“To Become Beautiful, You Must Endure Pain. To Become Perfect, You Must Hold In Sadness. Where Is The
“To become beautiful, you must endure pain. To become perfect, you must hold in sadness. Where is the flower which blooms without getting soaked by the pouring rain? Where is the flower which blooms without getting swayed by the wind?”
— BIGBANG Documentary (2006)
More Posts from Delightfulskywalker and Others
Largest Batch of Earth-size, Habitable Zone Planets
Our Spitzer Space Telescope has revealed the first known system of seven Earth-size planets around a single star. Three of these planets are firmly located in an area called the habitable zone, where liquid water is most likely to exist on a rocky planet.

This exoplanet system is called TRAPPIST-1, named for The Transiting Planets and Planetesimals Small Telescope (TRAPPIST) in Chile. In May 2016, researchers using TRAPPIST announced they had discovered three planets in the system.

Assisted by several ground-based telescopes, Spitzer confirmed the existence of two of these planets and discovered five additional ones, increasing the number of known planets in the system to seven.

This is the FIRST time three terrestrial planets have been found in the habitable zone of a star, and this is the FIRST time we have been able to measure both the masses and the radius for habitable zone Earth-sized planets.
All of these seven planets could have liquid water, key to life as we know it, under the right atmospheric conditions, but the chances are highest with the three in the habitable zone.

At about 40 light-years (235 trillion miles) from Earth, the system of planets is relatively close to us, in the constellation Aquarius. Because they are located outside of our solar system, these planets are scientifically known as exoplanets. To clarify, exoplanets are planets outside our solar system that orbit a sun-like star.

In this animation, you can see the planets orbiting the star, with the green area representing the famous habitable zone, defined as the range of distance to the star for which an Earth-like planet is the most likely to harbor abundant liquid water on its surface. Planets e, f and g fall in the habitable zone of the star.
Using Spitzer data, the team precisely measured the sizes of the seven planets and developed first estimates of the masses of six of them. The mass of the seventh and farthest exoplanet has not yet been estimated.

For comparison…if our sun was the size of a basketball, the TRAPPIST-1 star would be the size of a golf ball.
Based on their densities, all of the TRAPPIST-1 planets are likely to be rocky. Further observations will not only help determine whether they are rich in water, but also possibly reveal whether any could have liquid water on their surfaces.
The sun at the center of this system is classified as an ultra-cool dwarf and is so cool that liquid water could survive on planets orbiting very close to it, closer than is possible on planets in our solar system. All seven of the TRAPPIST-1 planetary orbits are closer to their host star than Mercury is to our sun.

The planets also are very close to each other. How close? Well, if a person was standing on one of the planet’s surface, they could gaze up and potentially see geological features or clouds of neighboring worlds, which would sometimes appear larger than the moon in Earth’s sky.

The planets may also be tidally-locked to their star, which means the same side of the planet is always facing the star, therefore each side is either perpetual day or night. This could mean they have weather patterns totally unlike those on Earth, such as strong wind blowing from the day side to the night side, and extreme temperature changes.

Because most TRAPPIST-1 planets are likely to be rocky, and they are very close to one another, scientists view the Galilean moons of Jupiter – lo, Europa, Callisto, Ganymede – as good comparisons in our solar system. All of these moons are also tidally locked to Jupiter. The TRAPPIST-1 star is only slightly wider than Jupiter, yet much warmer.
How Did the Spitzer Space Telescope Detect this System?
Spitzer, an infrared telescope that trails Earth as it orbits the sun, was well-suited for studying TRAPPIST-1 because the star glows brightest in infrared light, whose wavelengths are longer than the eye can see. Spitzer is uniquely positioned in its orbit to observe enough crossing (aka transits) of the planets in front of the host star to reveal the complex architecture of the system.

Every time a planet passes by, or transits, a star, it blocks out some light. Spitzer measured the dips in light and based on how big the dip, you can determine the size of the planet. The timing of the transits tells you how long it takes for the planet to orbit the star.

