Celebrating 17 Years Of NASA’s ‘Little Earth Satellite That Could’
Celebrating 17 Years of NASA’s ‘Little Earth Satellite That Could’
The satellite was little— the size of a small refrigerator; it was only supposed to last one year and constructed and operated on a shoestring budget — yet it persisted.
After 17 years of operation, more than 1,500 research papers generated and 180,000 images captured, one of NASA’s pathfinder Earth satellites for testing new satellite technologies and concepts comes to an end on March 30, 2017. The Earth Observing-1 (EO-1) satellite will be powered off on that date but will not enter Earth’s atmosphere until 2056.
“The Earth Observing-1 satellite is like The Little Engine That Could,” said Betsy Middleton, project scientist for the satellite at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
To celebrate the mission, we’re highlighting some of EO-1’s notable contributions to scientific research, spaceflight advancements and society.
Scientists Learn More About Earth in Fine Detail

This animation shifts between an image showing flooding that occurred at the Arkansas and Mississippi rivers on January 12, 2016, captured by ALI and the rivers at normal levels on February 14, 2015 taken by the Operational Land Imager on Landsat 8. Credit: NASA’s Earth Observatory
EO-1 carried the Advanced Land Imager that improved observations of forest cover, crops, coastal waters and small particles in the air known as aerosols. These improvements allowed researchers to identify smaller features on a local scale such as floods and landslides, which were especially useful for disaster support.

On the night of Sept. 6, 2014, EO-1’s Hyperion observed the ongoing eruption at Holuhraun, Iceland as shown in the above image. Partially covered by clouds, this scene shows the extent of the lava flows that had been erupting.
EO-1’s other key instrument Hyperion provided an even greater level of detail in measuring the chemical constituents of Earth’s surface— akin to going from a black and white television of the 1940s to the high-definition color televisions of today. Hyperion’s level of sophistication doesn’t just show that plants are present, but can actually differentiate between corn, sorghum and many other species and ecosystems. Scientists and forest managers used these data, for instance, to explore remote terrain or to take stock of smoke and other chemical constituents during volcanic eruptions, and how they change through time.
Crowdsourced Satellite Images of Disasters

EO-1 was one of the first satellites to capture the scene after the World Trade Center attacks (pictured above) and the flooding in New Orleans after Hurricane Katrina. EO-1 also observed the toxic sludge in western Hungary in October 2010 and a large methane leak in southern California in October 2015. All of these scenes, which EO-1 provided quick, high-quality satellite imagery of the event, were covered in major news outlets. All of these scenes were also captured because of user requests. EO-1 had the capability of being user-driven, meaning the public could submit a request to the team for where they wanted the satellite to gather data along its fixed orbits.

This image shows toxic sludge (red-orange streak) running west from an aluminum oxide plant in western Hungary after a wall broke allowing the sludge to spill from the factory on October 4, 2010. This image was taken by EO-1’s Advanced Land Imager on October 9, 2010. Credit: NASA’s Earth Observatory
Artificial Intelligence Enables More Efficient Satellite Collaboration

This image of volcanic activity on Antarctica’s Mount Erebus on May 7, 2004 was taken by EO-1’s Advanced Land Imager after sensing thermal emissions from the volcano. The satellite gave itself new orders to take another image several hours later. Credit: Earth Observatory
EO-1 was among the first satellites to be programmed with a form of artificial intelligence software, allowing the satellite to make decisions based on the data it collects. For instance, if a scientist commanded EO-1 to take a picture of an erupting volcano, the software could decide to automatically take a follow-up image the next time it passed overhead. The Autonomous Sciencecraft Experiment software was developed by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, and was uploaded to EO-1 three years after it launched.

This image of Nassau Bahamas was taken by EO-1’s Advanced Land Imager on Oct 8, 2016, shortly after Hurricane Matthew hit. European, Japanese, Canadian, and Italian Space Agency members of the international coalition Committee on Earth Observation Satellites used their respective satellites to take images over the Caribbean islands and the U.S. Southeast coastline during Hurricane Matthew. Images were used to make flood maps in response to requests from disaster management agencies in Haiti, Dominican Republic, St. Martin, Bahamas, and the U.S. Federal Emergency Management Agency.
The artificial intelligence software also allows a group of satellites and ground sensors to communicate and coordinate with one another with no manual prompting. Called a “sensor web”, if a satellite viewed an interesting scene, it could alert other satellites on the network to collect data during their passes over the same area. Together, they more quickly observe and downlink data from the scene than waiting for human orders. NASA’s SensorWeb software reduces the wait time for data from weeks to days or hours, which is especially helpful for emergency responders.
Laying the Foundation for ‘Formation Flying’

