Black-devil Anglerfish


Black-devil anglerfish
Melanoncetus johnsoni
The Black-devil anglerfish is a skilled predator that lurks in the darkness. It uses a bioluminescent organ, a top its head, to lure unsuspecting prey into its jaws. Even though these fish are terrifying to look at, they are about the size of a grape fruit. To save energy, they remain immobile in the water, yet they can detect even the slightest vibrations. Since finding a mate is hard at this depth, male fish will attach themselves to a female and slowly dissolve into her tissue; so she is able to use the sperm the male provides at any time. In addition, this is the fish that tried to eat Marlin and Dory in “Finding Nemo.”
Photo credit: https://underthevastblueseas.tumblr.com/post/40882487364/this-female-black-devil-anglerfish-with-her-flabby
https://www.pinterest.fr/pin/574631233709001328/
More Posts from Bioluminescentoceangoddess and Others

Squarenose Helmetfish
Scopelogadus beanii
The Squarenose Helmetfish is found between 800m to 4000m in the ocean. It received this unique name due to its scales reminding scientists of an armored helmet worn by medieval knights. It also has unusual holes around its face, and the white strands covering its face are sensory canals.
Photo credit: https://www.vistaalmar.es/especies-marinas/peces-extranos/449-que-peces-mas-extranos.html

Pram Bug
Phronima sedentaria
The Pram Bug is a deep sea amphipod that is located between 200 to 1000m in the ocean. It has a translucent exoskeleton and can see primarily blue light. It is also is contained in a hollowed out barrel that is used for protection and to house babies. The image above is a female pram bug carrying its young.
Photo Credit:https://ocean.si.edu/ocean-life/invertebrates/phronima-female-and-young

Periphyllopsis braueri
The Periphyllopsis braueri is a tiny, deep sea jellyfish that is only 6 cm in diameter. It is red-chocolate in color, and it has eight gonads. Furthermore, it is found at depths between 600m to 1000m.
Photo credit: https://oceanexplorer.noaa.gov/explorations/19gulfofalaska/logs/aug2/aug2.html

Threadfin Snailfish
Careproctus longifilis
The Threadfin Snailfish resembles a prehistoric tadpole that is ghostly white. The holes in its face are large sensory pores that help them detect changes in the ocean. It is often found at depths between 1900 to 2997 meters.
Photo credit: https://www.timeout.com/singapore/museums/creatures-of-the-deep


Spookfish
Winteria telescopa
The Spookfish’s eyes act as a telescope and are designed to maximize light in the deep ocean. Its eyes contain rod cells that help distinguish between ambient light and bioluminescent light. This adaptation helps avoid predators and catch prey.
Picture Credit: https://www.natureplprints.com/deep-sea/deep-sea-fish-winteria-telescopa-15230734.html


Glowing sucker octopus
Stauroteuthis syrtensis
The Glowing Sucker Octopus can be found at 2500 m in the deep ocean. This unique creature has two fins that look similar to elephant ears. They move elegantly through the water by moving these fins and contracting their mantle. Evidence of this creature has only been spotted in the Atlantic Ocean.
Photo credit: https://octolab.tv/species/glowing-sucker-octopus/
https://ferrebeekeeper.wordpress.com/2011/03/14/glowing-sucker-octopus/

Vampire Squid
Vampyroteuthis infernalis
Even though the Vampire Squid is named after a notorious monster, this gentle creature does not live up to its name. It is only a foot long and occupies depths between 650m to 1500m in the deep ocean. Unlike other squids, it has reduced musculature and collects particles in the water column. However, it is capable of huge bursts of speeds. It uses bioluminescence to confuse both predators.
Photo credit: https://ocean.si.edu/ocean-life/invertebrates/vampire-squid-hell


Giant Isopod
Bathynomus kensleyi
The Giant Isopod is an unsettling deep sea creature that crawls along the ocean floor scavenging for animal remains and detritus. These invertebrates are part of phenomenon known as abyssal gigantism, which is the tendency for deep-sea dwelling invertebrates to be larger than their shallower-water counter parts. The Giant Isopod is found between 310m to 2140m in the ocean.
Photo credit
https://seatrench.tumblr.com/post/615873390014791680/giant-isopod-bathynomus-sp-source
https://alchetron.com/Giant-isopod


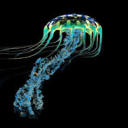
Atolla Jelly
Atolla wyvillei
The Atolla Jelly is a fiery, red jellyfish that has an extraordinary display of bioluminescence. When the jelly is attacked, it uses bioluminescence to produce thousands of vibrant, blue flashes; the blue flashes act as an alarm, which draws in bigger predators and warns prey. The jelly can be found at depths between 600 m to 1500m, and it also has a long hypertrophied tentacle that aids in reproduction.
Photo credit: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atolla_jellyfish
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atolla_jellyfish


