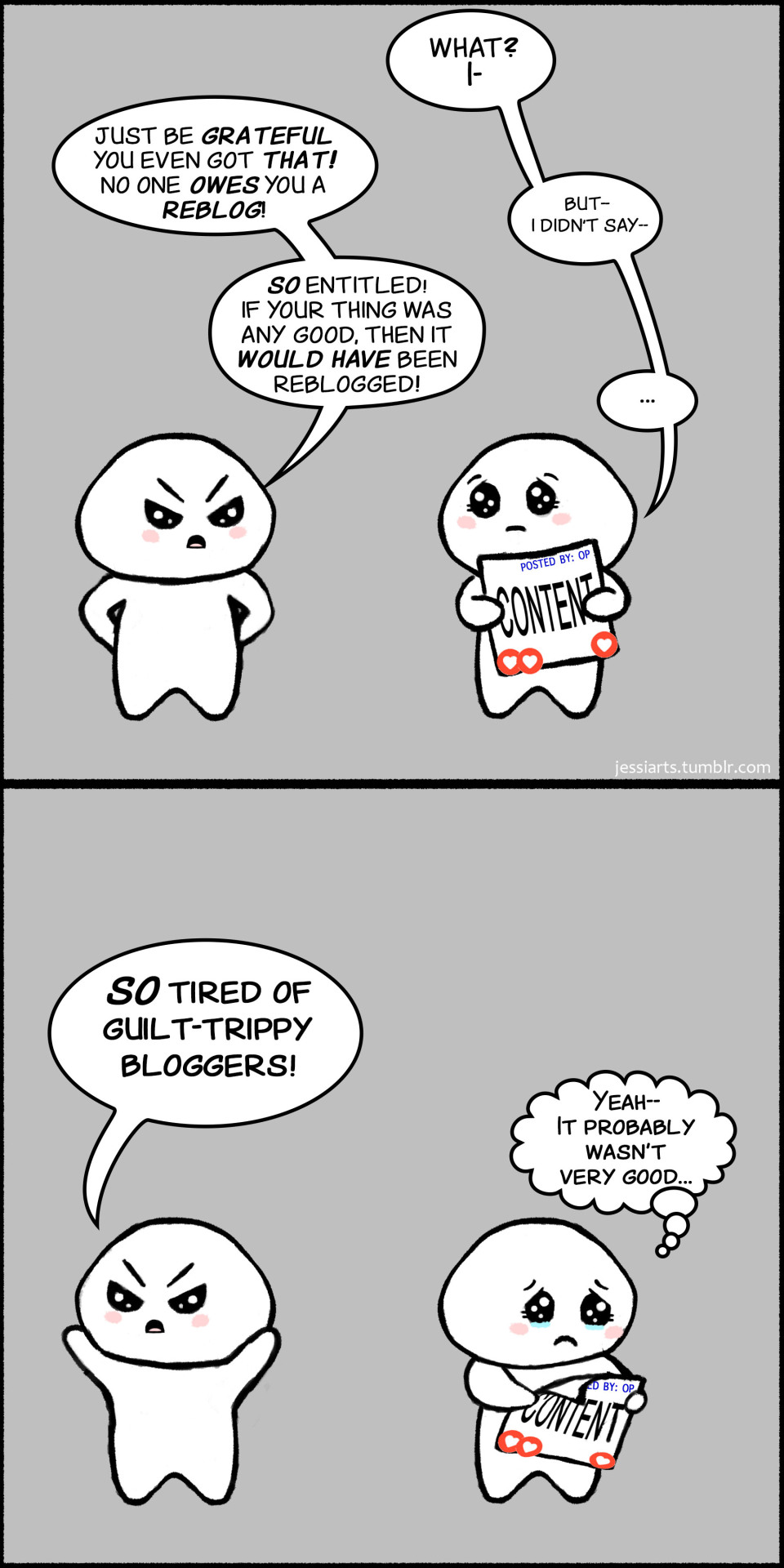
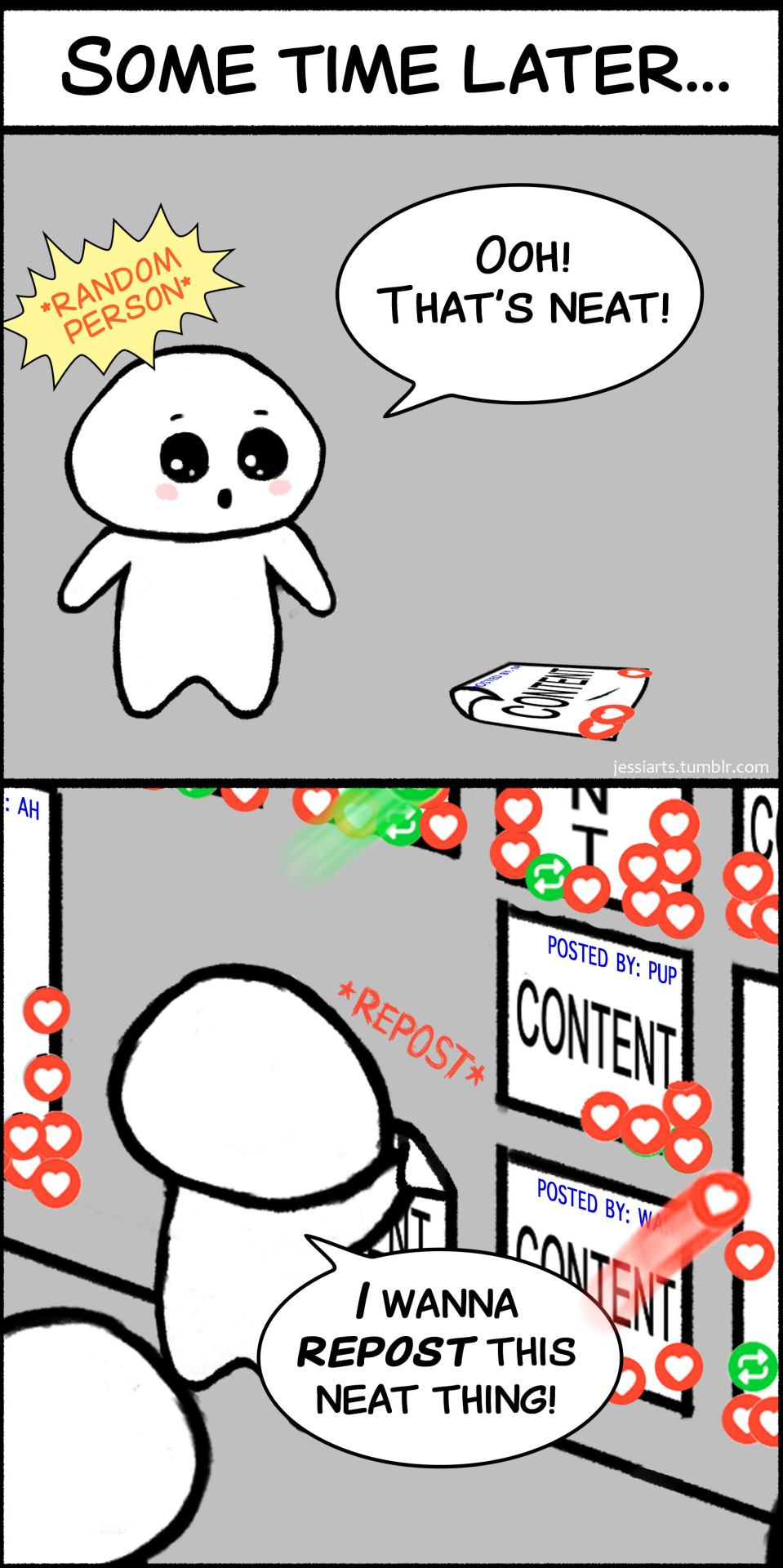
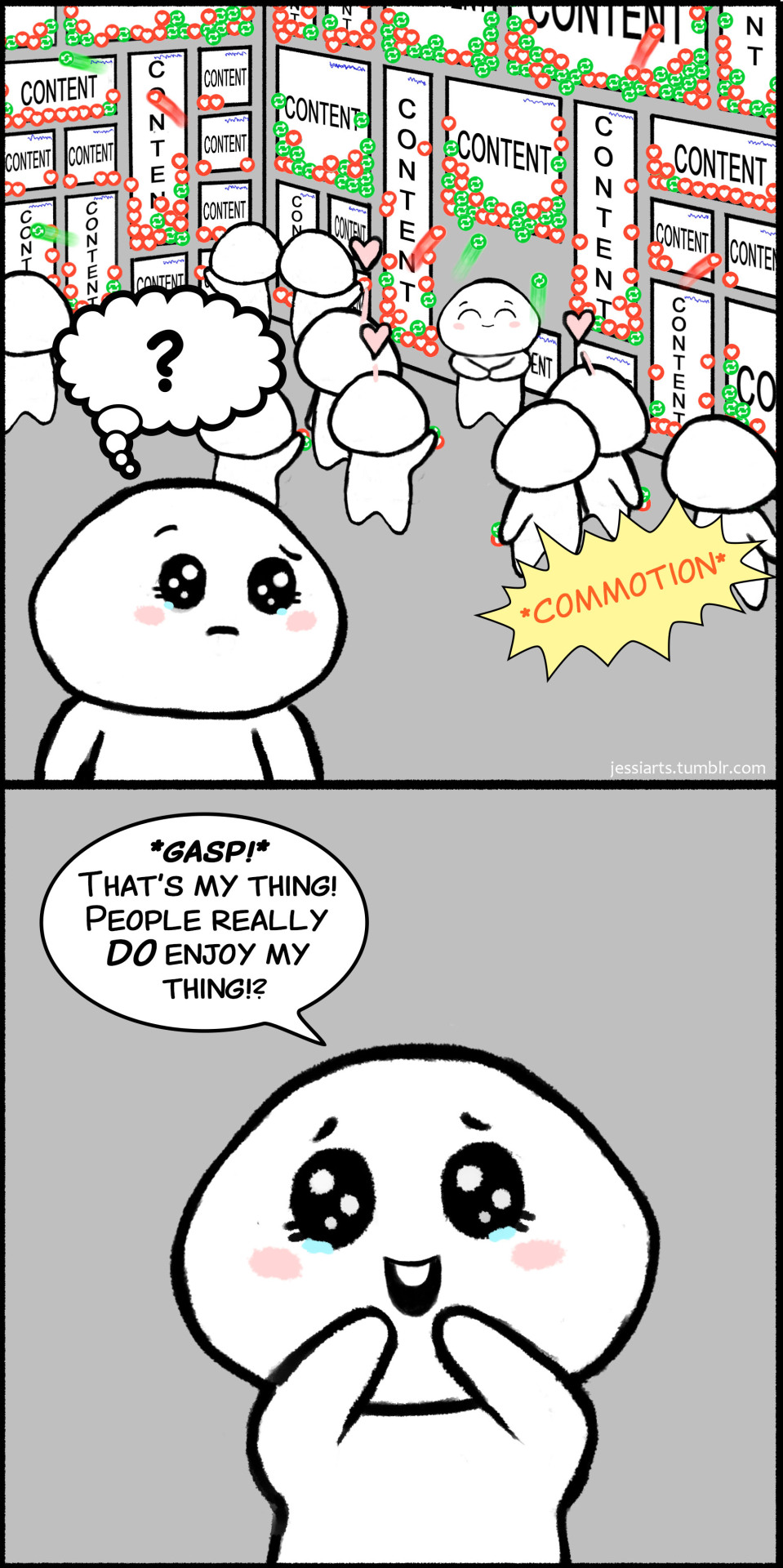
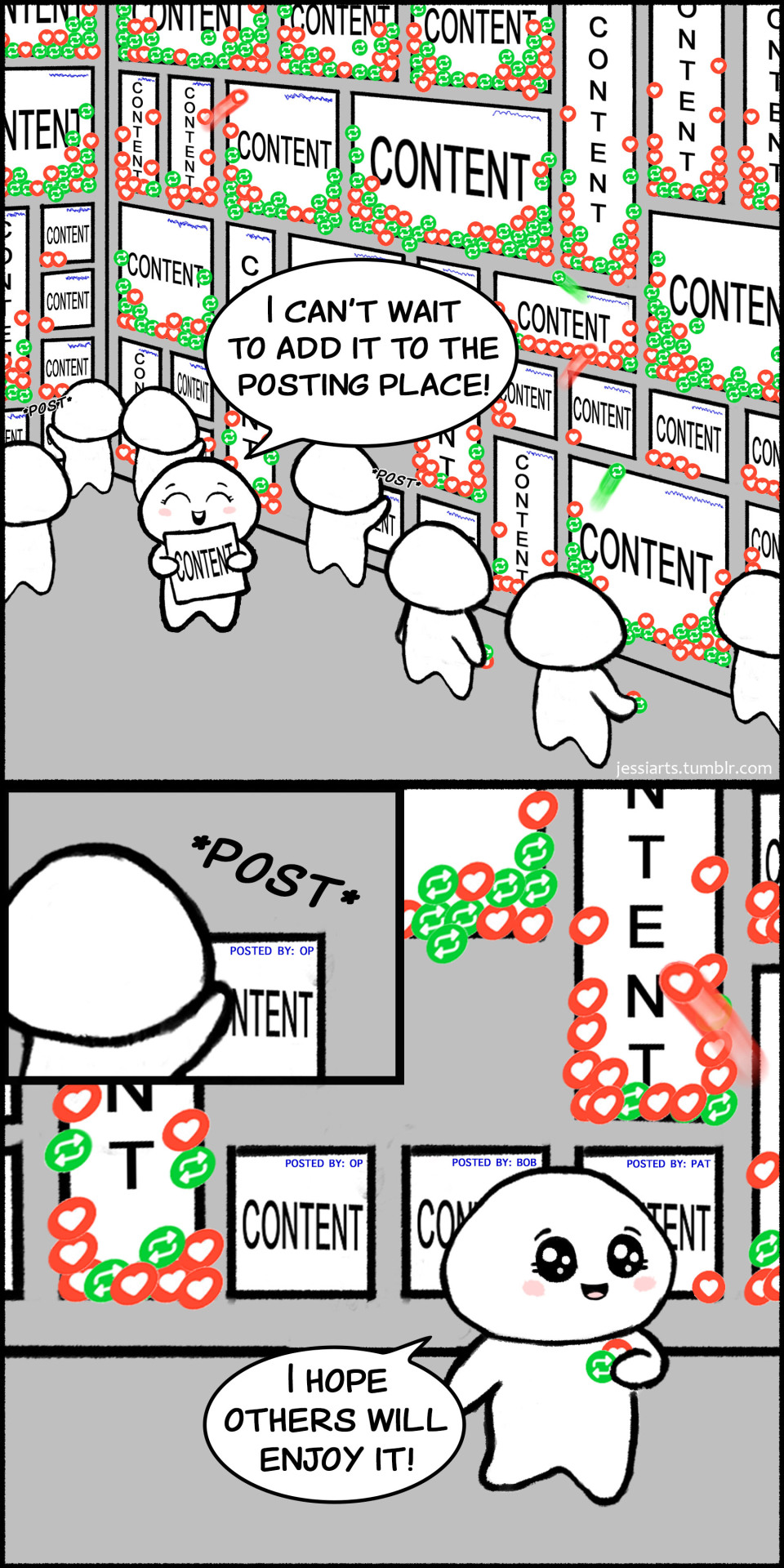
That's Amazing!
That's amazing!



















More Posts from Arieso226 and Others
The Black Women Movements
NO.1
Many movements came out after the Emancipation (freeing of the slaves) Proclamation, and even though some were hand-chosen, they were mostly male oriented, whereas women movements were pushed aside and forgotten.
The Black Women’s National Club Movement was the first woman movement set in the 1890s, where their primary concern was for family and the community. They desired freedom by using centering family values and unity, and the dynamic relationship between black women and men. ‘’Black women organized, throughout the nineteenth century, at first on a local, later on a state and