This animation shows the Rodeo-Chediski fire on July 7, 2002, that were taken one minute apart by Landsat 7 (burned areas in red) and EO-1 (burned areas in purple). This precision formation flying allowed EO-1 to directly compare the data and performance from its land imager and the Landsat 7 ETM+. EO-1’s most important technology goal was to test ALI for future Landsat satellites, which was accomplished on Landsat 8. Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
EO-1 was a pioneer in precision “formation flying” that kept it orbiting Earth exactly one minute behind the Landsat 7 satellite, already in orbit. Before EO-1, no satellite had flown that close to another satellite in the same orbit. EO-1 used formation flying to do a side-by-side comparison of its onboard ALI with Landsat 7’s operational imager to compare the products from the two imagers. Today, many satellites that measure different characteristics of Earth, including the five satellites in NASA’s A Train, are positioned within seconds to minutes of one another to make observations on the surface near-simultaneously.
For more information on EO-1’s major accomplishments, visit: https://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2017/celebrating-17-years-of-nasa-s-little-earth-satellite-that-could
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com/.
More Posts from Fillthevoid-with-space and Others
I just watched the 4 clearly visible planets march across the sky with the moon in the center, so here’s a short guide to the night sky as the last 3 move across.
mammenxTime lapse of the milky way rolling across the night sky, flanked by the planets Jupiter, Saturn & Mars. Taken from Diskit Ladakh, this place truly has some fantastic unobstructed views of the night sky

The last look before her descent in fire…
Five Famous Pulsars from the Past 50 Years
Early astronomers faced an obstacle: their technology. These great minds only had access to telescopes that revealed celestial bodies shining in visible light. Later, with the development of new detectors, scientists opened their eyes to other types of light like radio waves and X-rays. They realized cosmic objects look very different when viewed in these additional wavelengths. Pulsars — rapidly spinning stellar corpses that appear to pulse at us — are a perfect example.

The first pulsar was observed 50 years ago on August 6, 1967, using radio waves, but since then we have studied them in nearly all wavelengths of light, including X-rays and gamma rays.
Typical Pulsar
Most pulsars form when a star — between 8 and 20 times the mass of our sun — runs out of fuel and its core collapses into a super dense and compact object: a neutron star.

These neutron stars are about the size of a city and can rotate slowly or quite quickly, spinning anywhere from once every few hours to hundreds of times per second. As they whirl, they emit beams of light that appear to blink at us from space.
First Pulsar
One day five decades ago, a graduate student at the University of Cambridge, England, named Jocelyn Bell was poring over the data from her radio telescope - 120 meters of paper recordings.

Image Credit: Sumit Sijher
She noticed some unusual markings, which she called “scruff,” indicating a mysterious object (simulated above) that flashed without fail every 1.33730 seconds. This was the very first pulsar discovered, known today as PSR B1919+21.
Best Known Pulsar
Before long, we realized pulsars were far more complicated than first meets the eye — they produce many kinds of light, not only radio waves. Take our galaxy’s Crab Nebula, just 6,500 light years away and somewhat of a local celebrity. It formed after a supernova explosion, which crushed the parent star’s core into a neutron star.

The resulting pulsar, nestled inside the nebula that resulted from the supernova explosion, is among the most well-studied objects in our cosmos. It’s pictured above in X-ray light, but it shines across almost the entire electromagnetic spectrum, from radio waves to gamma rays.
Brightest Gamma-ray Pulsar
Speaking of gamma rays, in 2015 our Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope discovered the first pulsar beyond our own galaxy capable of producing such high-energy emissions.

Located in the Tarantula Nebula 163,000 light-years away, PSR J0540-6919 gleams nearly 20 times brighter in gamma-rays than the pulsar embedded in the Crab Nebula.
Dual Personality Pulsar
No two pulsars are exactly alike, and in 2013 an especially fast-spinning one had an identity crisis. A fleet of orbiting X-ray telescopes, including our Swift and Chandra observatories, caught IGR J18245-2452 as it alternated between generating X-rays and radio waves.

