Andromeda, If It Was Brighter

Andromeda, If It Was Brighter
One of the largest structures in the night sky is visible with the naked eye, but if you live in a city, it's literally hiding just out of sight. Even in a dark area, it's not the easiest to immediately see, but the above image has brightened it up for us, to show us what the galaxy would look like, if only the sky was dark enough and the galaxy was a bit brighter.
The moon comparison is the best one, that is something we can all see in the night sky (unless you live in the UK, where you see mostly clouds).
Now imagine that galaxy stretching several moon-spans across the sky. That I hope gives you a minor taste of what it's like when using a small telescope or even binoculars, you first come across it.
If you live in the Northern Hemisphere, then it's well worth the search.

Near sunset, look for 3 objects which should be easy to locate, Venus and Jupiter (I'll come to this in a moment) low in the sky, the W of Cassiopeia and the Seven Sisters (Pleiades), and from that, you should find the location. Bare in mind it's several times the size of the moon, so you don't have to be too accurate, but if you can find the stars of Andromeda, that will help refine your search.

And finally that brings me on to the real star of the sky currently, Jupiter and Venus, the two brightest planets, very close together.
In fact, if you do have a really good pair of binoculars, or small telescope, this is a great time to view them. Venus often appears as a crescent like a phase of the moon, and Jupiter has it's 4 Galilean moons to spot.

Happy Spotting !
More Posts from Ad-astra-affecte-spe and Others
Uranus- JWST NIRCam

This image also shows 14 of the planet’s 27 moons: Oberon, Titania, Umbriel, Juliet, Perdita, Rosalind, Puck, Belinda, Desdemona, Cressida, Ariel, Miranda, Bianca, and Portia.

This picture shows Uranus's north polar cap as well as a storm just below the polar edge.



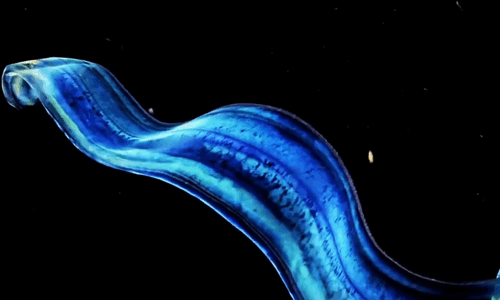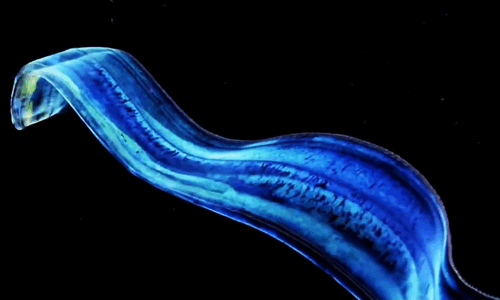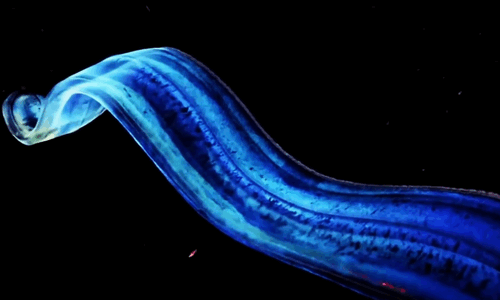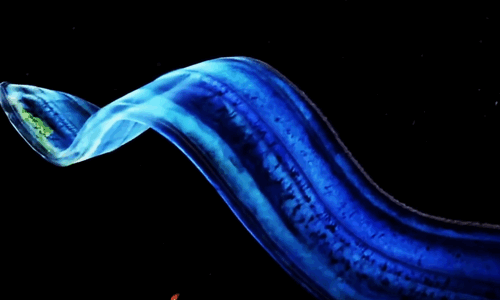




