Asteroid Bennu, The Storyteller
Asteroid Bennu, the Storyteller
Asteroids are the storytellers of our solar system’s youth. They are the closest we can get to the original material that makes up the sun, planets, and moons.
This week, our OSIRIS-REx spacecraft made history when it touched a pristine, ancient asteroid named Bennu to collect a sample from the surface. The intrepid spacecraft will now bring the asteroid sample – and its stories – back home to Earth.
Why is it that asteroid Bennu holds the history of our origins? Let’s go back to the beginning…

About 4.5 billion years ago, our solar system began as a spinning, swirling cloud made up of tiny bits of gaseous and rocky material. Most of that material – more than 99% of it – gathered in the center and went on to become the Sun.

The leftovers began to spin around the Sun, colliding into one another and forming larger and larger objects, eventually becoming planets, dwarf planets, and moons.

But asteroids didn’t become part of planets or moons. So, while the material in planets and moons were superheated and altered during the formation of the solar system and weathered by geologic processes over time, asteroids remained pristine.

Each asteroid holds knowledge from that special time in our solar system’s history. Each one contains information about the chemicals, minerals, and molecules that were present when the solar system was just starting to form.

With missions like OSIRIS-REx, we are going on a journey to these ancient worlds, seeking to learn what they remember, seeking to expand our knowledge, and deepen our understanding of our origins.

Learn more about the OSIRIS-REx mission HERE, or follow the mission on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Glaretum and Others
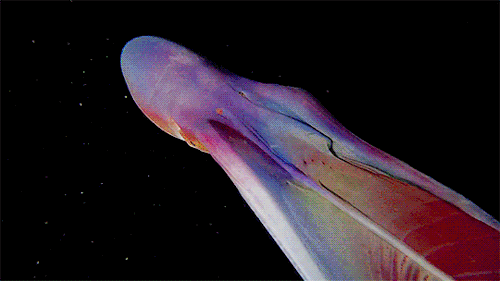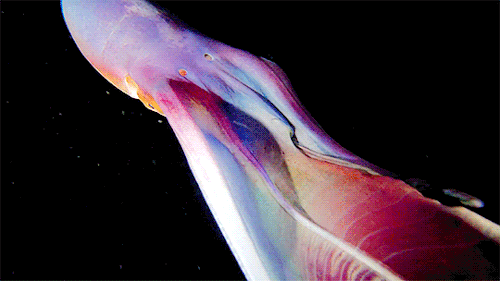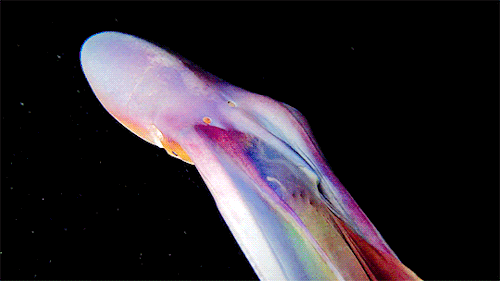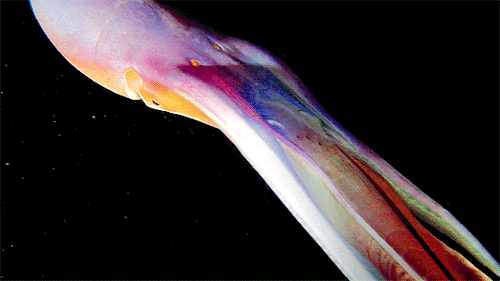