Scientists suspect these radical changes could be due to the rise and fall of gas streaming onto the pulsar from its companion star.
Transformer Pulsar
This just goes to show that pulsars are easily influenced by their surroundings. That same year, our Fermi Gamma Ray Space Telescope uncovered another pulsar, PSR J1023+0038, in the act of a major transformation — also under the influence of its nearby companion star.

The radio beacon disappeared and the pulsar brightened fivefold in gamma rays, as if someone had flipped a switch to increase the energy of the system.
NICER Mission
Our Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) mission, launched this past June, will study pulsars like those above using X-ray measurements.

With NICER’s help, scientists will be able to gaze even deeper into the cores of these dense and mysterious entities.
For more information about NICER, visit https://www.nasa.gov/nicer
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com










Black Holes Are Real And Spectacular, And So Are Their Event Horizons
“Originally estimated to be slightly larger than its M87 counterpart, the black hole at the center of the Milky Way — known as Sagittarius A* — has not yet had its event horizon imaged. When you observe the Universe, you don’t always get what you expect; sometimes, you get what it gives you. Instead, it was M87’s black hole that came through first, which was a much brighter and a much cleaner signal.
What we’ve found is spectacular. Those dark pixels at the center of the image are actually the silhouette of the event horizon itself. The light that we observe comes from the accelerated, heated matter around it, which must emit electromagnetic radiation. Where the matter exists, it emits radio waves, and the dark circle we see is where the background radio waves are blocked by the event horizon itself.”
We have an event horizon, folks! It wasn’t the one at the center of our galaxy that came through first, but rather the one at the center of Messier 87: a black hole over 1,000 times more massive, but some 2,000 times farther away, than the one contained in the Milky Way. This is an ultramassive black hole that’s almost the size of the entire Solar System, and its event horizon is real.
Come get the full story on what we know, now that we have our image, about black holes in the aftermath of the Event Horizon Telescope!
Until I get this show rolling, I’m going to be posting some of the things I’ve collected over the years that might make for interesting things to do podcasts about down the line!
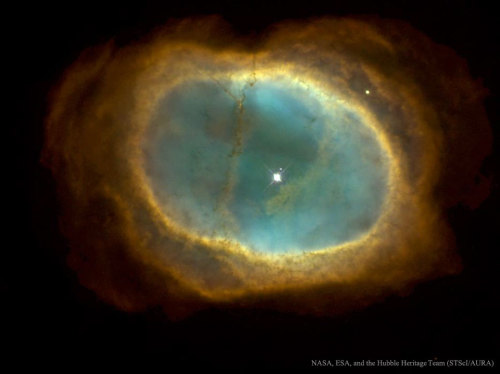
NGC 3132: The Eight Burst Nebula : Its the dim star, not the bright one, near the center of NGC 3132 that created this odd but beautiful planetary nebula. Nicknamed the Eight-Burst Nebula and the Southern Ring Nebula, the glowing gas originated in the outer layers of a star like our Sun. In this representative color picture, the hot blue pool of light seen surrounding this binary system is energized by the hot surface of the faint star. Although photographed to explore unusual symmetries, its the asymmetries that help make this planetary nebula so intriguing. Neither the unusual shape of the surrounding cooler shell nor the structure and placements of the cool filamentary dust lanes running across NGC 3132 are well understood. via NASA
js
Will NASA send astronauts to the moon again or any other planet within the next ten years?

@nasaorion spacecraft will launch on the Space Launch system (the largest spacecraft every built, even bigger than the Saturn V rocket!). Both are under construction @nasa currently, and this is the spacecraft that will take us beyond the low earth orbit of the International Space Station, whether that be the Moon, Mars, or beyond. We will conduct test missions with astronauts on Orion in the early 2020s, and a first mission will take us 40,000 miles beyond the Moon!