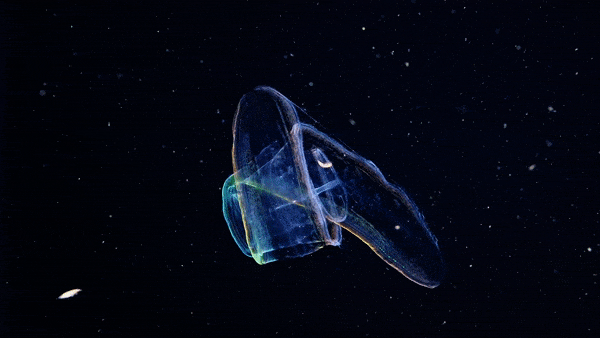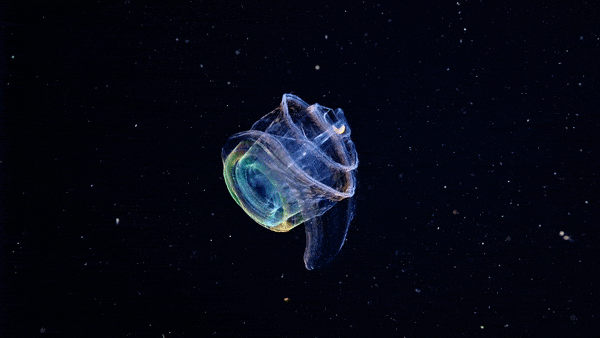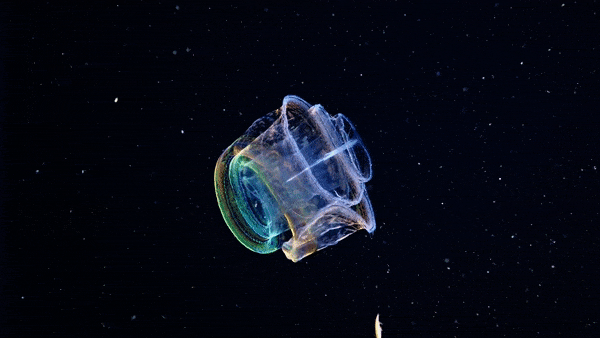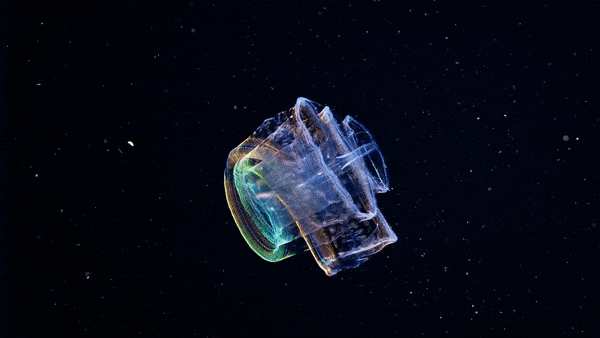
The Venus girdle (Cestum veneris) is a comb jelly in the family Cestidae. The colorless species are transparent when suspended in water, except for their iridescent rows of comb plates. In other words, they majestic as fuck. Love to sea it 🌊





Star Trails in Western Australia by Trevor Dobson

Cosmic Cliffs in Carina © JWST

Sagittarius dwarf irregular galaxy (sagDIG) © Hubble
okay so. does anybody remember this creepy image? and yes, it's real, by the way.

this is barnard 68, a dark nebula that does not allow light to pass through. it's quite close to us too, and so dense that the stars behind it can't be observed from earth. it's just a molecular cloud, though! looks like a tear in the fabric of existence itself, but it's just a very big dark blob of gas floating in space. barnard 68 is often confused with the boötes void, which is also referred to as "the great nothing".
what's that, you say? oh, well... it's a region in space about 330 million light years wide. this is about 0.27% of the width of the entire observable universe. an area this large is expected to have around 2000 galaxies, but this one only has 60. everything else is just... dead, empty space.

okay, what if i told you that we actually are within a void ourselves? it's called the kbc void. another name is uhh.. local hole. anyways. it's theoretically the largest void we know of, about 2 billion light years across. it's extremely speculative, but it might account for the hubble tension; that is, shit seems to be flying away from us faster than it should be.

some people claim other things cause the discrepancy in our observations of the hubble constant, some debate whether it's consistent with our current cosmological model at all. it isn't completely accepted by the astrophysics community, but it's not a preposterous claim to make either. i personally think it's cool.
maybe shit does fly away faster from us because we live in a local hole. the rest of the universe is an intergalactic party, and we're not invited.

