Cassini Top 10 Images And Science Results Of 2015
Cassini Top 10 Images and Science Results of 2015
As our Cassini spacecraft enters its final 20 months before its plunge into Saturn, the mission’s science team has selected their top 10 images from 2015 (above), a year of historic discoveries, as well as the top science results (below). Take a look:
1. First Deep Seafloor Hydrothermal Vents Found Beyond Earth

Cassini found the first evidence of active hot-water chemistry beyond planet Earth. An extensive, four-year analysis of data from the spacecraft, computer simulations and laboratory experiments led researchers to the conclusion the tiny silica (SiCO2) grains most likely form when hot water containing dissolved minerals from the moon’s rocky interior travels upward, coming into contact with cooler water.
2. Global Ocean Beneath Enceladus’ Surface

A global ocean lies beneath the icy crust of Saturn’s geologically active moon Enceladus. Scientists analyzed more than seven years’ worth of images of Enceladus taken by the spacecraft, which has been orbiting Saturn since mid-2004. As a result, they found Enceladus has a tiny, but measurable wobble as it orbits Saturn. This proves that there must be a global layer of liquid separating the surface from the core.
3. Titan Observed Outside of Saturnian Magnetosphere

During Cassini’s flyby of Titan, the giant moon happened to be on the sunward side of Saturn when a powerful outburst of solar activity reached the planet. The strong surge in the solar wind so compressed the sun-facing side of Saturn’s magnetosphere that the bubble’s outer edge was pushed inside the orbit of Titan. This left the moon exposed to, and unprotected from, the raging stream of energetic solar particles. The region of space dominated by Saturn’s magnetic field is called the magnetosphere.
4. Density of a Ring Particles May Indicate Recent Origins

Saturn’s A ring was found to be warmer than expected at the planet’s equinox, and also had an unusually large thermal asymmetry about the equinox. This could be due to the A ring being mostly composed of denser particles made primarily of solid ice, with a thin top layer of fluffy regolith.
5. Titan Southern Polar Ice Cloud

Scientists have detected a monstrous new cloud of frozen compounds in Titan’s low- to mid-stratosphere – a stable atmospheric region above the troposphere, or active weather layer.
6. Curtain Vents on Enceladus?

New research using data from Cassini suggests most of the eruptions from Saturn’s moon Enceladus might actually be diffuse curtains rather than discrete jets. Many features that appear to be individuals jets of material erupting along the length of prominent “tiger stripe” fractures in the moon’s south polar region might be phantoms created by an optical illusion, according to the new study.
7. Discovery of Tethys Red Arcs

Like graffiti sprayed by an unknown artist, unexplained arc-shaped, reddish streaks are visible on the surface of Saturn’s icy moon Tethys. The origin of the features and their reddish color is a mystery to scientists.
8. Saturn’s 30-year Giant Storms Powered by Water Convection

Changes in temperature and the composition of the hydrogen-laden air within the remnants of a giant storm system on Saturn reveal that air was lofted more than 120 miles in altitude from the deeper water condensation levels.
9. Seasonal Change Seen at Saturn’s Poles

Saturn’s polar regions have displayed extreme seasonal changes during Cassini’s decade-long watch, providing the most comprehensive view ever obtained of seasonal change on a giant planet.
10. Huygens Probe Imaging Mosaic of Titan’s Surface and Descent Movie

Ten years ago, an explorer from Earth, the Huygens probe, was released from the Cassini spacecraft and parachuted into the haze of an alien moon toward an uncertain fate. After a gentle descent lasting more than two hours, it landed with a thud on a frigid floodplain on Titan, surrounded by icy cobblestones.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Intergalacticnerd and Others
What’s Up for May 2016?

What’s Up for May? Two huge solar system highlights: Mercury transits the sun and Mars is closer to Earth than it has been in 11 years.

On May 9, wake up early on the west coast or step out for coffee on the east coast to see our smallest planet cross the face of the sun. The transit will also be visible from most of South America, western Africa and western Europe.

A transit occurs when one astronomical body appears to move across the face of another as seen from Earth or from a spacecraft. But be safe! You’ll need to view the sun and Mercury through a solar filter when looking through a telescope or when projecting the image of the solar disk onto a safe surface. Look a little south of the sun’s Equator. It will take about 7 ½ hours for the tiny planet’s disk to cross the sun completely. Since Mercury is so tiny it will appear as a very small round speck, whether it’s seen through a telescope or projected through a solar filter. The next Mercury transit will be Nov. 11, 2019.

Two other May highlights involve Mars. On May 22 Mars opposition occurs. That’s when Mars, Earth and the sun all line up, with Earth directly in the middle.

Eight days later on May 30, Mars and Earth are nearest to each other in their orbits around the sun. Mars is over half a million miles closer to Earth at closest approach than at opposition. But you won’t see much change in the diameter and brightness between these two dates. As Mars comes closer to Earth in its orbit, it appears larger and larger and brighter and brighter.

During this time Mars rises after the sun sets. The best time to see Mars at its brightest is when it is highest in the sky, around midnight in May and a little earlier in June.

Through a telescope you can make out some of the dark features on the planet, some of the lighter features and sometimes polar ice and dust storm-obscured areas showing very little detail.

After close approach, Earth sweeps past Mars quickly. So the planet appears large and bright for only a couple weeks.