national level, to undertake educational, philanthropic and welfare activities. Urbanization, the urgent needs of the poor in a period of rapid industrialization and the presence of a sizeable group of educated women with leisure led to the emergence of a national club movement of white women after the Civil War. Similar conditions did not begin to operate in the black communities until the 1890s, when local clubs in a number of different cities began almost simultaneously to form federations.’’
Other movements, like the National Federal of African American women started in 1895, where their concerns were resistance to slavery, black women’s concern for education, the lynching of children, men and women, sexual abuse from white men, healthcare, childcare for orphans, care for the elderly, job training for the youth and various but broad subject for social justice.
The National Council of Negro Women was another important movement, ‘’ founded and organized in 1935 by the late Dr. Mary McLeod Bethune for the purpose of planning and directing Negro women to greater economic, social, educational and cultural development in local communities and on the national and international levels. The aspects of the national program are therefore varied and include departments which deal specifically with citizenship education, human relations, international relations, education, labor and industry, archives and museums, public relations, religious education and fellowship, social welfare and youth conservation. The National Program Committee feels that conferences may be used effectively as a technique to synthesize the activities of these various departments.’’
NO. 2
Most of these movements were discarded and disbanded because of the lack of support from black men and the racism they were also receiving by white women and men alike. The attitudes of sexism and racism go hand in hand, and as we progress through the centuries, a study comes out of that: Black Women’s Studies. ‘’Black Women’s Studies emerged in part because of the failure of Black and Women’s Studies to address adequately the unique experiences of black women in America and throughout the world. Attempts to celebrate the existence of distinct black female literary tradition in America, which can be traced further back in time, also fall under the rubric of Black Women’s Studies because they acknowledge the politics of sex as well as the politics of race in the texts of black women writers. This celebration has taken place in two phases. The first phase is characterized by efforts to document that such a tradition exists.’’