Giant Bell Jelly
Scrippsia pacifica
The Giant Belly Jelly has 256 tentacles attached to a gelatinous bell-shaped base. Like most cnidarians, the Giant Belly Jelly uses specialized stinging cells called nematocysts to catch its prey. When fish and other prey swim into its tentacles, the sensory projection on the cnidocyte (cell that holds the nematocysts) is activated. Then the nematocysts and barb are released, hitting the vulnerable prey and releasing a toxin into the prey’s body. The Giant Bell Jelly is found at 400 m in the ocean. It is related to the jellyfish, but it is categorized as a Hydrozoa (similar to the Portuguese- man-o-war)
https://vimeo.com/42551565
Photo Credit: https://www.pinterest.cl/pin/467107792572034837/
https://courses.lumenlearning.com/ivytech-bio1-1/chapter/phylum-cnidaria/
-
 hmmmmho liked this · 3 years ago
hmmmmho liked this · 3 years ago -
 astrotracksuitbattalion liked this · 3 years ago
astrotracksuitbattalion liked this · 3 years ago -
 acolorcollective liked this · 3 years ago
acolorcollective liked this · 3 years ago -
 despair-with-walnuts liked this · 3 years ago
despair-with-walnuts liked this · 3 years ago -
 slime-gargoyyyle liked this · 3 years ago
slime-gargoyyyle liked this · 3 years ago -
 in-soft-grass liked this · 3 years ago
in-soft-grass liked this · 3 years ago -
 spiralmovements liked this · 3 years ago
spiralmovements liked this · 3 years ago -
 leitharstjarna liked this · 3 years ago
leitharstjarna liked this · 3 years ago -
 creaturedeityendless liked this · 3 years ago
creaturedeityendless liked this · 3 years ago -
 crazyyanderefangirlfan reblogged this · 3 years ago
crazyyanderefangirlfan reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 ashthegenderfluidfella liked this · 3 years ago
ashthegenderfluidfella liked this · 3 years ago -
 sweet-sea-monster reblogged this · 3 years ago
sweet-sea-monster reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 recovery-witch liked this · 3 years ago
recovery-witch liked this · 3 years ago -
 yesunieyee reblogged this · 3 years ago
yesunieyee reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 yesunieyee liked this · 3 years ago
yesunieyee liked this · 3 years ago -
 cherry-cola-beagle liked this · 3 years ago
cherry-cola-beagle liked this · 3 years ago -
 godlambus liked this · 3 years ago
godlambus liked this · 3 years ago -
 mintytrifecta liked this · 3 years ago
mintytrifecta liked this · 3 years ago -
 sadviper liked this · 3 years ago
sadviper liked this · 3 years ago -
 bewareofdragon liked this · 3 years ago
bewareofdragon liked this · 3 years ago -
 lilaccatholic liked this · 3 years ago
lilaccatholic liked this · 3 years ago -
 arlothia reblogged this · 3 years ago
arlothia reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 arlothia liked this · 3 years ago
arlothia liked this · 3 years ago -
 terribleteej reblogged this · 3 years ago
terribleteej reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 terribleteej liked this · 3 years ago
terribleteej liked this · 3 years ago -
 rugletthewren liked this · 3 years ago
rugletthewren liked this · 3 years ago -
 brines liked this · 3 years ago
brines liked this · 3 years ago -
 ultravioletpeony reblogged this · 3 years ago
ultravioletpeony reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 ultravioletpeony liked this · 3 years ago
ultravioletpeony liked this · 3 years ago -
 chiefangelpeanutghost reblogged this · 3 years ago
chiefangelpeanutghost reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 ssodom16 liked this · 3 years ago
ssodom16 liked this · 3 years ago -
 sharkyz liked this · 4 years ago
sharkyz liked this · 4 years ago -
 caviarfluid liked this · 4 years ago
caviarfluid liked this · 4 years ago -
 phobic-human liked this · 4 years ago
phobic-human liked this · 4 years ago -
 alux-ulkan reblogged this · 4 years ago
alux-ulkan reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 alux-ulkan liked this · 4 years ago
alux-ulkan liked this · 4 years ago -
 that-lesbian-phenotype liked this · 4 years ago
that-lesbian-phenotype liked this · 4 years ago -
 myartrefblog reblogged this · 4 years ago
myartrefblog reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 rabbitsartcorner liked this · 4 years ago
rabbitsartcorner liked this · 4 years ago -
 ocean-happiness-sunset-blog liked this · 4 years ago
ocean-happiness-sunset-blog liked this · 4 years ago -
 ailinenelpaisdelasmaravillas liked this · 4 years ago
ailinenelpaisdelasmaravillas liked this · 4 years ago -
 internal-nonsense liked this · 4 years ago
internal-nonsense liked this · 4 years ago -
 unceasingly-infatuated liked this · 4 years ago
unceasingly-infatuated liked this · 4 years ago
Bioluminescence is a chemical reaction that produces light. Many deep sea animals use bioluminescence. This blog is dedicated to educating the public about the amazing creatures that thrive in the deep sea.
57 posts