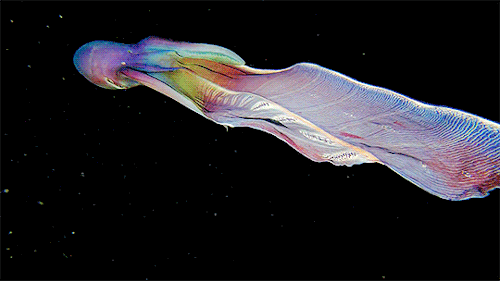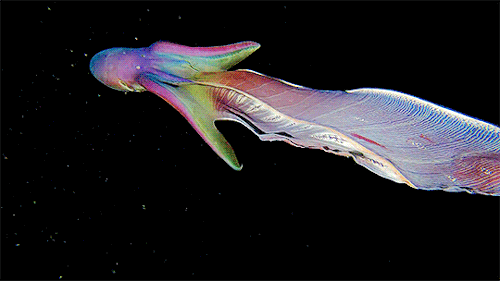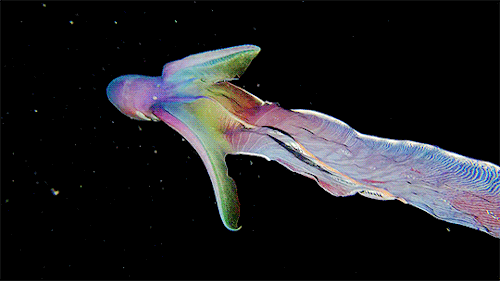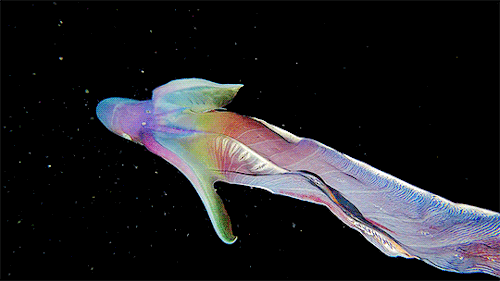


A close up of the Blanket Octopus during a blackwater dive with The Three P diving club , Romblon Island, Philippines. Credit: Joseph Elayani
Vía Láctea desde San Pedro Mártir, Baja California Norte México 🇲🇽
Crédito: Silvia Del Rincón

La imagen ganadora presentada fue tomada sobre el lago glacial más grande de Islandia . El fotógrafo combinó seis exposiciones para capturar no solo dos anillos de auroras verdes , sino también sus reflejos en el lago sereno. Visible en el cielo de fondo distante es la banda de nuestra Vía Láctea y la galaxia de Andrómeda .
Créditos: Stephane Vetter

Aurora Boreal.
Crédito: Ollie Taylor
@olliemtaylor

Luna desde Pinnacle Mountain State Park.
Crédito: Robert Fedez
https://www.facebook.com/RobertFedezz
https://instagram.com/robert_fedez
~Antares

'' Arboreal Chiaroscuro ''
Crédito: IG: Kiravictoriar
EXIF:
IS06400,17mm, f/2.8, 15.0 sec
Nikon D850,14-24mm (f2.8),
Induro CLT303 Classic Series 3 Stealth Carbon Fiber Tripod,
Indulto BHD2 Ball Head, Edited in LR

Sirio, Constelación de Orión y parte de la constelación de Tauro. Sus estrellas son algunas que nos indican el tiempo de frío en el hemisferio Norte.
Fotografía tomada desde Marble Canyon, Arizona.
Crédito: Evan Amos
https://instagram.com/evanamos
~Antares

Las colas del cometa NEOWISE tomada el 22 de julio de 2020. La segunda imagen muestra un primer plano del coma y el falso núcleo del cometa. Fue capturado con un smartphone a través del telescopio C11 EdgeHD.
Crédito: Sebastián Voltmer
https://instagram.com/sebastianvoltmer
https://www.voltmer.de/
~Antares


En septiembre de 2006 como parte de la Misión STS-115, el astronauta de la CSA, Steve MacLean se convirtió en el primer canadiense en operar Canadarm2 en el espacio y el segundo canadiense en realizar una caminata espacial.
Crédito: @NASA

Esta fotografía fue tomada desde la nave espacial Apollo 8 con una lente de longitud focal larga, mirando hacia el sur hacia el gran cráter Goclenius, que está en primer plano.
Crédito: NASA / JSC