But don’t worry if you miss 2016’s close approach. 2018’s will be even better, as Mars’ close approach will be, well, even closer.
You can find out about our #JourneytoMars missions at mars.nasa.gov, and you can learn about all of our missions at http://www.nasa.gov.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
LIGO Gravitational Wave Chirp - Chirp pattern of gravitational waves detected by LIGO on September 14, 2015. Credit: LIGO http://www.ligo.org/

A stunning high res photo of Saturn’s Moon Enceladus
why am i sad
I don’t have any answer to this but I hope you feel better :’( But here is a great example of astronomy and how awesome humanity can be


Southern Cross by Carlos Fairbairn
js

Saturn and its largest moon reflect their true colors http://ift.tt/1lnhm8l
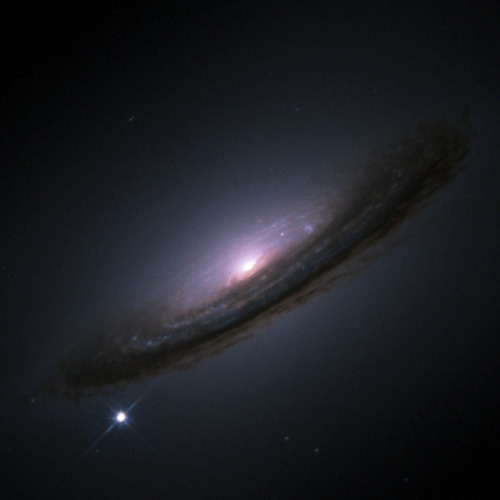

The bright spot in the lower left is SN 1994D, a star in the midst of a supernova, in the galaxy NGC 4526. During this final performance, the star will briefly outshine its parent galaxy. No supernovae have been observed in our galaxy in over four hundred years.
js
WHOA look at the moon
me literally every night no matter what phase the moon is in (via purple-space-freak)



We’ve always defined ourselves by the ability to overcome the impossible. And we count these moments. These moments when we dare to aim higher, to break barriers, to reach for the stars, to make the unknown known. We count these moments as our proudest achievements. But we lost all that. Or perhaps we’ve just forgotten that we are still pioneers. And we’ve barely begun. And that our greatest accomplishments cannot be behind us, because our destiny lies above us. - Interstellar, 2014.
-
 monaxikos-skantzoxoiros liked this · 7 years ago
monaxikos-skantzoxoiros liked this · 7 years ago -
 thorns-of-a-soul reblogged this · 7 years ago
thorns-of-a-soul reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 oksanadolna reblogged this · 7 years ago
oksanadolna reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 stfuwytefandoms liked this · 7 years ago
stfuwytefandoms liked this · 7 years ago -
 nightninja4 reblogged this · 7 years ago
nightninja4 reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 bamboocounting liked this · 7 years ago
bamboocounting liked this · 7 years ago -
 speedynoise liked this · 7 years ago
speedynoise liked this · 7 years ago -
 realgarn reblogged this · 7 years ago
realgarn reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 thestorieswelovecollection reblogged this · 7 years ago
thestorieswelovecollection reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 thestorieswelovecollection liked this · 7 years ago
thestorieswelovecollection liked this · 7 years ago -
 garlic-bulbs-5000 liked this · 7 years ago
garlic-bulbs-5000 liked this · 7 years ago -
 magicalmischel liked this · 8 years ago
magicalmischel liked this · 8 years ago -
 waywardbf reblogged this · 8 years ago
waywardbf reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 ninarosehotchkiss liked this · 8 years ago
ninarosehotchkiss liked this · 8 years ago -
 felunax liked this · 8 years ago
felunax liked this · 8 years ago -
 hoghbf liked this · 8 years ago
hoghbf liked this · 8 years ago -
 slachelchild reblogged this · 8 years ago
slachelchild reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 goddamnitnerds liked this · 8 years ago
goddamnitnerds liked this · 8 years ago -
 trisomylazarus liked this · 8 years ago
trisomylazarus liked this · 8 years ago -
 twilighttraveler-blog liked this · 8 years ago
twilighttraveler-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 androgynousprincepoetry-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
androgynousprincepoetry-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 andrevvfredrick liked this · 8 years ago
andrevvfredrick liked this · 8 years ago -
 letstake liked this · 9 years ago
letstake liked this · 9 years ago -
 corrupt-whore-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago
corrupt-whore-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 corrupt-whore-blog liked this · 9 years ago
corrupt-whore-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 chaostheorm liked this · 9 years ago
chaostheorm liked this · 9 years ago -
 latenightphilosopher reblogged this · 9 years ago
latenightphilosopher reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 mac-n-cheese25 liked this · 9 years ago
mac-n-cheese25 liked this · 9 years ago -
 adreamerinthemoonbeam liked this · 9 years ago
adreamerinthemoonbeam liked this · 9 years ago -
 vaikne-kosmos reblogged this · 9 years ago
vaikne-kosmos reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 rosys-life-lover-blog liked this · 9 years ago
rosys-life-lover-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 lektim reblogged this · 9 years ago
lektim reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 thehermitsacedia liked this · 9 years ago
thehermitsacedia liked this · 9 years ago -
 peachie3 liked this · 9 years ago
peachie3 liked this · 9 years ago
"Astronomy compels the soul to look upwards and leads us from this world to another." - Plato
147 posts