Send Me To Mars With Party Supplies Before Next August 5th

Send me to Mars with party supplies before next august 5th
More Posts from Dotmpotter and Others










Brand: Christie Brown
Designer: Aisha Obuobi
Coupe de Classe Winter 2015 Collection
Tumblr: cutfromadiffcloth.tumblr.com | Twitter: @IAM_CFDC | Instagram: @IAMCFDC | Facebook: CUT FROM A DIFFERENT CLOTH | Website: www.cutfromadiffcloth.com

Iceland to Help Develop Geothermal Energy in Ethiopia
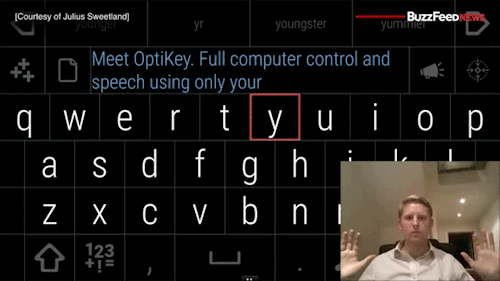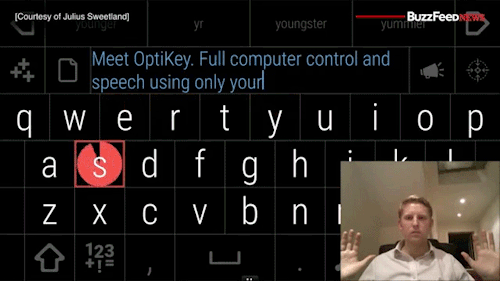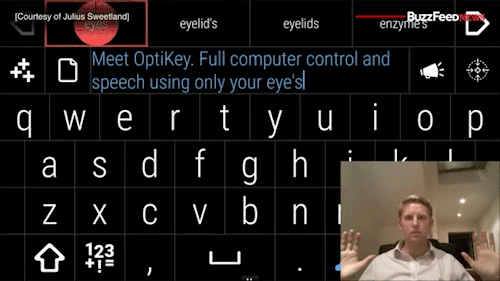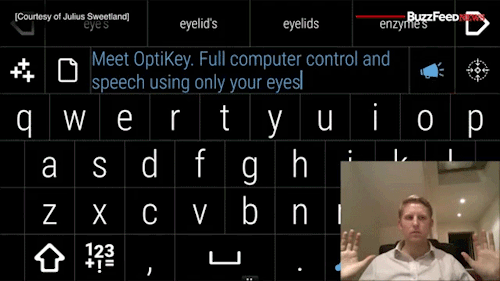





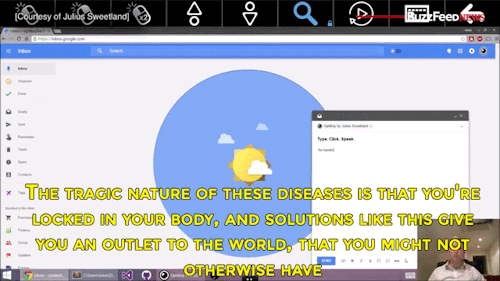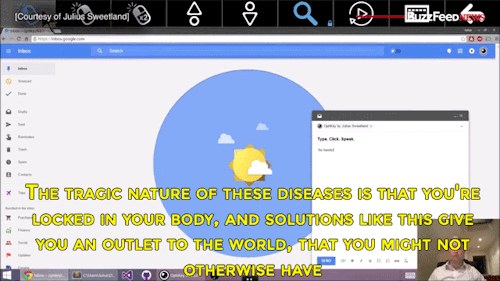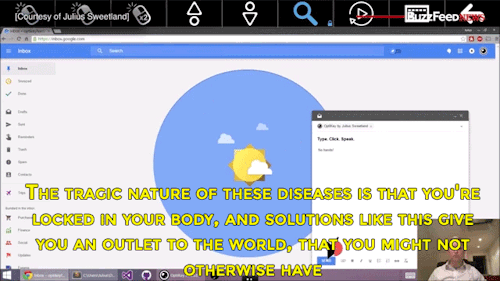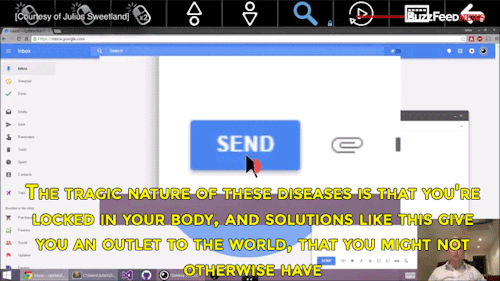