Education is power, since knowledge, the knowledge of our past and our present can only help us persevere to our future, and that has been denied to us since the time of slavery. ‘’Education has persisted as one of the most consistent themes in the life, thought, struggle, and protest of black Americans. It has been viewed as a major avenue for acquiring first class citizenship. There is a large body of research that takes into account the educational experiences of Afro-Americans. Black female educators such as Mary McLeod Bethune, Charlotte Hawkins Brown, Lucy Laney, Fanny Jackson Coppin and Nannie Helen Burroughs are mentioned in some Afro-American history sources and in some instances are receiving attention in theses and dissertations. While this publication documents ‘the historical significance of black female educators in twentieth century America, beyond the role of teacher’, it is important that we establish to some extent an historical context for understanding the very basic struggle in which black women have been engaged to acquire an education and to utilize that education as a professional.’’
NO. 3
The main statement discussed repeatedly in Black Women studies is centered around race, class, gender and sexuality, which all have an important part to play while surviving in America. That it is why it is so important to discuss such serious topics with like-minded individuals, those who yearn for the freedom and privileges that other citizens have, because even though we have our freedom, oppression is still prevalent. Around the world, women of every origin face the same problems. ‘’ The history of women’s movements in the Middle East has received much attention in recent years. Studies have been devoted to the advent of these movements, their development, activities, politics, organizing style and central figures. Preliminary attempts at comparative analysis of these women’s movements have also been made. In 1999, Ellen Fleishmann published a comprehensive comparative article entitled, ‘The Other ‘Awakening’: The Emergence of Women’s Movements in the Modern Middle East, 1900-1940’. In this first stage, ‘The Awakening’, women and men began to raise the issue of women’s status and to question related social practices. This stage is also typified by the emergence of varied women’s organizations and by women’s efforts to enhance girls’ education. In the second stage, ‘‘Women and Nationalism’, women adopted nationalism as a liberating discourse linking their involvement in nationalist movements with women’s emancipation. The third stage, designated ‘State Feminism’, is characterized by ‘women’s co-optation by, and collusion and/or collision with, the state-building project, resulting in the evolution of state feminism.’’
NO. 4
In Ireland, the ‘problems is that most mechanisms for choosing representatives tend to refract, not reflect, the composition of society, and some groups will always be marginalized even if not formally. The Northern Ireland Women’s Coalition is only one example of a movement party. Though unusual, more than 50 women’s parties have formed the world over 1945, in places such as Israel, Belarus, Russia, India, the Philippines, Belgium, and Iran. The experiences of these parties are diverse but in at least two other situations, Iceland and Israel, strong scholarship demonstrates that women’s parties have succeeded in drawing public attention to issues of female marginalization and put ‘gender politics on the political map for the first time.’ In Iceland, in particular, the effect of the women’s party in pressuring the other parties to adapt their behavior and policy commitments to facilitate inclusiveness is well documented.’’
In conclusion, women deserve to get attention for their efforts to change society just as much as anybody else who has felt the sting of oppression no matter what the gender. Race, sex, class and gender all define who we are in the society, and it is without the benefits of education given to all the people no matter where they come from, are we truly lost.








Based on actual events
The Federal Reserve
NO. 1
Today, we’re going to asking some questions all focused on the Federal Reserve. Who created the Federal Reserve? What is its purpose? And how does it continue to control us, poor and middle-class folks, today? The Federal Reserve Act was signed by President Woodrow Wilson on December 23, 1913. Generally speaking, it has five general functions, ‘‘like conducts the nation's monetary policy to promote maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates in the U.S. economy; promotes the stability of the financial system; promotes the safety and soundness of individual financial institutions; fosters payment and settlement system safety and efficiency and promoting consumer protection and community development.

NO. 2
The first myth about the Federal Reserve, is that it is controlled by the federal government, hence the name. But in actuality, it is a private institution whose shareholders are commercial banks, hence the term, ‘bankers bank’. The word ‘federal’ is designed deliberately to create the impression that it is a public entity. Indeed, misrepresentation of its ownership is not merely by implication or impression created by its name. More importantly, it is also officially and explicitly stated on its website: ‘The Federal Reserve System fulfills its public mission as an independent entity within government. It is not owned by anyone and is not a private, profit-making institution” [1]. To unmask this blatant misrepresentation, the late Congressman Louis McFadden, Chairman of the House Banking and Currency Committee in the 1930s, described the Fed in the following words: ‘Some people think that the Federal Reserve Banks are United States Government institutions. They are private monopolies which prey upon the people of these United States for the benefit of themselves and their foreign customers; foreign and domestic speculators and swindlers; and rich and predatory money lenders.”

NO. 3
Henry Ford quoted, ‘It is well enough that people of the nation do not understand our banking and monetary system, for if they did, I believe there would be a revolution before tomorrow morning.” In simplistic terms, the Federal Reserve basically controls the money supply, and average citizens, like you and me, work for any valuable company, and in order to receive those paychecks, you used where only a fraction of bank deposits are backed by actual cash on hand and available for withdrawal. This is called fractional reserve banking, and it is done to theoretically expand the economy by freeing capital for lending. Every single person on this planet is working under the Federal Reserve.