The TRAPPIST-1 system provides one of the best opportunities in the next decade to study the atmospheres around Earth-size planets. Spitzer, Hubble and Kepler will help astronomers plan for follow-up studies using our upcoming James Webb Space Telescope, launching in 2018. With much greater sensitivity, Webb will be able to detect the chemical fingerprints of water, methane, oxygen, ozone and other components of a planet’s atmosphere.
At 40 light-years away, humans won’t be visiting this system in person anytime soon…that said…this poster can help us imagine what it would be like:

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
If I was Qui-Gon :





Cassini Spacecraft: Top Discoveries
Our Cassini spacecraft has been exploring Saturn, its stunning rings and its strange and beautiful moons for more than a decade.

Having expended almost every bit of the rocket propellant it carried to Saturn, operators are deliberately plunging Cassini into the planet to ensure Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration – in particular, the ice-covered, ocean-bearing moon Enceladus, but also Titan, with its intriguing pre-biotic chemistry.
Let’s take a look back at some of Cassini’s top discoveries:
Titan

Under its shroud of haze, Saturn’s planet-sized moon Titan hides dunes, mountains of water ice and rivers and seas of liquid methane. Of the hundreds of moons in our solar system, Titan is the only one with a dense atmosphere and large liquid reservoirs on its surface, making it in some ways more like a terrestrial planet.

Both Earth and Titan have nitrogen-dominated atmospheres – over 95% nitrogen in Titan’s case. However, unlike Earth, Titan has very little oxygen; the rest of the atmosphere is mostly methane and traced amounts of other gases, including ethane.

There are three large seas, all located close to the moon’s north pole, surrounded by numerous smaller lakes in the northern hemisphere. Just one large lake has been found in the southern hemisphere.
Enceladus

The moon Enceladus conceals a global ocean of salty liquid water beneath its icy surface. Some of that water even shoots out into space, creating an immense plume!

For decades, scientists didn’t know why Enceladus was the brightest world in the solar system, or how it related to Saturn’s E ring. Cassini found that both the fresh coating on its surface, and icy material in the E ring originate from vents connected to a global subsurface saltwater ocean that might host hydrothermal vents.

With its global ocean, unique chemistry and internal heat, Enceladus has become a promising lead in our search for worlds where life could exist.
Iapetus

Saturn’s two-toned moon Iapetus gets its odd coloring from reddish dust in its orbital path that is swept up and lands on the leading face of the moon.

The most unique, and perhaps most remarkable feature discovered on Iapetus in Cassini images is a topographic ridge that coincides almost exactly with the geographic equator. The physical origin of the ridge has yet to be explained…

It is not yet year whether the ridge is a mountain belt that has folded upward, or an extensional crack in the surface through which material from inside Iapetus erupted onto the surface and accumulated locally.
Saturn’s Rings

Saturn’s rings are made of countless particles of ice and dust, which Saturn’s moons push and tug, creating gaps and waves.

Scientists have never before studied the size, temperature, composition and distribution of Saturn’s rings from Saturn obit. Cassini has captured extraordinary ring-moon interactions, observed the lowest ring-temperature ever recorded at Saturn, discovered that the moon Enceladus is the source for Saturn’s E ring, and viewed the rings at equinox when sunlight strikes the rings edge-on, revealing never-before-seen ring features and details.
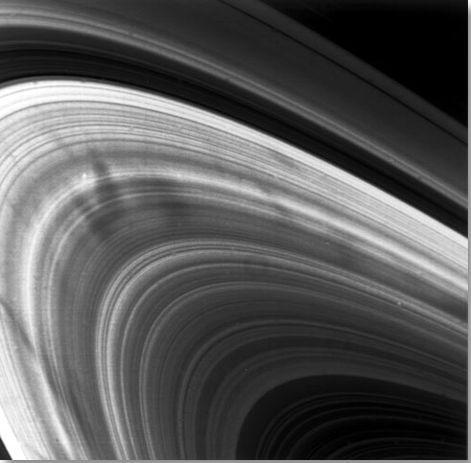
Cassini also studied features in Saturn’s rings called “spokes,” which can be longer than the diameter of Earth. Scientists think they’re made of thin icy particles that are lifted by an electrostatic charge and only last a few hours.
Auroras

The powerful magnetic field that permeates Saturn is strange because it lines up with the planet’s poles. But just like Earth’s field, it all creates shimmering auroras.

Auroras on Saturn occur in a process similar to Earth’s northern and southern lights. Particles from the solar wind are channeled by Saturn’s magnetic field toward the planet’s poles, where they interact with electrically charged gas (plasma) in the upper atmosphere and emit light.
Turbulent Atmosphere

Saturn’s turbulent atmosphere churns with immense storms and a striking, six-sided jet stream near its north pole.