Watch the video of this man giving away his software for free to help people with degenerative diseases communicate

A good way to remember the human bones in the body. Dope pic
www.learninghumananatomy.com
It’s estimated that the world yields 110 million tons of citrus fruits annually, with oranges accounting for more than half of that production volume. Given that not every part of the fruit is put to use, that’s a lot of waste. But researchers at Flinders University in Adelaide, Australia, have made a breakthrough that will allow humans to use citrus waste to suck the highly poisonous metal mercury out of land and sea.
Orange Peel Waste Can Help Remove Mercury Pollution From Oceans | GOOD

Ever wonder how coal formed?

Can an army of voluntary "mappers" (like you) help end child slavery on Lake Volta, Ghana?



LEARN MORE about being a “mapper” here.
Consider a 100% tax-deductible DONATION to free a child from slavery on Lake Volta here: madeinafreeworld.com/ghana

The New England Climate Adaptation Project (NECAP) got local citizens and officials in four coastal towns to engage in role-playing games about climate change tailored to their communities, while conducting local polling about attitudes and knowledge about climate risks. In so doing, the project helped the towns reach new conclusions about local initiatives to address the threats posed by climate change— which in coastal communities may include rising sea levels and increased storm surges that can lead to flooding.
“One hour of conversation can completely alter people’s sense [and show] that this is a problem they can work on locally,” says Lawrence Susskind, the Ford Professor in Urban Studies in MIT’s Department of Urban Studies and Planning (DUSP), who led the project and has now co-authored a new book detailing its results. “There are a bunch of things local governments can do, and people can do for themselves — that communities can do.”
The findings stem from years of research and organizing in four places: Wells, Maine; Dover, New Hampshire; Barnstable, Massachusetts; and Cranston, Rhode Island. The new book on the effort, “Managing Climate Risks in Coastal Communities,” has just been released by the academic publisher Anthem Press.
Among the many findings of the project is that residents of these coastal communities were typically far more concerned about the consequences of climate change than local politicians realized.
KARMA POLICE: GCHQ's plan to track every Web user in the world