For more information, please watch the documentary ‘Capital in the Twenty-First Century’, based on Thomas Piketty's best-selling book, on Netflix. They give a widespread selling of how far back the plans to implement the Federal Reserve goes.

Housing Discrimination
NO. 1
Racial exclusion, or segregation had real damage to the black communities persistent in their fight for freedom to own and be included in everything whites were already allowed in; the fight for equality, economic security, for education, and for fair housing was just beginning. Racial exclusion was such a severe enough problem, since in every near northern city, black newcomers crammed into old and run-down housing, mainly in dense central neighborhoods left behind by upwardly mobile whites. White builders, in charge of housing and agencies related could dictate who could own, and William Levitt, of Leviittown where massive developments were made in the suburb, was no exception.
These types of houses were ‘affordable for the common man’, and remade America’s landscape after World War II. The iconic images of little ranches and Cape Cods, set in spacious yards on curvilinear streets, stood for everything that America celebrated in the Cold War era. These subdivisions attracted a heterogenous mix of surburnites, blue-collar workers employed by U.S Steel factories, teachers, clerks, and administrators. Levitt celebrated the ‘American-ness’ of these houses, saying ‘’No man who owns his house and lot can be a communist. He has much to do.’’ Don’t really know how owning a house can get in the way of your political ideologies, but alright. And when Levitt was questioned about the racial homogeneity of his planned community, he responded, ‘’We can solve a housing problem or we can try to solve a racial problem, but we cannot combine the two.’’ But the housing and racial problem was connected, as blacks could not get these houses because they were black. One instance of racial exclusion was in metropolitan Philadelphia, where between 1946, only 347 of 120,000 new homes built were open to blacks. Langston Hughes, popular poet described black neighborhoods as the ‘land of rats and roaches, where a nickel cost a dime.
NO. 2
Economist Robert Weaver spoke, ‘’among the basic consumer goods, only housing for Negroes are traditionally excluded freely competing in the market.’’ The struggle to open housing was not just a matter of free access to a market excluded to blacks. Racial segregation had high stakes. In post war America, where you lived shaped your educational options, your access to jobs, and your quality of life. The housing markets also provided most Americans with their only substantial financial asset. Real estate was the most important vehicle for the accumulation of wealth. Breaking open the housing market would provide blacks to access to better-funded, higher-quality schools. It would give them the opportunity to live in growing communities–near the shopping malls, office centers, and industrial parks where almost all new job growth happened. And more importantly, it would narrow the wealth-gap between blacks and whites. The battle against housing discrimination in Levingttown, or anywhere else would be the most important in the entire northern freedom struggle.
NO. 3
Housing segregation in the north was built on a sturdy foundation of racial restrictions encoded in private regulations and public policy. In the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, the Midwest–and especially Indiana and Illinois, were dotted with ‘sundown towns’ places whose residents drove blacks off by force, enacted ordinances to prohibit black occupancy (although such ordinances were struck down by the Supreme Court in 1917), and sometimes posted signs, like that in Wendell Willkie’s Elwood, Indiana, warning blacks of the dire consequences of staying around after sunset. Such crude techniques succeeded in driving blacks out of small towns, but they were less effective in the major northern metropolitan areas that attracted the vast majority of African American migrants beginning in World War I.
Three devices were used to help housing discrimination: first, private but legally enforecable restrictive covenants—attached to nearly every housing development built between 1928 and 1948— forbade the use or sale of a property to anyone other than whites. Second, federal housing policies, enacted during the Depression, mandated racial homogeneity in new developments and created a separate, unequal housing market, underwritten with federal dollars, for blacks and whites. And third, real estate agents staunchly defended the ‘freedom of association and the right of home owners and developers to rent or sell to whom they pleased, steering blacks into racially mixed or all-black neighborhoods. Whites in the North had economic reasons to fear the ‘Negro invasion’ as they called it. Their ability to secure mortgages and loans were at risk. But their motivations were not solely economic. Intertwined concerns about property values were fears of black predation. North and South recoiled at the prospect of miscegenation. In the South, they feared the legal restrictions on intermarriage and racial mixing in public spaces; the North feared the regulation of housing markets.
The Legend of the Holy Grail
The Grail legend is one of the most popular and reiterated myths told around the world. The legend is basically connected to the King Arthur tales as well, as the king and his noble knights embark on a heroic quest in search for the ‘Grail’, a shining cup claimed to be the sustainer of all life or a mysterious vessel that provides sustenance, which is guarded in a castle that is difficult to find.