-
 seeliecourtcatherineruiz liked this · 3 years ago
seeliecourtcatherineruiz liked this · 3 years ago -
 d0wntherabbiith0le liked this · 3 years ago
d0wntherabbiith0le liked this · 3 years ago -
 eonaeera liked this · 3 years ago
eonaeera liked this · 3 years ago -
 powerfrog reblogged this · 4 years ago
powerfrog reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 edsonlima17 liked this · 4 years ago
edsonlima17 liked this · 4 years ago -
 sherlocksittinginthelittlecouch liked this · 4 years ago
sherlocksittinginthelittlecouch liked this · 4 years ago -
 gamerbeforeitwascool liked this · 4 years ago
gamerbeforeitwascool liked this · 4 years ago -
 thelastoreo liked this · 4 years ago
thelastoreo liked this · 4 years ago -
 trashcatsstuff liked this · 4 years ago
trashcatsstuff liked this · 4 years ago -
 whaleb0ness liked this · 4 years ago
whaleb0ness liked this · 4 years ago -
 littlequeenrdc liked this · 4 years ago
littlequeenrdc liked this · 4 years ago -
 generaldisregard liked this · 4 years ago
generaldisregard liked this · 4 years ago -
 jackthebard reblogged this · 4 years ago
jackthebard reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 pinkiepieaddict reblogged this · 4 years ago
pinkiepieaddict reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 pickledbiscuit liked this · 4 years ago
pickledbiscuit liked this · 4 years ago -
 pepperoni4 liked this · 4 years ago
pepperoni4 liked this · 4 years ago -
 justanotherjess87 liked this · 4 years ago
justanotherjess87 liked this · 4 years ago -
 bobagrub liked this · 4 years ago
bobagrub liked this · 4 years ago -
 thehkr liked this · 4 years ago
thehkr liked this · 4 years ago -
 united-twosday reblogged this · 4 years ago
united-twosday reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 rubynye reblogged this · 4 years ago
rubynye reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 phoneticgrip reblogged this · 4 years ago
phoneticgrip reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 den1990 reblogged this · 4 years ago
den1990 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 kimbermcleod reblogged this · 4 years ago
kimbermcleod reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 lupinedrake liked this · 4 years ago
lupinedrake liked this · 4 years ago -
 silentwithatee liked this · 4 years ago
silentwithatee liked this · 4 years ago -
 art-or-something-else reblogged this · 4 years ago
art-or-something-else reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 amuseddragonfly liked this · 4 years ago
amuseddragonfly liked this · 4 years ago -
 delightfulpaperpost liked this · 4 years ago
delightfulpaperpost liked this · 4 years ago -
 evilgnome liked this · 4 years ago
evilgnome liked this · 4 years ago -
 eavidreader reblogged this · 4 years ago
eavidreader reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 cyphorical reblogged this · 4 years ago
cyphorical reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 mrrenhoeck liked this · 4 years ago
mrrenhoeck liked this · 4 years ago -
 virtualzonkslimepickle liked this · 4 years ago
virtualzonkslimepickle liked this · 4 years ago -
 alexandrblog reblogged this · 4 years ago
alexandrblog reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 alexandrblog liked this · 4 years ago
alexandrblog liked this · 4 years ago -
 kimbermcleod liked this · 4 years ago
kimbermcleod liked this · 4 years ago -
 heyndrix reblogged this · 4 years ago
heyndrix reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 lizardking90 reblogged this · 4 years ago
lizardking90 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 textorone liked this · 4 years ago
textorone liked this · 4 years ago -
 sloth-butts liked this · 4 years ago
sloth-butts liked this · 4 years ago -
 pink-crackhead liked this · 4 years ago
pink-crackhead liked this · 4 years ago -
 futuristicmagnificenthologram reblogged this · 4 years ago
futuristicmagnificenthologram reblogged this · 4 years ago

Glaretum fundado en el 2015 con el objetivo de divulgar la ciencia a través de la Astronomía hasta convertirnos en una fuente de conocimiento científico veraz siendo garantía de información seria y actualizada.
248 posts