Saturn’s north and south poles are also each beautifully (and violently) decorated by a colossal swirling storm. Cassini got an up-close look at the north polar storm and scientists found that the storm’s eye was about 50 times wider than an Earth hurricane’s eye.

Unlike the Earth hurricanes that are driven by warm ocean waters, Saturn’s polar vortexes aren’t actually hurricanes. They’re hurricane-like though, and even contain lightning. Cassini’s instruments have ‘heard’ lightning ever since entering Saturn orbit in 2004, in the form of radio waves. But it wasn’t until 2009 that Cassini’s cameras captured images of Saturnian lighting for the first time.

Cassini scientists assembled a short video of it, the first video of lightning discharging on a planet other than Earth.

Cassini’s adventure will end soon because it’s almost out of fuel. So to avoid possibly ever contaminating moons like Enceladus or Titan, on Sept. 15 it will intentionally dive into Saturn’s atmosphere.

The spacecraft is expected to lose radio contact with Earth within about one to two minutes after beginning its decent into Saturn’s upper atmosphere. But on the way down, before contact is lost, eight of Cassini’s 12 science instruments will be operating! More details on the spacecraft’s final decent can be found HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Characteristics of the moons of Saturn
Saturn has 62 natural satellites. Here are some features of some of its moons, with mountains, valleys, and striking marks on their surfaces, often marked by asteroid bombardments causing small, huge craters.

Iapetus - Equatorial ridge
Iapetus’s equatorial ridge was discovered when the Cassini spacecraft imaged Iapetus on 31 December 2004. Peaks in the ridge rise more than 20 km above the surrounding plains, making them some of the tallest mountains in the Solar System. The ridge forms a complex system including isolated peaks, segments of more than 200 km and sections with three near parallel ridges.

Tethys - Odysseus crater
Odysseus is the largest crater on Saturn’s moon Tethys. It is 445 km across, more than 2/5 of the moon’s diameter, and is one of the largest craters in the Solar System.

Tethys - Ithaca Chasma
Ithaca Chasma is a valley (graben) on Saturn’s moon Tethys, named after the island of Ithaca, in Greece. It is up to 100 km wide, 3 to 5 km deep and 2,000 km long, running approximately three-quarters of the way around Tethys’ circumference, making it one of the longer valleys in the Solar System. Ithaca Chasma is approximately concentric with Odysseus crater.

Tethys - Red arcs
Unusual arc-shaped, reddish streaks cut across the surface of Saturn’s ice-rich moon Tethys in this enhanced-color mosaic. The red streaks are narrow, curved lines on the moon’s surface, only a few miles (or kilometers) wide but several hundred miles (or kilometers) long.

Rhea - Inktomi crater
Inktomi, also known as The Splat, is a prominent rayed impact crater 47.2 kilometres (29.3 mi) in diameter located in the southern hemisphere of Saturn’s moon Rhea.

Mimas - Herschel Crater
Herschel is a huge crater in the leading hemisphere of the Saturnian moon Mimas, on the equator at 100° longitude. It is so large that astronomers have expressed surprise that Mimas was not shattered by the impact that caused it. It measures 139 kilometres (86 miles) across, almost one third the diameter of Mimas. If there were a crater of an equivalent scale on Earth it would be over 4,000 km (2,500 mi) in diameter – wider than Canada – with walls over 200 km (120 mi) high.

Enceladus - Surface with fractures
Close up of one of the ‘tiger stripes” or fissures called Baghdad Sulcus. Both heat and occasional geysers issue from this formidable crack. Some of the material coating the landscape may be snow condensed from vapor. This closeup of the surface of Enceladus on November 21, 2009, viewed from approximately 1,260 miles (2,028 kilometers) away.