The first Grail legend first appears in an unfinished romance called Perceval ou Le conte du Graal by Chretien de Troyes dated to about 1190. The basic outline would be the mysterious vessel being guarded in the castle, and the owner of that castle is sickly or unable to care for it; the surrounding land would almost always be barren, and the owner can only be restored if a brave knight finds the castle, and after seeing a ‘mysterious procession’, asks a certain question. If he fails at this task, everything will remain as before, and the search must begin again. After many adventures, the hero knight returns to the castle and asks the correct question which, hereby cures the king and restores the land. After, the knight succeeds the wounded monarch and becomes king instead, and becomes the guardian of the castle and its contents. The Crusades were the backdrop of this awesome tale, and the fall of Jerusalem occurred in 1187 just before the legend appeared as a literary motif, and Chretien’s romance was written at the behest of his patron, the crusader knight, Count Philip of Flanders.

‘‘In Chretien’s romance, the knight Perceval sees the grail during a feast at a mysterious castle controlled by the Fisher King, a lame man whom he had met before. Chretien calls the object simply ‘un graal’, and its appearance is just one of the unusual events which take place during the feast. Indeed at this time, Perceval is also shown a broken sword that must be mended. The two objects together, sword and grail, are symbols of Perceval’s development as a true knight. Chretien died before he could finish the romance, but the story was completed by other writers. The Continuations, as they are referred to in critical literature, expand several themes and the grail gradually acquires a more ‘sacramental’ character. The First Continuation is also incomplete and the author is unknown, but it can be dated before the year 1200. Besides Perceval, Gawain also has a grail adventure (the womanizing Gawain is the type of the perfect worldly knight and regularly forms a contrast to Perceval in these romances). During a procession which Gwain sees, ‘the rich grail’ (as it is now called) floats about the hall and provides food for all; the bleeding lance is later identified as the Lance of Longinus (the spear used by Longinus to pierce Christ’s side at the Crucifixion) and the broken sword belonging to a dead knight who is laid out of the bier. He who mends the sword will know the secrets of the grail castle (thereby strengthening the link between sword and grail.) Other medieval writers took up this theme; Burgandian poet, Robert de Boron, also wrote, at the behest of a crusader patron, the Lord of Montfacon, produced three romances, Joseph d’ Arimathie, Merlin, and Perceval. All these romances treat the grail theme, even into the context of Christ’ passion.’’

The Holy Grail legends are not only entertaining, with valiant heroes and dangerous but awesome quests, but they also speak of patience and knowledge that these heroes gain along the way. Perceval and Lancelot aren’t heroes because they are searching for a beguiled, golden chalice, but for greater understanding of themselves. These legends have been written and re-written for ages, and even in the modern years, people are still fascinated by the great quest for the Holy Grail. I know I am.





Imagine the best, funniest, most successful version of yourself. Then live in it to the fullest.
Research on the Elongated Skulls
There is evidence of elongated skulls in many different places around the world. In Egypt, these skulls are often found in graves from the Old and Middle Kingdom periods. They are also found in Peru and have been used in religious ceremonies for centuries. In North America, many Native communities have traditionally worn these types of headdresses and jewelry. The presence of elongated skulls in ancient history proves that human anatomy has been changing for thousands of years.

The Egyptians appear to have used the elongated skulls as ornaments for their tombs. ‘‘The priests of the time believed that the gods would transfer their souls to the bodies of their ancestors after they died, so it was important to provide the deceased with nice things to help them reach the afterlife. They also may have had practical uses. They believed they used them to drain water from their underground temples, prone to flooding. The Indigenous people’s of Peru also used the elongated skulls as grave goods. Because they believed that the spirits of their dead ancestors resided inside the skulls, they were buried with these artifacts near the head of the body to aid their passage into the afterlife. According to the Inca civilization, it was up to the priests to pass judgment on whether or not a person was worthy enough to enter the afterlife. They also used the skulls for divination and a good luck charm to protect them from harm.’’

There are many theories about how elongated skulls came to exist. One theory is that they are the remains of an extinct race of people that lived on Earth thousands of years ago. These "giants" may have lived alongside the Native Americans or descended from an earlier human civilization during the Ice Age. Another theory is that they were created artificially using clay, metal, or wood molds. ‘‘As the Spanish colonized the Americas, many different cultures were exposed to new ideas about science and medicine. As a result, many of these people began experimenting with new ways to create artificial body parts. Besides tattooing, intentional scarring, piercing, and teeth sharpening, intentional cranial deformation is another form of mutilation of the human body and is associated with the cultural background of society. It has been related to religion, aestheticism, beauty, or facilitating tribal identity.’’

