Writing From Scratch #3
Writing from Scratch #3
Flash Fiction: A Simple Plot
The first writing prompts we’re going to tackle will be flash fiction pieces. Flash fiction is a complete story written in under 1,500 words. We’ll be aiming for 250-500 words at first – that is one or two pages double spaced written in Times New Roman 12 pt. font.
The type of flash fiction I’ll encourage you to write will be Eighteen Sentence Stories*, and each of these sentences will have a very specific job.
The first Three sentences will provide the main character, the setting, and the genre (which clues the audience in on what kind of story they are about to read).
The main character should be introduced via an action that reveals their attitude at the start and with one defining job or trait that relates them to the plot. For example, a character may be both a father of three and a pilot. If the problem of the plot will deal with the kidnapping of one of his daughters, then “father” or “father of three” will be the defining job; if the problem of the plot will deal with the starship he’s piloting falling under attack, then “pilot” will be the defining job.
The setting should be introduced via a grounding sensory detail. The lingering scent of cookies left to burn when the parents received the ransom note. Or the pressure of being pinned back into the pilot’s seat under g forces.
The genre should be introduced via something specific and unique to the story. A ransom note is not specific or unique; a ransom note scrawled on the back of a picture that went missing off the fridge the week before is. A space ship is not specific or unique; a living space ship with a giant brain in its core that the pilot must psychically link to via the tentacles that suction onto his temples is.
Read More on WordPress
More Posts from Feralpaules and Others
Structuring a Series: Part III
Structuring a Series Part III: Planning a Series from 1 Book
Welcome back to Part III of Structuring a Series! If you haven’t read Parts I and II yet, you might want to. Or at least familiarize yourself with Dan Wells’s 7 Point Plot Structure. (No word on which one is a bigger time commitment.) Ok, so… you want to write a trilogy (or some other type of close-ended series with at least one arc running through the whole thing), BUT you only know what you…
View On WordPress
Writing from Scratch #7: The Event Plot
The Event Plot
The problem of an Event plot is a disruption to the status quo. The solution comes either from setting everything right again or adapting to the change. The Event plot is probably what most people think of when they think “what is a plot?” Any story that deals with a life-changing or world-changing event is an Event.
The first plot I analyzed, from The Expanse television series, is an Event plot. Let’s look at another: The Princess Diaries. As we did with Lord of the Rings, we’ll look at the movie rather than books because more people will be familiar with the movie (which is a damn shame).
The Event: Mia Thermopolis’s grandmother tells Mia that she is the princess of small European kingdom Genovia, and she must take the throne.
Read More on WordPress
Writing from Scratch #8: Complex Plots, Part 1
Complex Plots, Part 1: Dependency
Now that we have gone over the four simple plot-problems (1, 2, 3, 4) and how they are solved through try-fail cycles, we’ll take a look at how to make complex, compound, and compound-complex plots through the same devices as sentence creation.
The first way we’ll try complicating a plot is by making the solution of the first noted plot-problem dependent on the solution of a second plot-problem, which stands in for easy solution prevention. We’re typically going to use dependent plots to strengthen audience satisfaction when the character is finally able to succeed. Or, like in the case-study we’ll look at today, they can be used to draw what appeared to be disparate plots together in longer works.
Let’s look at an example from Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban, Chapter Seventeen, “Cat, Rat, and Dog.”
The first plot-problem to arise an Event. Ron has been tackled by a large black dog that has been stalking Harry all school year and dragged underground. Harry succinctly gives the stakes as, “That thing’s big enough to eat him; we haven’t got time.” And what’s preventing them from going directly after Ron to save him is the Whomping Willow, which triggers an Inquiry plot – How does one get past the Whomping Willow to the tunnel?
First Harry tries to dodge through. He’s unable to get to the tunnel entrances and is thrashed by the branches for his trouble.
Then, Crookshanks appears and places his paw on a knot on the Whomping Willow’s trunk, which temporarily stills the whomping. This answers the question, and Harry and Hermione take the opportunity to dash beneath the stilled branches and into the tunnel.
Now, we return to the Event plot; Harry and Hermione will try to reestablish the status quo by rescuing Ron from the dog. If you’ve read the book, you know how that try-fail cycle continues on.
As we begin to add plots together in various ways, it is always important to remember that the plot-solutions should come in reverse order to the introductions of the plot-problems. The first plot problem introduced should be the last one solved (even when they are right on top of each other).
