occupy a very tiny place in the heavens.


It was just discovered that there is a large ocean of water deep within the surface of Saturn’s icy moon, Enceladus.
John Nelson Creates Stunning Visuals of Earth ‘Breathing’

John Nelson, noted for creating remarkable visualizations depicting weather conditions of the planet, has come up with a pulsating GIF that shows the heartbeat of the Earth in a course of seasonal changes through NASA’s satellite photography. View his other amazing GIF below.
Keep reading
WHOA look at the moon
me literally every night no matter what phase the moon is in (via purple-space-freak)
How do you feel about space movies like Gravity or the Martian etc?
I thought they were great. I watched them both here aboard the International Space Station. Movie night looks like this!


Saturn and its largest moon reflect their true colors http://ift.tt/1lnhm8l
deep sea documentaries have me like

Views of Pluto
10 Images to Celebrate the Historic Exploration of the Pluto System
One year ago, our New Horizons mission made history by exploring Pluto and its moons – giving humankind our first close-up look at this fascinating world on the frontier of our solar system.

Since those amazing days in July 2015, the New Horizons spacecraft has transmitted numerous images and many other kinds of data home for scientists and the public alike to study, analyze, and just plain love. From Pluto’s iconic “heart” and sweeping ice-mountain vistas to its flowing glaciers and dramatic blue skies, it’s hard to pick just one favorite picture. So the mission team has picked 10 – and in no special order, placed them here.
Click the titles for more information about each image. You’ve seen nine of them before, and the team added a 10th favorite, also sure to become one of New Horizons’ “greatest hits.”
Vast Glacial Flows

In the northern region of Pluto’s Sputnik Planum, swirl-shaped patterns of light and dark suggest that a surface layer of exotic ices has flowed around obstacles and into depressions, much like glaciers on Earth.
Jagged Ice Shorelines and Snowy Pits

This dramatic image from our New Horizons spacecraft shows the dark, rugged highlands known as Krun Macula (lower right), which border a section of Pluto’s icy plains.
Blue Skies

Pluto’s haze layer shows its blue color in this picture taken by the New Horizons Ralph/Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC). The high-altitude haze is thought to be similar in nature to that seen at Saturn’s moon Titan.
Charon Becomes a Real World

At half the diameter of Pluto, Charon is the largest satellite relative to its planet in the solar system. Many New Horizons scientists expected Charon to be a monotonous, crater-battered world; instead, they’re finding a landscape covered with mountains, canyons, landslides, surface-color variations and more.
The Vistas of Pluto

Our New Horizons spacecraft looked back toward the sun and captured this near-sunset view of the rugged, icy mountains and flat ice plains extending to Pluto’s horizon. The backlighting highlights over a dozen layers of haze in Pluto’s tenuous but distended atmosphere.
The Dynamic Duo: Pluto and Charon in Enhanced Color

The color and brightness of both Pluto and Charon have been processed identically to allow direct comparison of their surface properties, and to highlight the similarity between Charon’s polar red terrain and Pluto’s equatorial red terrain. Pluto and Charon are shown with approximately correct relative sizes, but their true separation is not to scale.
Strange Snakeskin Terrain

A moment’s study reveals surface features that appear to be texturally ‘snakeskin’-like, owing to their north-south oriented scaly raised relief. A digital elevation model created by the New Horizons’ geology shows that these bladed structures have typical relief of about 550 yards (500 meters). Their relative spacing of about 3-5 kilometers makes them some of the steepest features seen on Pluto.
Pluto’s Heart

This view is dominated by the large, bright feature informally named the “heart,” which measures approximately 1,000 miles (1,600 kilometers) across. The heart borders darker equatorial terrains, and the mottled terrain to its east (right) are complex. However, even at this resolution, much of the heart’s interior appears remarkably featureless—possibly a sign of ongoing geologic processes.
Far Away Snow-Capped Mountains

One of Pluto’s most identifiable features, Cthulhu (pronounced kuh-THU-lu) stretches nearly halfway around Pluto’s equator, starting from the west of the great nitrogen ice plains known as Sputnik Planum. Measuring approximately 1,850 miles (3,000 kilometers) long and 450 miles (750 kilometers) wide, Cthulhu is a bit larger than the state of Alaska.
Colorful Composition Maps of Pluto