When the sun sets on Stonehenge on the shortest day of the year, it’s rays align with several important stones. Twice a year, the streets of Manhattan also line up with the setting sun, a phenomenon dubbed “Manhattanhenge”. Really, most cities with grid systems will see a similar effect (though it’s most dramatic in cities with tall buildings and a view of the true horizon). You can use a great tool called The Photographer’s Ephemeris to find out the “henge” dates for your city grid - or even individual streets.
Yesterday, (Friday, January 24th) the sun lined up with New York Avenue, a street in DC that runs diagonally up to the White House. (The orange line indicates alignment with the setting sun).
I went out with our multimedia intern Meg Vogel, and captured some images of the sun setting in line with a rather Stonehenge-y sculpture that sits in the middle of that street.
Here are dates for sunset “henge” events in some cities this year:
Manhattan May 25th, July 17th
Philadelphia April 5th, September 6th
Washington DC March 18th, September 24th
Chicago March 16th, September 26th
Phoenix March 20th, September 22nd
Portland, OR March 18th, September 24th
Is your city/town a grid? When’s your henge?
-
 lensclear reblogged this · 4 years ago
lensclear reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 lensclear liked this · 4 years ago
lensclear liked this · 4 years ago -
 kittiescatscats liked this · 4 years ago
kittiescatscats liked this · 4 years ago -
 gta5moneygenerator liked this · 4 years ago
gta5moneygenerator liked this · 4 years ago -
 hasunoto-blog liked this · 7 years ago
hasunoto-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 keycaribe liked this · 7 years ago
keycaribe liked this · 7 years ago -
 liviwithwifi liked this · 7 years ago
liviwithwifi liked this · 7 years ago -
 kro1026-blog liked this · 7 years ago
kro1026-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 allisoncheri reblogged this · 7 years ago
allisoncheri reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 havingfun09 liked this · 7 years ago
havingfun09 liked this · 7 years ago -
 fezzy-dingo liked this · 7 years ago
fezzy-dingo liked this · 7 years ago -
 shawn1965 liked this · 7 years ago
shawn1965 liked this · 7 years ago -
 entirely-of-flaws liked this · 7 years ago
entirely-of-flaws liked this · 7 years ago -
 etceterodactyl reblogged this · 7 years ago
etceterodactyl reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 mistermaf liked this · 7 years ago
mistermaf liked this · 7 years ago -
 islandpeeps liked this · 8 years ago
islandpeeps liked this · 8 years ago -
 beckyinmywildestdreams liked this · 8 years ago
beckyinmywildestdreams liked this · 8 years ago -
 rivendwellers liked this · 8 years ago
rivendwellers liked this · 8 years ago -
 openfire55 liked this · 8 years ago
openfire55 liked this · 8 years ago -
 fishkinger reblogged this · 8 years ago
fishkinger reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 tumbleweed-chaser liked this · 8 years ago
tumbleweed-chaser liked this · 8 years ago -
 fleurdebach5-blog liked this · 8 years ago
fleurdebach5-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 sixthrangerknight reblogged this · 8 years ago
sixthrangerknight reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 utot-atbp liked this · 8 years ago
utot-atbp liked this · 8 years ago -
 azhdarcho reblogged this · 8 years ago
azhdarcho reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 nochg reblogged this · 8 years ago
nochg reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 hybridefiant-archive reblogged this · 8 years ago
hybridefiant-archive reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 w122w122 reblogged this · 8 years ago
w122w122 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 ca00-blog liked this · 8 years ago
ca00-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 smileytechie liked this · 8 years ago
smileytechie liked this · 8 years ago -
 jchapa13 liked this · 8 years ago
jchapa13 liked this · 8 years ago -
 evilislikeevildoes liked this · 8 years ago
evilislikeevildoes liked this · 8 years ago -
 magnetic-terp-input reblogged this · 8 years ago
magnetic-terp-input reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 youarenothem reblogged this · 8 years ago
youarenothem reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 theironfrogg liked this · 8 years ago
theironfrogg liked this · 8 years ago -
 alvesdacosta liked this · 8 years ago
alvesdacosta liked this · 8 years ago -
 buzz-london reblogged this · 8 years ago
buzz-london reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 wrangletangle reblogged this · 8 years ago
wrangletangle reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 cynical-nerd reblogged this · 8 years ago
cynical-nerd reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 cynical-nerd liked this · 8 years ago
cynical-nerd liked this · 8 years ago -
 eergene59 liked this · 8 years ago
eergene59 liked this · 8 years ago -
 edisee-eieyes-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
edisee-eieyes-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
A podcast project to fill the space in my heart and my time that used to be filled with academic research. In 2018, that space gets filled with... MORE SPACE! Cheerfully researched, painstakingly edited, informal as hell, definitely worth everyone's time.
243 posts






