We’re going to continue with writing flash fiction. Using the Eighteen Sentence Story breakdown, we’ll expand just a little out from there. In the two sentences introducing the plot-problem, you’ll create a second plot-problem to prevent the first from being solved easily. Add 5-10 sentences for a try-fail cycle and plot solution to this second plot-problem, and then continue with the 5 sentence try-fail, 5 sentence solution, and 3 sentence wrap-up for the original plot-problem.
Prompt: write a flash fiction with a Milieu plot involving a treasure hunt; complicate the Milieu plot by first requiring an Inquiry plot answering “where” before moving onto the Milieu plot solution.
This was first published in July 2020, and I’ve written much more since on my website theferalcollection.com
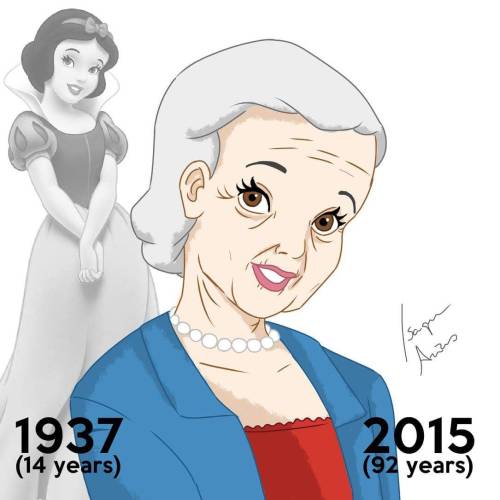
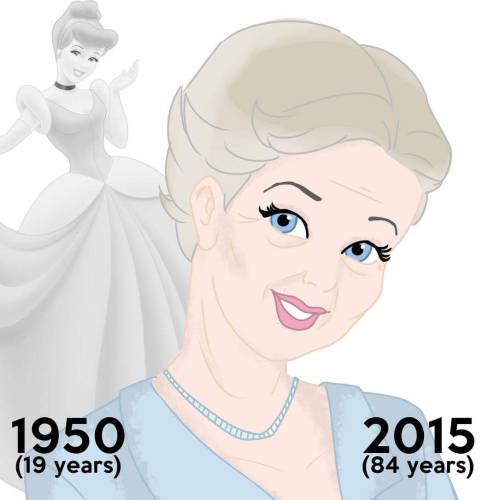
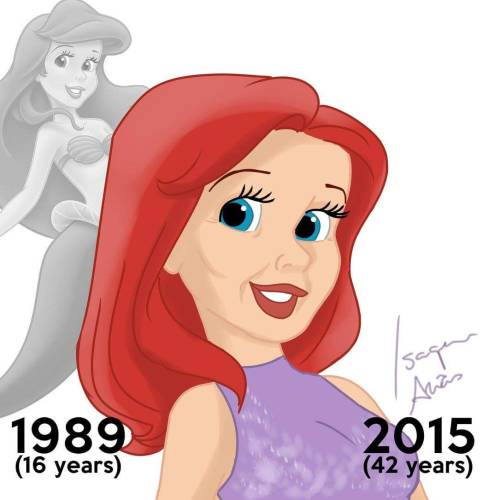
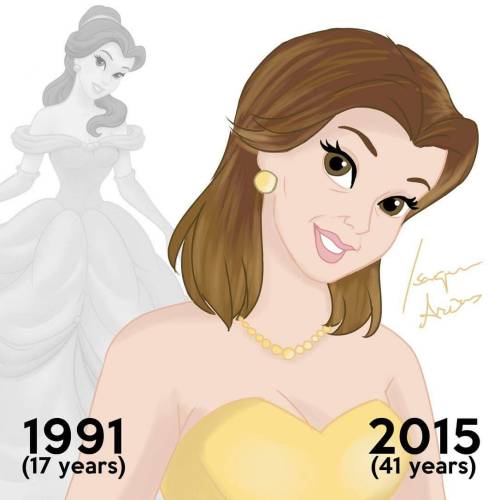
Disney Princesses at their Current Ages
Structuring a Series: Part I
Structuring a Series: Part I
Last Tuesday, my writing group did a mini-workshop of Dan Wells’s 7 Point Plot Structure, which is awesome and everyone not familiar with it should go check it out (if you don’t have time to watch the whole thing just now, I’ll go over the basics in this post, but I still suggest seeing his presentation for more details). Anyway, Two is trying to plot a trilogy, which got me thinking about how…
View On WordPress
Writing from Scratch #6
The Character Plot
The problem of a Character plot involves a character’s worldview – their beliefs, values, desires, and fears. Many but not all stories include a Character plot, often called a character arc, in which a character’s worldview shifts. A Character plot is entirely concerned with the internal state of the character in question and as such is rarely seen on its own. When it is on its own, as it is in “Miss Brill” by Katherine Mansfield, you can end up with an extraordinary story.