The powerful instruments on New Horizons not only gave scientists insight on what Pluto looked like, their data also confirmed (or, in many cases, dispelled) their ideas of what Pluto was made of. These compositional maps – assembled using data from the Linear Etalon Imaging Spectral Array (LEISA) component of the Ralph instrument – indicate the regions rich in ices of methane (CH4), nitrogen (N2) and carbon monoxide (CO), and, of course, water ice (H2O).
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
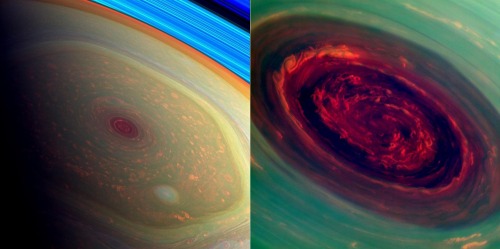
Saturn’s hexagonal storm system in it’s north pole
-
 mystillnessofheart reblogged this · 10 months ago
mystillnessofheart reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 mona-vainy reblogged this · 2 years ago
mona-vainy reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 mona-vainy liked this · 2 years ago
mona-vainy liked this · 2 years ago -
 ilaydaisbitch liked this · 5 years ago
ilaydaisbitch liked this · 5 years ago -
 delirioustea liked this · 8 years ago
delirioustea liked this · 8 years ago -
 mickeyangelo liked this · 8 years ago
mickeyangelo liked this · 8 years ago -
 magont reblogged this · 8 years ago
magont reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 this-cherry-blossom-girl reblogged this · 8 years ago
this-cherry-blossom-girl reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 this-cherry-blossom-girl liked this · 8 years ago
this-cherry-blossom-girl liked this · 8 years ago -
 studyingreatviews reblogged this · 8 years ago
studyingreatviews reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 slcr303 liked this · 8 years ago
slcr303 liked this · 8 years ago -
 dancewriteandbehappy liked this · 9 years ago
dancewriteandbehappy liked this · 9 years ago -
 deeperintowonderland liked this · 9 years ago
deeperintowonderland liked this · 9 years ago -
 finchness reblogged this · 9 years ago
finchness reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 pizzarolesnotgenderroles liked this · 9 years ago
pizzarolesnotgenderroles liked this · 9 years ago -
 agentshit reblogged this · 9 years ago
agentshit reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 modularflesh reblogged this · 9 years ago
modularflesh reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 modularflesh liked this · 9 years ago
modularflesh liked this · 9 years ago -
 as-warm-as-choco liked this · 9 years ago
as-warm-as-choco liked this · 9 years ago -
 imogenwrites reblogged this · 9 years ago
imogenwrites reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 angiebeni liked this · 9 years ago
angiebeni liked this · 9 years ago -
 spitfirealiceagra liked this · 9 years ago
spitfirealiceagra liked this · 9 years ago -
 ludicrousy reblogged this · 9 years ago
ludicrousy reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 missydfw liked this · 9 years ago
missydfw liked this · 9 years ago -
 fgulla liked this · 9 years ago
fgulla liked this · 9 years ago -
 joe-kwin reblogged this · 9 years ago
joe-kwin reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 my-thoughts-collected reblogged this · 9 years ago
my-thoughts-collected reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 fornothingatall liked this · 9 years ago
fornothingatall liked this · 9 years ago -
 ezrh reblogged this · 9 years ago
ezrh reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 19x94-blog liked this · 9 years ago
19x94-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 ibruno-reis reblogged this · 9 years ago
ibruno-reis reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 awk-1 liked this · 9 years ago
awk-1 liked this · 9 years ago -
 islandofnim reblogged this · 9 years ago
islandofnim reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 1individual liked this · 9 years ago
1individual liked this · 9 years ago -
 1individual reblogged this · 9 years ago
1individual reblogged this · 9 years ago
"Astronomy compels the soul to look upwards and leads us from this world to another." - Plato
147 posts