For ten years the stargazer dreamed of taking a picture like this. The dreamer knew that the White Desert National Park in Egypt's Western Desert is a picturesque place hosting numerous chalk formations sculpted into surreal structures by a sandy wind. The dreamer knew that the sky above could be impressively dark on a clear moonless night, showing highlights such as the central band of our Milky Way Galaxy in impressive color and detail. So the dreamer invited an even more experienced astrophotographer to spend three weeks together in the desert and plan the composite images that needed to be taken and processed to create the dream image. Over three days in mid-March, the base images were taken, all with the same camera and from the same location. The impressive result is featured here, with the dreamer -- proudly wearing a traditional Bedouin galabyia -- pictured in the foreground.

The Milky Way in the direction of Vulpecula and Cygnus // AC1000
-
 thamit liked this · 1 year ago
thamit liked this · 1 year ago -
 etceterodactyl reblogged this · 1 year ago
etceterodactyl reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 pasparal liked this · 1 year ago
pasparal liked this · 1 year ago -
 dihydrogenmonoxide-appreciation liked this · 1 year ago
dihydrogenmonoxide-appreciation liked this · 1 year ago -
 eyekandie reblogged this · 1 year ago
eyekandie reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 clifferilnamidew liked this · 1 year ago
clifferilnamidew liked this · 1 year ago -
 akheloisthemoon liked this · 1 year ago
akheloisthemoon liked this · 1 year ago -
 bondar-the-strong liked this · 1 year ago
bondar-the-strong liked this · 1 year ago -
 andromedaxg liked this · 1 year ago
andromedaxg liked this · 1 year ago -
 drgluckenstein reblogged this · 1 year ago
drgluckenstein reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 emeraldlabyrinth liked this · 1 year ago
emeraldlabyrinth liked this · 1 year ago -
 lost-soul675 liked this · 1 year ago
lost-soul675 liked this · 1 year ago -
 ad-astra-affecte-spe reblogged this · 2 years ago
ad-astra-affecte-spe reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 shallowimages reblogged this · 2 years ago
shallowimages reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 havinxmsblog reblogged this · 2 years ago
havinxmsblog reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 havinxmsblog liked this · 2 years ago
havinxmsblog liked this · 2 years ago -
 wthrwings liked this · 2 years ago
wthrwings liked this · 2 years ago -
 ptolemaeic liked this · 2 years ago
ptolemaeic liked this · 2 years ago -
 blklxry liked this · 2 years ago
blklxry liked this · 2 years ago -
 commentariolus reblogged this · 2 years ago
commentariolus reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 estefferson liked this · 2 years ago
estefferson liked this · 2 years ago -
 rathden liked this · 2 years ago
rathden liked this · 2 years ago -
 tantakataan liked this · 2 years ago
tantakataan liked this · 2 years ago -
 su-alteza-emia liked this · 2 years ago
su-alteza-emia liked this · 2 years ago -
 chijaru700 liked this · 2 years ago
chijaru700 liked this · 2 years ago -
 sergrusso reblogged this · 2 years ago
sergrusso reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 kre1depr1nzzz liked this · 2 years ago
kre1depr1nzzz liked this · 2 years ago -
 marklees-watermelon liked this · 2 years ago
marklees-watermelon liked this · 2 years ago -
 reilbec liked this · 2 years ago
reilbec liked this · 2 years ago -
 ou2tre-blog liked this · 2 years ago
ou2tre-blog liked this · 2 years ago -
 thefunkyperson liked this · 2 years ago
thefunkyperson liked this · 2 years ago -
 starrynightsxo liked this · 2 years ago
starrynightsxo liked this · 2 years ago -
 dietspam16 reblogged this · 2 years ago
dietspam16 reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 sueisfine liked this · 2 years ago
sueisfine liked this · 2 years ago -
 asterthebeloved liked this · 2 years ago
asterthebeloved liked this · 2 years ago -
 detaras reblogged this · 2 years ago
detaras reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 esmat19 liked this · 2 years ago
esmat19 liked this · 2 years ago -
 siempre-hay-mas-de-lo-que-crees liked this · 2 years ago
siempre-hay-mas-de-lo-que-crees liked this · 2 years ago -
 itame84 liked this · 2 years ago
itame84 liked this · 2 years ago -
 escape1599 liked this · 2 years ago
escape1599 liked this · 2 years ago -
 knots-math liked this · 2 years ago
knots-math liked this · 2 years ago -
 tonyguerra87 liked this · 2 years ago
tonyguerra87 liked this · 2 years ago

★•Astronomy, Physics, and Aerospace•★ Original and Reblogged Content curated by a NASA Solar System Ambassador
204 posts