Because a Character plot is entirely internal, the try-fail cycles don’t work out exactly the same as they do when dealing with an external/physical problem and solution; they are also up for interpretation by the reader when done subtly and beautifully as in “Miss Brill.” Character plot try-fails are often not even done intentionally as typically the character does not realize a change in the worldview needs to occur. So, read “Miss Brill” (it’s short, less than 2,000 words) and try for yourself to determine the problem – it’s not stated directly – and identify the try-fails. After, you can read over my interpretation, please let me know in the comments how our thoughts compare!
Read More on WordPress
Writing from Scratch #1
Welcome to Writing from Scratch!
I’ve been writing a long time, and sometimes it feels like I lose the trees for the forest. Writing from Scratch is a chance for me (and you!) to get back to the basics of storytelling.
If you’ve never written a story before, if you’ve never felt like you could come up with one that would be worth writing, my hope is that if you follow along with me here, you will have the confidence and know-how to come up with an idea, build it into a story, and share it with the world.
These posts will be little, easy-to-digest nuggets. At the end of every post, look for a prompt and share your response in the comments!
What Is a Story?
A story can be defined by what it contains: at least one plot, character, and setting, and a style through which it is told.
Story Bits
To begin, let’s take a look at the second smallest unit of a story – the sentence. A sentence is a set of words that conveys a complete thought. And communication is fractal, meaning each part shares the same pattern as the whole. A story and its components, therefore, will also convey a Complete Thought.
A simple sentence is an independent clause, containing a subject and a predicate. It may have any number of phrases attached to it, but in its simplest form, a sentence can be as short as two words.
A complex sentence is a sentence containing an independent clause and at least one dependent or subordinate clause (a set of words containing a subject and predicate but that is dependent on another clause for a complete understanding of its meaning).
A compound sentence is a sentence containing at least two independent clauses.
And a compound-complex sentence is a sentence containing at least two independent clauses and at least one dependent or subordinate clause.
Plots are exactly the same as sentences. A simple plot can be broken into two parts, a subject and a predicate, or, better, a problem and a solution. It can then be complicated or compounded with additional plots.
Next week, we’ll look at what exactly we’re talking about when we’re talking about plots.
Share in the comments:
How else have you heard “story” defined? What aspects of storytelling are you most interested in? What makes a story worthwhile to you?
If you want to read more, you can check out the over 80 posts on my website, theferalcollection.com
Writing from Scratch #8
Now that we have gone over the four simple plot-problems (1, 2, 3, 4) and how they are solved through try-fail cycles, we’ll take a look at how to make complex, compound, and compound-complex plots through the same devices as sentence creation.
The first way we’ll try complicating a plot is by making the solution of the first noted plot-problem dependent on the solution of a second plot-problem, which stands in for easy solution prevention. We’re typically going to use dependent plots to strengthen audience satisfaction when the character is finally able to succeed. Or, like in the case-study we’ll look at today, they can be used to draw what appeared to be disparate plots together in longer works.
Read more on WordPress
Structuring a Series: Part II
Structuring a Series: Part II: Extrapolating Complete Episodes from the Trilogy #writerslife
Welcome back! If you haven’t checked out Part I already, go ahead and do that; we’ll be right here when you get back. Extrapolating Complete Episodes from the Trilogy (more…)
View On WordPress
My 90yr old Irish Catholic grandpa doesn’t miss with my gender. He’s never gotten my name wrong, or my pronouns, never even faltered over it.
It’s all so natural too: son, big man, young man…
We’ve never talked about it. He’s the only one who hasn’t pushed for details. He just accepted it and carried on because it’s not a huge deal.
It’s so comforting.
-
 theferalcollection reblogged this · 4 years ago
theferalcollection reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 feralpaules reblogged this · 4 years ago
feralpaules reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 feralpaules reblogged this · 4 years ago
feralpaules reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 theferalcollection reblogged this · 4 years ago
theferalcollection reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 theferalcollection reblogged this · 4 years ago
theferalcollection reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 feralpaules reblogged this · 4 years ago
feralpaules reblogged this · 4 years ago
check out my main blog www.theferalcollection.wordpress.com and find fandoms and funstuff on www.theferalcollection.tumblr.com
103 posts