A hero can go anywhere, challenge anyone, as long as has the nerve
#percyjackson#heroesofolympus (via demigod26)
#percyjackson#pipermcclean
so I got into grad school today with my shitty 2.8 gpa and the moral of the story is reblog those good luck posts for the love of god
-
 fitisfreedom liked this · 1 month ago
fitisfreedom liked this · 1 month ago -
 faunie-sanctuaryworldsystem reblogged this · 1 month ago
faunie-sanctuaryworldsystem reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 yakitako reblogged this · 2 months ago
yakitako reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 redautumnleaves liked this · 2 months ago
redautumnleaves liked this · 2 months ago -
 strangecollectionperson liked this · 2 months ago
strangecollectionperson liked this · 2 months ago -
 eyestumblin liked this · 2 months ago
eyestumblin liked this · 2 months ago -
 soap5person liked this · 2 months ago
soap5person liked this · 2 months ago -
 amberleaff liked this · 2 months ago
amberleaff liked this · 2 months ago -
 jingledbells reblogged this · 2 months ago
jingledbells reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 jingledbells liked this · 2 months ago
jingledbells liked this · 2 months ago -
 jacky-rubou reblogged this · 2 months ago
jacky-rubou reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 jacky-rubou liked this · 2 months ago
jacky-rubou liked this · 2 months ago -
 catisteard reblogged this · 2 months ago
catisteard reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 anotherfanartist liked this · 2 months ago
anotherfanartist liked this · 2 months ago -
 pasamelasal liked this · 3 months ago
pasamelasal liked this · 3 months ago -
 princeoftenderness liked this · 3 months ago
princeoftenderness liked this · 3 months ago -
 manga-wolfsengel reblogged this · 3 months ago
manga-wolfsengel reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 chaotic-lav3 liked this · 4 months ago
chaotic-lav3 liked this · 4 months ago -
 lynnhua reblogged this · 4 months ago
lynnhua reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 ignoremejustpassingthrough liked this · 4 months ago
ignoremejustpassingthrough liked this · 4 months ago -
 theoneintheshadows-blog1 liked this · 4 months ago
theoneintheshadows-blog1 liked this · 4 months ago -
 douxmae liked this · 4 months ago
douxmae liked this · 4 months ago -
 mrscaracal liked this · 4 months ago
mrscaracal liked this · 4 months ago -
 in-case-you-havent-noticed liked this · 5 months ago
in-case-you-havent-noticed liked this · 5 months ago -
 spectruminterests liked this · 7 months ago
spectruminterests liked this · 7 months ago -
 gales-reblog-blog reblogged this · 7 months ago
gales-reblog-blog reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 eldritchgf-butdeep reblogged this · 7 months ago
eldritchgf-butdeep reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 superbpuppylove reblogged this · 7 months ago
superbpuppylove reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 superbpuppylove liked this · 7 months ago
superbpuppylove liked this · 7 months ago -
 sailorbill1 liked this · 9 months ago
sailorbill1 liked this · 9 months ago -
 hetatheory liked this · 10 months ago
hetatheory liked this · 10 months ago -
 lesonicaro reblogged this · 10 months ago
lesonicaro reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 lesonicaro liked this · 10 months ago
lesonicaro liked this · 10 months ago -
 digitalribbon liked this · 10 months ago
digitalribbon liked this · 10 months ago -
 starzak liked this · 11 months ago
starzak liked this · 11 months ago -
 latinpukia reblogged this · 11 months ago
latinpukia reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 lowkeyqueer reblogged this · 1 year ago
lowkeyqueer reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 lowkeyqueer liked this · 1 year ago
lowkeyqueer liked this · 1 year ago -
 coffe-bits liked this · 1 year ago
coffe-bits liked this · 1 year ago -
 insert-clever-username-1133 reblogged this · 1 year ago
insert-clever-username-1133 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 insert-clever-username-1133 liked this · 1 year ago
insert-clever-username-1133 liked this · 1 year ago -
 tired-trans-matcha-lover reblogged this · 1 year ago
tired-trans-matcha-lover reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 lavonee reblogged this · 1 year ago
lavonee reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 pearlscarf liked this · 1 year ago
pearlscarf liked this · 1 year ago -
 frannii-san liked this · 1 year ago
frannii-san liked this · 1 year ago -
 marymarvels-blog liked this · 1 year ago
marymarvels-blog liked this · 1 year ago -
 strayer-comic liked this · 1 year ago
strayer-comic liked this · 1 year ago
26-year-old Anthro-Influencer Anthropology, blogger, traveler, mythological buff! Check out my ebook on Mythology today👉🏾 https://www.ariellecanate.com/
208 posts