The KARMA POLICE program is detailed in newly released Snowden docs published on The Intercept; it began as a project to identify every listener to every Internet radio station (to find people listening to jihadi radio) and grew into an ambitious plan to identify every Web user and catalog their activities from porn habits to Skype contacts.
The program began in 2007/8 and it mined BLACK HOLE, which is GCHQ’s repository for all the data sucked up by its fiber taps (which it calls “probes”). It attempted to map IP addresses to peoples’ identities, and cross reference users’ identities on various systems and in various locations, collecting them into “a web browsing profile for every visible user on the Internet.”
Part of this was accomplished by looking at a users’ cookies – if you log into Google on your phone and your laptop, GCHQ use its surveillance views into that cookie to connect all the traffic from your laptop and phone with a single identity. The agency exploited cookies from a wide variety of popular websites that put like/share buttons, beacons, and other assets on a many other sites. The targeted cookies came from Google, Microsoft, Facebook, Reddit, the BBC, Amazon, WordPress, Yahoo, and others.
KARMA POLICE drew on a frankly bewildering array of other programs, which sucked up data from a variety of sources. These programs were given exotic codenames by GCHQ: SOCIAL ANTHROPOID, MEMORY HOLE, MARBLED GECKO, INFINITE MONKEYS, etc. These logged different kinds of Internet events – search queries, Google Maps searches, and BBS/message-board posts.
The UK spy agency had an extraordinary view into the world’s Internet traffic thanks to the number of oceanic fiber links that make landfall in the UK.
Like the NSA, GCHQ relied on secret interpretations of the laws on spying to paper over its activities, so that it could tell its governmental overseers that all its activities were lawful. It amassed records on people from all over the world, including Britons, and routinely allows its spying partners to search its databases. The US NSA, as well as spy agencies from Canada, Australia, and New Zealand all have access to its data on British citizens and people from all over the world.
Read the rest
-
 paulbettner-blog liked this · 2 weeks ago
paulbettner-blog liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 not-ricochet reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
not-ricochet reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 cwicseolfor reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
cwicseolfor reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 alyzu reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
alyzu reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 jadzbot liked this · 2 weeks ago
jadzbot liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 thesilencedmasses reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
thesilencedmasses reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 maydayfromspace reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
maydayfromspace reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 tatsuki-fujimotos-toe-beans reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
tatsuki-fujimotos-toe-beans reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 kittycatcarla reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
kittycatcarla reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 aer0wave liked this · 3 weeks ago
aer0wave liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 saltysupercomputer liked this · 1 month ago
saltysupercomputer liked this · 1 month ago -
 waeylin liked this · 1 month ago
waeylin liked this · 1 month ago -
 xvierrax liked this · 1 month ago
xvierrax liked this · 1 month ago -
 kittycatcarla reblogged this · 1 month ago
kittycatcarla reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 cupcakesmoothie reblogged this · 1 month ago
cupcakesmoothie reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 cupcakesmoothie liked this · 1 month ago
cupcakesmoothie liked this · 1 month ago -
 immunetogloom liked this · 1 month ago
immunetogloom liked this · 1 month ago -
 point-of-void reblogged this · 2 months ago
point-of-void reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 crowned-with-stars liked this · 2 months ago
crowned-with-stars liked this · 2 months ago -
 moths-and-radio-talk reblogged this · 2 months ago
moths-and-radio-talk reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 honey-stick reblogged this · 2 months ago
honey-stick reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 lira-is-a-blob liked this · 2 months ago
lira-is-a-blob liked this · 2 months ago -
 rod-serlings-eyebrows liked this · 2 months ago
rod-serlings-eyebrows liked this · 2 months ago -
 obsessedwithecho liked this · 2 months ago
obsessedwithecho liked this · 2 months ago -
 exiledtroll liked this · 2 months ago
exiledtroll liked this · 2 months ago -
 charwashere liked this · 2 months ago
charwashere liked this · 2 months ago -
 crazyhairadult reblogged this · 2 months ago
crazyhairadult reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 crazyhairadult liked this · 2 months ago
crazyhairadult liked this · 2 months ago -
 youalwaysenviedmortals liked this · 2 months ago
youalwaysenviedmortals liked this · 2 months ago -
 no-longer-babygirl reblogged this · 2 months ago
no-longer-babygirl reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 babygirlismpersonified liked this · 2 months ago
babygirlismpersonified liked this · 2 months ago -
 sleepyman liked this · 2 months ago
sleepyman liked this · 2 months ago -
 yolbert liked this · 2 months ago
yolbert liked this · 2 months ago -
 dreamingdruka reblogged this · 2 months ago
dreamingdruka reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 dreamingdruka liked this · 2 months ago
dreamingdruka liked this · 2 months ago -
 johnlocked-swiftie liked this · 2 months ago
johnlocked-swiftie liked this · 2 months ago -
 emmabrine liked this · 2 months ago
emmabrine liked this · 2 months ago -
 shitposts-and-shit liked this · 2 months ago
shitposts-and-shit liked this · 2 months ago -
 gazingatmydoom reblogged this · 2 months ago
gazingatmydoom reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 whitewomansonicfan reblogged this · 2 months ago
whitewomansonicfan reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 halberdex reblogged this · 2 months ago
halberdex reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 halberdex liked this · 2 months ago
halberdex liked this · 2 months ago -
 veelyra liked this · 2 months ago
veelyra liked this · 2 months ago -
 leathemage liked this · 2 months ago
leathemage liked this · 2 months ago -
 oramn reblogged this · 2 months ago
oramn reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 oramn liked this · 2 months ago
oramn liked this · 2 months ago -
 whiteboardartstudios reblogged this · 2 months ago
whiteboardartstudios reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 whiteboardartstudios liked this · 2 months ago
whiteboardartstudios liked this · 2 months ago -
 hoisanwa liked this · 2 months ago
hoisanwa liked this · 2 months ago