Dione - Contrasts
This image from NASA’s Cassini spacecraft shows a part of Dione’s surface that is covered by linear, curving features, called chasmata. One possibility is that this stress pattern may be related to Dione’s orbital evolution and the effect of tidal stresses over time. This view looks toward the trailing hemisphere of Dione.
Learn more: Iapetus, Tethys, Rhea, Mimas, Enceladus and Dione.
Images: NASA/JPL-Caltech

-
 notsalehaenough reblogged this · 4 years ago
notsalehaenough reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 winterblackrose liked this · 4 years ago
winterblackrose liked this · 4 years ago -
 a-stranger-song reblogged this · 5 years ago
a-stranger-song reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 luckistheonlythingihaveleft liked this · 5 years ago
luckistheonlythingihaveleft liked this · 5 years ago -
 below-my-s0ul liked this · 5 years ago
below-my-s0ul liked this · 5 years ago -
 always-sober-botts liked this · 5 years ago
always-sober-botts liked this · 5 years ago -
 multistanasitsfinest liked this · 5 years ago
multistanasitsfinest liked this · 5 years ago -
 roxcroix liked this · 5 years ago
roxcroix liked this · 5 years ago -
 dinoindavinci liked this · 5 years ago
dinoindavinci liked this · 5 years ago -
 brokenbystars reblogged this · 5 years ago
brokenbystars reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 monsters-trained-to-kill liked this · 5 years ago
monsters-trained-to-kill liked this · 5 years ago -
 bet2805 reblogged this · 5 years ago
bet2805 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 bet2805 liked this · 5 years ago
bet2805 liked this · 5 years ago -
 this-isnotthe-end reblogged this · 5 years ago
this-isnotthe-end reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 abnormallyaddicted liked this · 5 years ago
abnormallyaddicted liked this · 5 years ago -
 ellie-perrette liked this · 5 years ago
ellie-perrette liked this · 5 years ago -
 dayzeedo reblogged this · 5 years ago
dayzeedo reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 boom-kaka-laka liked this · 5 years ago
boom-kaka-laka liked this · 5 years ago -
 tabi-ears reblogged this · 5 years ago
tabi-ears reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 delightfulskywalker reblogged this · 6 years ago
delightfulskywalker reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 delightfulskywalker liked this · 6 years ago
delightfulskywalker liked this · 6 years ago -
 abril0888 liked this · 6 years ago
abril0888 liked this · 6 years ago -
 fleurdelaluna reblogged this · 6 years ago
fleurdelaluna reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 fleurdelaluna liked this · 6 years ago
fleurdelaluna liked this · 6 years ago -
 ephemeral-vesper reblogged this · 6 years ago
ephemeral-vesper reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 jamie-rvp reblogged this · 6 years ago
jamie-rvp reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 jamie-rvp liked this · 6 years ago
jamie-rvp liked this · 6 years ago -
 anhtran1211998 reblogged this · 6 years ago
anhtran1211998 reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 anhtran1211998 reblogged this · 6 years ago
anhtran1211998 reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 anhtran1211998 liked this · 6 years ago
anhtran1211998 liked this · 6 years ago -
 rakeei reblogged this · 6 years ago
rakeei reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 rakeei liked this · 6 years ago
rakeei liked this · 6 years ago -
 lunachab liked this · 6 years ago
lunachab liked this · 6 years ago -
 silverrose72 reblogged this · 6 years ago
silverrose72 reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 silverrose72 liked this · 6 years ago
silverrose72 liked this · 6 years ago -
 seungribubus reblogged this · 6 years ago
seungribubus reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 seungribubus liked this · 6 years ago
seungribubus liked this · 6 years ago -
 daesungindistress liked this · 6 years ago
daesungindistress liked this · 6 years ago -
 jiandtabi reblogged this · 6 years ago
jiandtabi reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 jiandtabi liked this · 6 years ago
jiandtabi liked this · 6 years ago -
 misslilmeow-meow reblogged this · 6 years ago
misslilmeow-meow reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 twigsandgrace liked this · 6 years ago
twigsandgrace liked this · 6 years ago -
 rebeccafultz-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago
rebeccafultz-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 rebeccafultz-blog liked this · 6 years ago
rebeccafultz-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 squishyzelo liked this · 6 years ago
squishyzelo liked this · 6 years ago -
 fantasticcrayon liked this · 6 years ago
fantasticcrayon liked this · 6 years ago -
 hugs4uwu liked this · 6 years ago
hugs4uwu liked this · 6 years ago -
 huluhalkpop liked this · 6 years ago
huluhalkpop liked this · 6 years ago -
 mostlydaesung reblogged this · 6 years ago
mostlydaesung reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 ephemeral-vesper liked this · 6 years ago
ephemeral-vesper liked this · 6 years ago
"Hope is like the sun. If you only believe it when you see it, you'll never make it through the night." -Princess Leia
286 posts